Robotic hip replacement is one of the interesting operations of joint replacement surgery due to the satisfactory results it achieves as it combines the experience of the surgeon with the infinite precision of the robot.
What is a robotic hip replacement?
Hip replacement is major surgery, yet more than 95% of people who have the surgery experience relief from chronic hip bone pain.
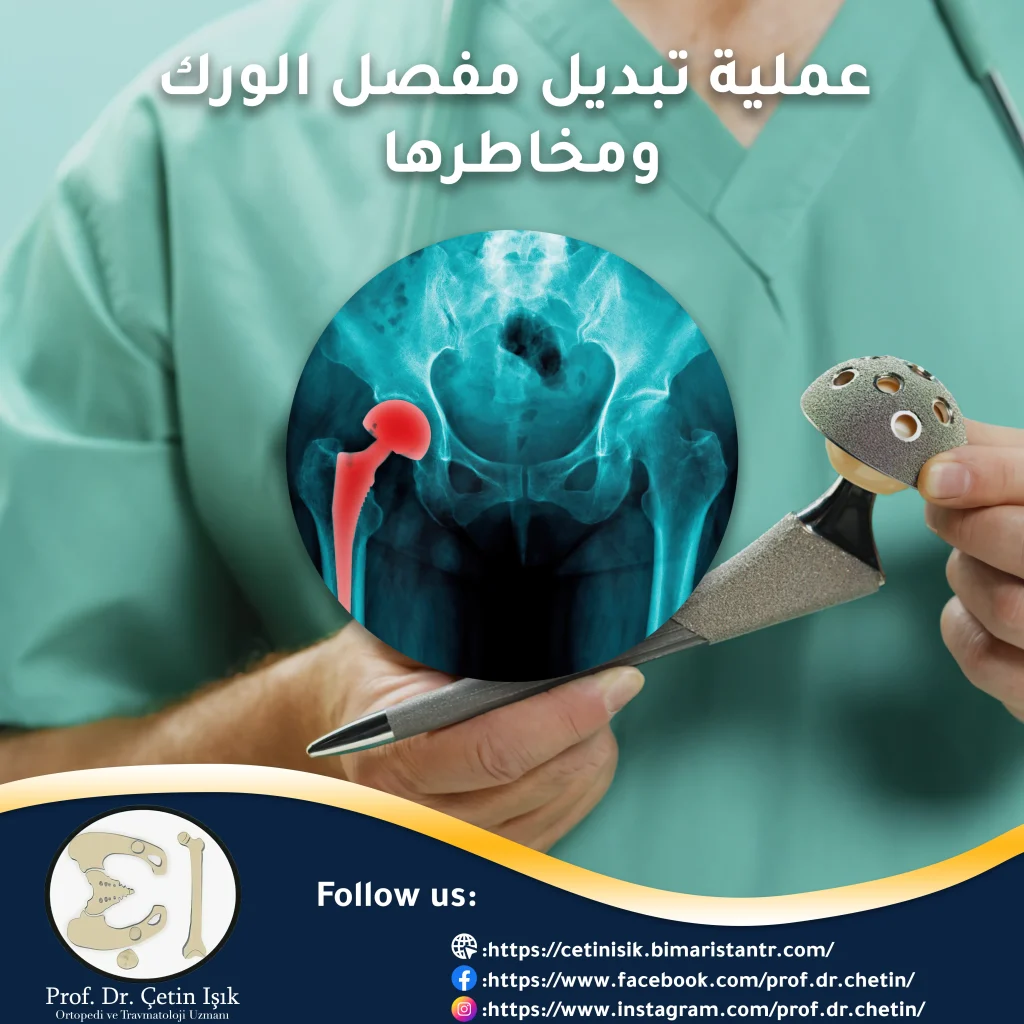
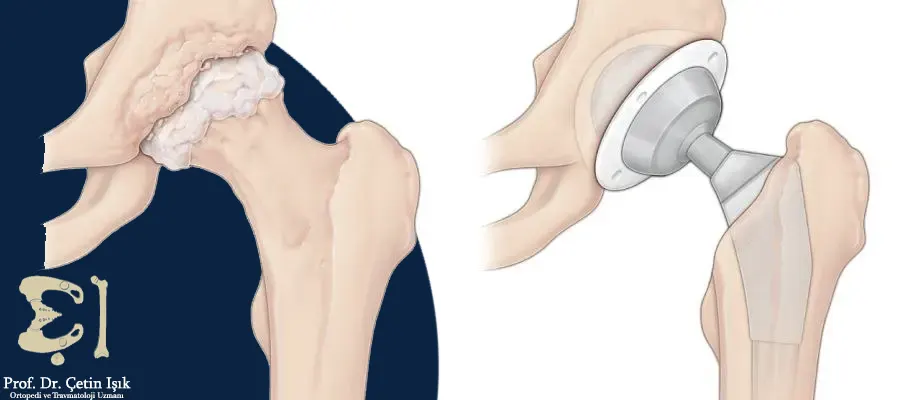
During the robotic hip replacement operation, the damaged hip joint or its damaged parts are replaced with an artificial one called an implant, which may be made of plastic, steel, or porcelain. The surgeon remains fully responsible for the course of the surgery, but he uses a sophisticated robotic arm that enables him to create a plan Optimization of the patient's condition and implant placement with high precision to achieve consistent results.
What is robotic surgery?
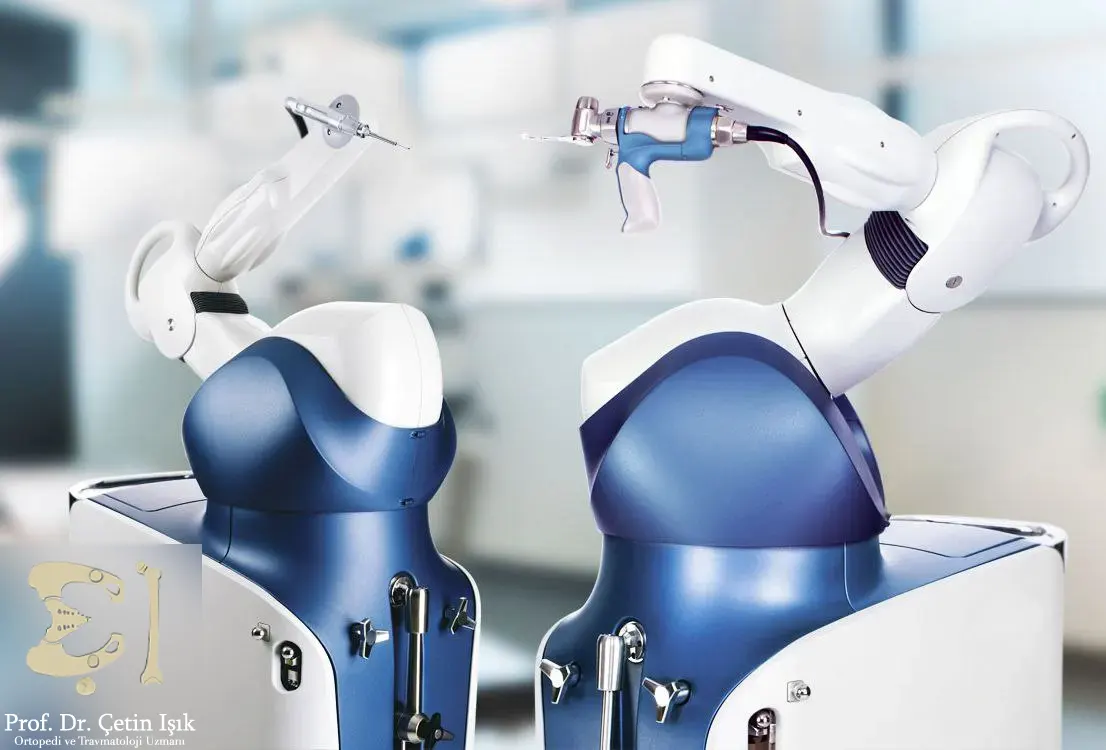
Robotic-assisted hip or knee replacement surgery uses specialized technology that enhances the ability of the surgeon's hands, and allows operations in hard-to-reach areas through small incisions. Partial or complete replacement of the knee and hip joints can be performed.
The robot used in this field consists of:
- Surgical arms: equipped with precise instruments with wrist controls at their ends
- A special camera: provides a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical area
- Surgical unit: where the surgeon controls every movement of the instrument and camera within the hip or knee joint

Advantages of robotic hip replacement
It is considered Hip replacement one of the most successful orthopedic procedures, the use of robots during surgery improves its success rate by taking the accuracy of the operation to new heights, as it reaches 4 to 6 times the accuracy of traditional artificial joint replacement surgery.
Benefits of using a robotic hip replacement include:
Patient-specific 3D planning: The automated planning system creates a 3D computerized model of the pelvic joint, allowing the surgeon to create a surgical plan best suited to the patient's specific anatomy.
Better control: The robotic arm brings more precision and consistency to the surgeon's hand, helping to reduce the risks of leg length discrepancies, bleeding, dislocation and other complications of manual surgery.
Minimally injuring healthy tissue: The surgery using the robotic arm allows it to operate within a narrow space and through smaller incisions, without any cutting of the muscles around the hip, by adopting a minimally invasive anterior approach.
Positive results: through the rapid recovery time and the return of the normal function of the joint after the initiation of physical therapy within days after surgery.
Who needs a robotic hip replacement?
Robotic hip replacement can be performed to treat people with:
- Arthritis moderate to severe, which is the most common condition that damages the hip joint and requires its replacement after other treatments, such as arthroscopic cleaning of the joint have failed to relieve symptoms.
- Types of hip fracture
- Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (death of bone due to lack of blood supply)
- loss of movement
- Severe pelvic pain
The robotic hip replacement procedure
On the day of the robotic hip replacement surgery, the patient is given general or local anesthesia to keep him comfortable and the surgery is expected to take between one and two hours
The surgeon usually uses an anterior approach in hip replacement, which means he makes a small incision in the front of the hip to spare the muscles and tendons.
The robotic system (MAKO) provides real-time feedback and enhanced flexibility as it accurately removes damaged bone in a pre-determined amount according to the patient's CT scan.
When it is time to insert the prosthesis, the robot guides the surgeon to the exact location through auditory, visual and tactile cues to ensure proper alignment of the implant components and avoid differences in the length of the legs.
Once the prosthesis is in place, the incision is closed with stitches, and the patient is taken to the hospital recovery room for 45 minutes.
There is usually no restriction on mild to moderate activities, and physical therapy can be expected to begin soon after surgery.
It requires a robotic hip or knee replacement Advisor An experienced specialist in surgical technology within a leading hospital in the field of advanced surgery.
Sources:
Common questions
In most cases, robotic-assisted joint replacement surgeries take just over an hour.
Many details play a role in extending the life of the implant, including the patient's age, weight, activity level, and the quality of his bone stock.
However, proper alignment and placement of the implant is critical to life expectancy, and with the robotic system used, the surgeon can achieve a highly accurate positioning of the prosthesis.
The recovery process is different for each patient after robotic-assisted hip and knee replacement surgery.
Most often, you can return to work within 3 to 6 weeks.