Treatment of a skull fracture in adults is usually simple, except when the head injury is severe, the brain is damaged, and serious complications such as brain bleeding occur, the treatment must be surgical.
The treatment of skull fracture in adults includes two types of treatment: conservative treatment and surgical treatment, and one of them is chosen depending on the symptoms and signs present and their severity after evaluating the patient. However, adult skull fractures are often treated conservatively by observing the patient in the hospital between 24 to 48 hours and treating some symptoms and rarely treating skull fractures in adults through surgery, except when complications occur.
In this article, we will learn about the most important methods of treating adult skull fractures. What is the first aid before treating a skull fracture in adults? And how Treating a skull fracture in adults without surgery?
Treatment of skull fracture in adults
Differs Treatment of a linear skull fracture For the treatment of other types of fractures in the body, such as leg fractures or Hand joint fractures Which is often fixed. There are two types of treatment for cracks: conservative and surgical treatment. One of the two treatments is chosen depending on the complications of the crack, the severity of the crack and according to its type if it is a simple crack or a serious crack, and the patient's age. Therefore, treating skull fractures in adults may be conservative through observation in the hospital and treatment of existing symptoms and pain or through surgery when a blood clot or other serious complications occur.
Symptoms that need treatment
A skull fracture is a simple fracture or crack in one cranial or facial bone. It may not require treatment of a skull fracture in adults, or it may be a serious fracture, and it includes many symptoms, but there are some symptoms and signs that need to be monitored and treated, the most important of which are:
- Severe bleeding in the head or face
- Severe headache
- confusion
- rampage
- Runny blood or cerebrospinal fluid from the nose or ear
- vomiting
- Altered level of consciousness as a result of brain injury
- Loss of balance
- respiratory failure
- The appearance of blue or black circles under the eyes or behind the ears
- Slurred speech
- Weakness and inability to move an arm or a leg
- Having seizures
- One of the eye's pupils dilates and does not respond to light
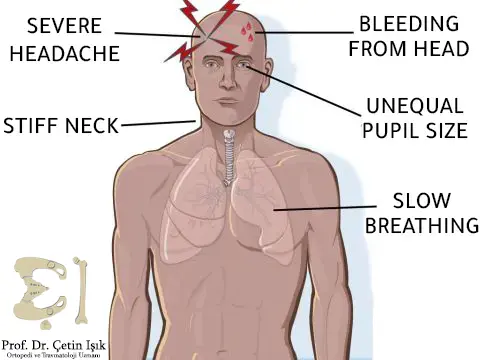
Patients at risk of cracking
To treat a skull fracture in adults, it must be known that there are people who are more at risk from head injuries than others and that the people at risk are:
- Patients over 60 years of age
- Patients who have undergone previous brain surgeries
- Patients who take anticoagulant-thinning medications
- Patients who drink drugs or alcohol
First aid before starting treatment
Head injuries may cause fractures of the cervical spine or Skull fractures For adults, first aid for skull fractures is determined according to the injured person's condition and the apparent symptoms. First aid in the hospital before starting treatment for skull fractures in adults is:
- Evaluation of the patient, where the patient's awareness must be evaluated if the patient is not responding to breathing normally, then the integrity of the airway must be maintained by tilting the head back and raising the chin because the unconscious patient may bounce his tongue back and obstruct the airway.
- Helping the patient to take a comfortable position for him, and when there are signs of a brain concussion, the patient's sports activities should be stopped because continuing to practice sports activities may cause brain damage.
- Give some simple analgesics To treat bone pain When needed, such as paracetamol or anti-inflammatory drugs, until a doctor examines the patient.
- Cover scalp wounds with a sterile dressing to prevent continued bleeding and protect the brain from infection.
- Putting the bandage on the area where the cerebrospinal fluid or blood from the nose or ear leaks and not pulling the bandage strongly.
- The patient must be constantly monitored for breathing and consciousness and checked for other injuries to treat them.
- Maintaining the normal body temperature of the patient.
Treating a skull fracture in adults without surgery
Simple cranial bone fractures are often monitored for 24 to 48 hours in the hospital and treated conservatively as follows:
- Take some medications to relieve pain after the crack or fracture, such as taking acetaminophen.
- You should not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin, as this may make any bleeding worse.
- Treatment of a skull fracture in adults may require stitches or surgical sutures. If open wounds accompany the cracks, these wounds are covered with a sterile dressing.
- The patient must be closely monitored, even if the crack is simple because head injuries need intensive monitoring to protect the patient from complications that may worsen. Therefore, the patient must be monitored and not let the patient sleep a lot but be woken up every two hours to check for new symptoms.
- Patients who have had severe brain trauma may be given anti-epileptic drugs, as the patient may experience epileptic seizures in the week following the injury, and diuretics may also be given when pressure rises within the brain because diuretics increase fluid secretion and thus help relieve pressure.
- Medication may be given to put the patient into an induced coma if there is a serious head injury, such as damage to the blood vessels. When a person is in a coma, the brain does not need as much oxygen and nutrients.
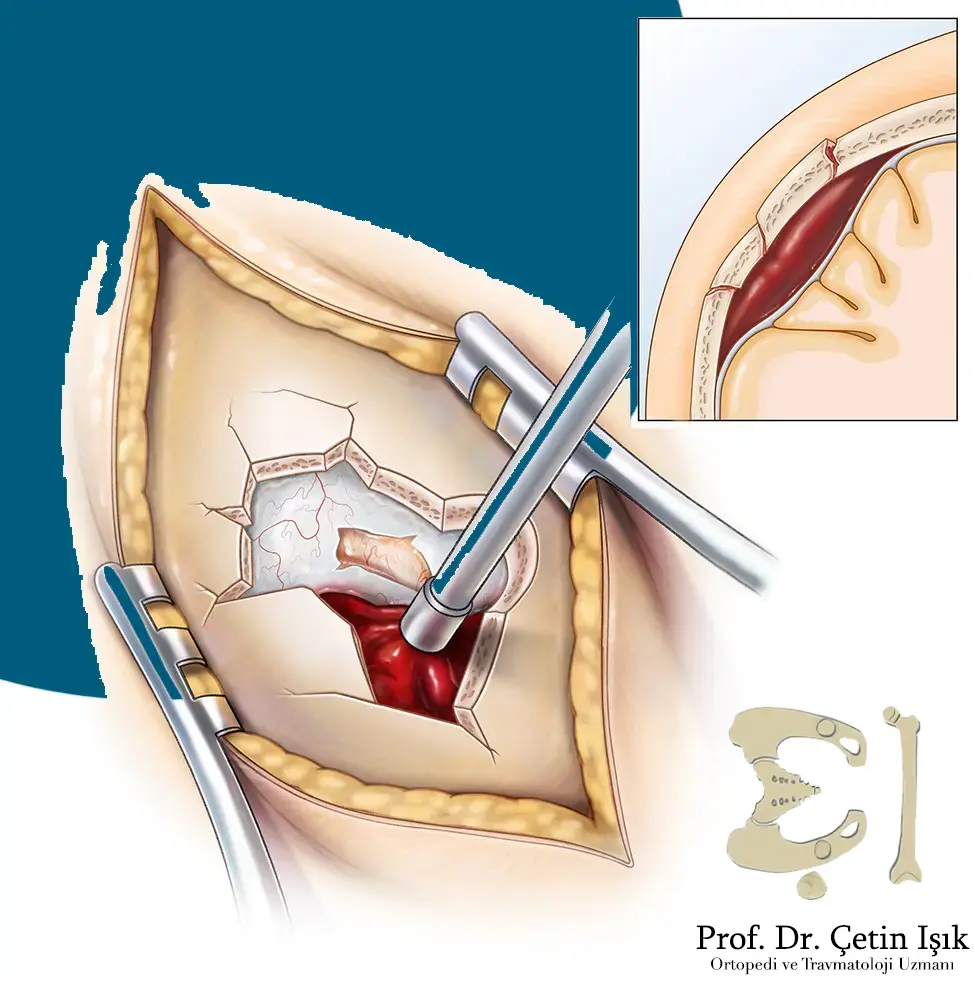
Surgical treatment of skull fractures in adults
The patient may need to resort to surgeries when strong bruises, serious cracks, and brain damage are present to:
- Removing the hematoma, especially when there are subdural hematomas, to relieve pressure on the brain
- Reducing intracranial pressure
- The patient may also need surgery to repair a skull fracture with very deep cracks
At the end of the article, the treatment of skull fracture in adults has two treatment options, either surgical or conservative treatment, depending on the severity of the crack and the complications associated with it, such as brain bleeding or other complications. Still, in general, the treatment of skull fracture in adults is often the observation between 24 to 48 hours, Treating the symptoms associated with the crack. The patient is discharged with a warning to review the hospital if serious symptoms appear, as minor cracks heal automatically within several months, and surgical treatment is rarely resorted to in adults.
Sources:
Common questions
The crack in the skull in adults is often not dangerous when the separation between the two ends of the crack is not large and does not contain major complications such as bleeding or brain damage.
The duration varies from one patient to another and according to the severity of the crack, but the fracture in the skull often heals on its own, and the duration of skull bone healing in general for simple cracks ranges from 6 to 8 weeks.
Drinking water helps reduce blood density and transport nutrients and oxygen through the body and thus helps bring in the important elements for repairing damaged cells.
The sooner the patient sees a doctor and diagnoses the crack early, the faster the recovery will be. Complete rest for the injured person and good nutrition, such as eating foods that contain Vitamin D And calcium in accelerating the treatment of the crack.
When symptoms of a serious head injury appear, such as loss of consciousness, a seizure, or when there is bleeding from the nose and ear.
Some signs appear such as a decrease in pain or a lack of bruising and swelling, and recovery is often confirmed through radiography after a doctor's review.
The treatment of a skull fracture in adults is often conservative and without surgery, except for serious and severe injuries and the appearance of symptoms of brain injury.