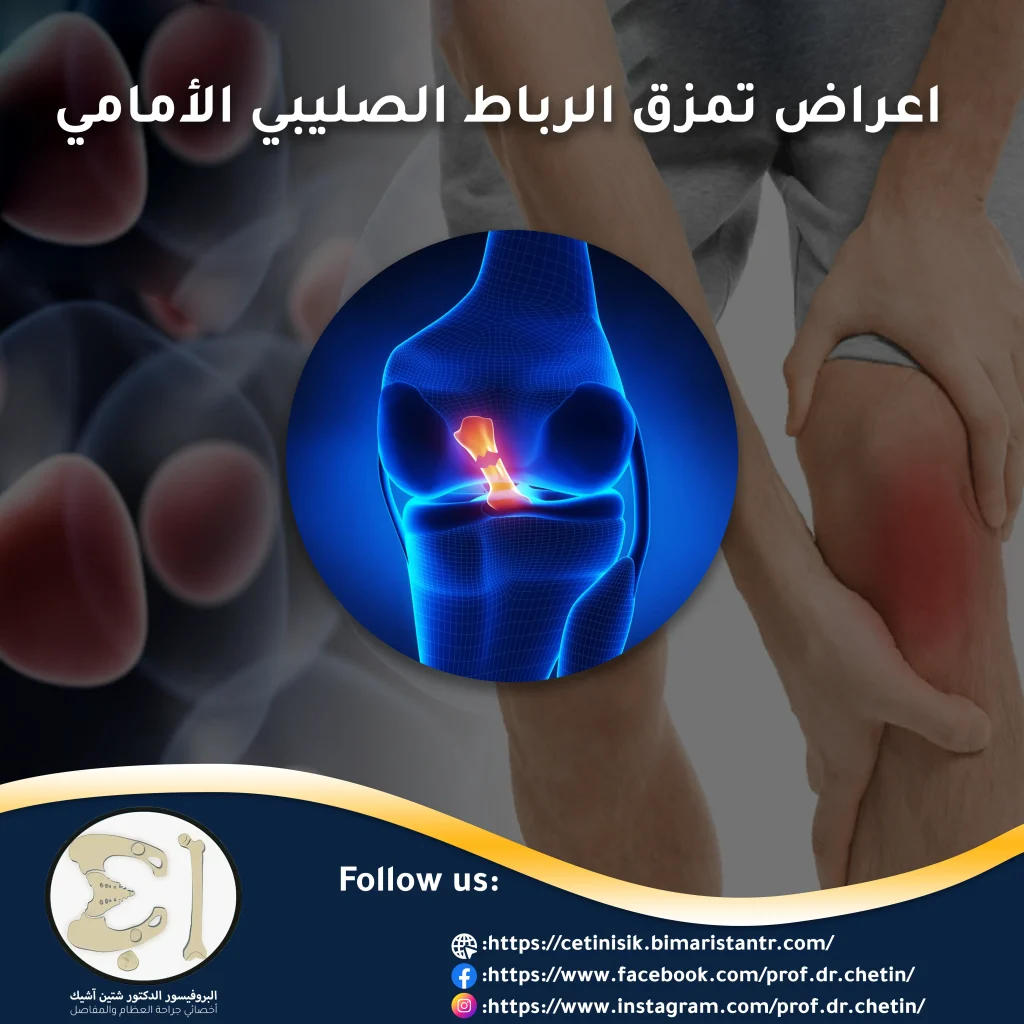
Symptoms of an ACL tear occur when your knee feels like it has collapsed or given up, you may feel or hear a pop, and the knee begins to swell, it's a common injury that usually affects athletes.
Symptoms of ACL tear
When the anterior cruciate ligament is torn or severed, the patient feels symptoms and signs of a ruptured ligament injury instantly. The most common symptoms are:
- Feeling or hearing a loud popping sound, at the time of the injury.
- Severe pain, which increases when trying to stand on the injured leg.
- Inability to continue the activity.
- Rapid swelling within 6 hours, and it may last 2-4 weeks.
- loss of normal range of motion.
- Feeling of instability in the knee.
As for the less severe symptoms of ACL rupture, especially in people with a sedentary lifestyle, the patient notices difficulty in walking, and that his knee is unstable and unable to bear his body weight.
What is the anterior cruciate ligament?
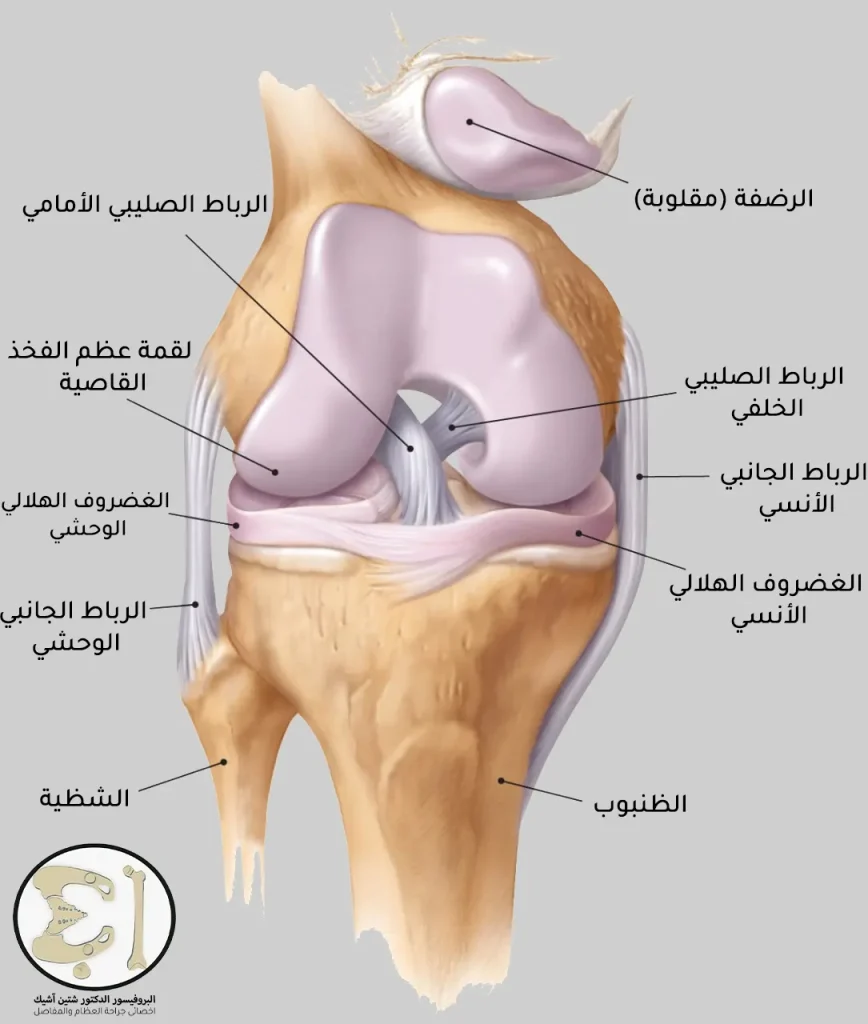
The knee joint in humans consists of bones, cartilage, and ligaments, and it is located in an area between the end of the thigh bone and the beginning of the shin bone in the leg.
The anterior cruciate ligament extends diagonally inside the knee, and with the posterior cruciate ligament, it gives a cruciate shape, and it helps maintain the stability of the rotation of the knee, prevents the tibia from sliding in front of the femur, and is one of the four main ligaments in this joint:
- Medial collateral ligament: prevents the knee from twisting inward.
- Lateral collateral ligament: prevents the knee from twisting outward.
- Posterior cruciate ligament: prevents the tibia from shifting backwards under the femur.
- Anterior cruciate ligament: prevents the tibia from shifting outward in front of the femur.
ACL tear
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear is a rupture or overstretching of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the knee. it could be a partial or a total tear.
Injuries to the knee usually occur during sports and activities that cause stress and pressure on the knee, such as tennis, football and basketball. Tear and rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament is one of the most common knee injuries. The injury occurs when the tibia extends forward too much, or if the knee is twisted.
Causes of an ACL tear
An ACL injury occurs if:
- Sudden cessation of running
- Sudden slowdown and change of speed and direction while running
- injury by a sudden strong blow to the side of the knee, such as when hitting another player or when falling
- Overextension of the knee
- Wrong landing after jumping
or any activity that causes severe twisting, bending, or stress on the knee joint, which can rupture the ACL.
If you have symptoms of an anterior cruciate ligament rupture or have any questions about the subject, you can Contact us and doctor Çetin Işık will answer you for all your inquiries.
Risk factors
There are several factors that increase the chance of a rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament, including:
- Females are affected four times more often than males, due to differences in anatomy, muscle strength, and the effect of hormones.
- Sports activities such as football, volleyball and basketball.
- Moving the knee incorrectly in some exercises.
- Not wearing appropriate shoes
Degrees of ACL rupture
The degree of an ACL tear or rupture is categorized by severity from one to three, with three being the most severe:
- First degree: occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament is only stretched, as it remains able to stabilize and support the knee.
- Second degree: It occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament is stretched and relaxed, and this is called a partial rupture, and it is a rare condition.
- Third degree: It occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament ruptures in two parts, which it is a severe condition.
First aid for ACL tear
Immediately after the injury and the emergence of symptoms of rupture of the ACL, you must stop the activity, avoid standing on the foot of the injured limb, and take measures to reduce inflammation, such as:
- Raise the leg above the level of the heart
- Putting ice on the injured knee
- Take pain killers such as NSAIDs
- avoid moving and bending the knee and not returning to exercises or activities until the knee is treated.
Then you must go to consult an orthopedic doctor, who will order tests to diagnose the injury and start treating the anterior cruciate ligament rupture.
Diagnosis of an ACL tear
A cruciate ligament rupture is usually diagnosed clinically, by comparing the healthy and injured knee joints, and after ruling out other causes of knee pain whose symptoms may be similar to those of an ACL rupture, the doctor may order a radiograph or may order magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which can detect any injury to other ligaments.
Treatment of ACL tear in Turkey
After signs and symptoms of an ACL rupture appear and are diagnosed, the torn ACL is treated surgically. Some patients may have another option, which is non-surgical treatment, but this depends on the severity of the injury and the opinion of the specialist doctor.
Non-surgical treatment of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
Surgery is not necessary for all patients with an ACL rupture, especially if the person is inactive and his lifestyle does not include activities that put high pressure on his knee.
The patient can then not resort to surgery if the knee joint is stable, but he must know that the anterior cruciate ligament that was torn will not heal on its own.
Non-surgical treatment is based on conservative treatment, by resting and taking anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation and remove symptoms of anterior cruciate ligament rupture. A special belt or strap can be worn that applies pressure to the knee to stabilize it during activity.
Surgical treatment of ACL rupture
Before the surgery
You must wait until the symptoms of the rupture of the ACL and knee swelling disappear, which may last 2-4 weeks, and make sure that full range of motion is returned.
It may take up to 3 weeks for full range of motion to return, and if full range of motion is not returned before surgery, recovery may be difficult.
Preoperative physical therapy may be referred to restore full range of motion.
You should also wait until the knee muscles are strong enough, and all activities that involve jumping, twisting or turning should be avoided.
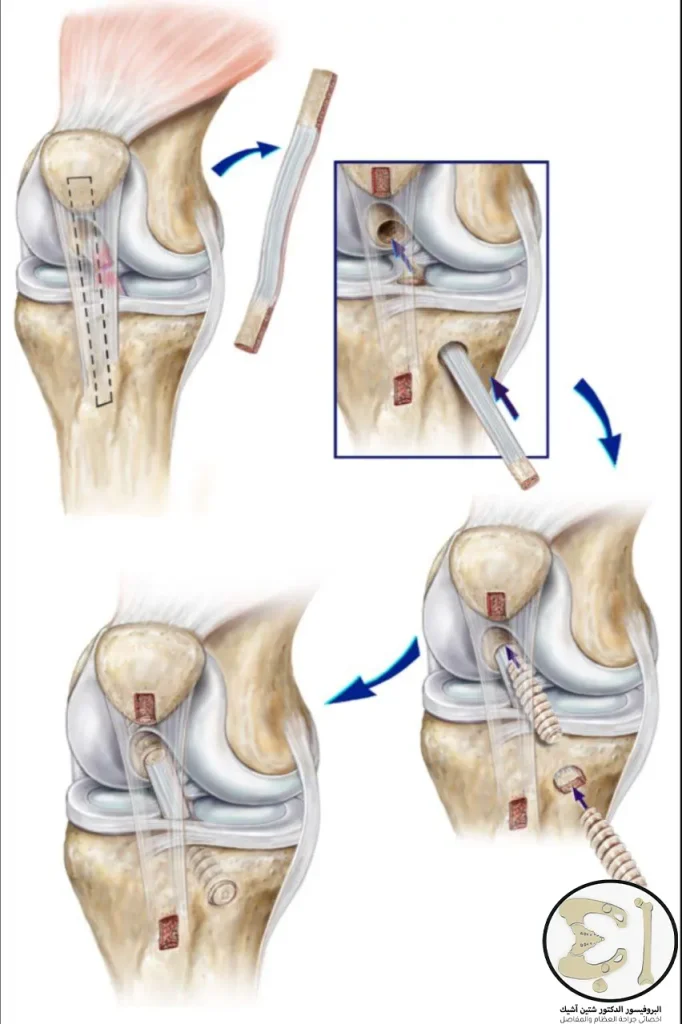
ACL reconstruction surgery
The torn anterior cruciate ligament cannot be repaired by suturing its ends together, but rather reconstructing it by using a graft and attaching it to the torn anterior cruciate ligament.
The tendon graft is obtained from the patient's own body, such as the popliteal tendon or the patellar tendon that connects the kneecap to the tibia.
The skin is usually not cut to a large distance because the surgery is performed using an arthroscope, which is a special device that inserts the knee through a small incision.
after surgery
Keep the wound clean and dry, apply ice to reduce swelling and pain, and wear a belt or use crutches.
Physical therapy after surgery plays an important role in strengthening the muscles of the affected limb and knee, in addition to doing exercises in the rehabilitation program.
Athletes are often able to return to their activities after 6-9 months.
Prevention from ACL tear
It is difficult for an athlete to completely avoid injury, especially in sports such as football and basketball, which require a lot of jumping, landing, changing direction and accelerating movement.
While the sudden change of direction of movement or the so-called “cut” maneuver, and the landing after the jump account for 70% of all ACL tears, there are a range of techniques used by sports practitioners to reduce the risk of injury:
- Do warm-up exercises for a sufficient amount of time before starting the sports activity
- Strengthen the core muscles of the body, including the hips, pelvis, and lower abdominal muscles
- Strengthening the leg muscles to ensure a good balance for the joint
- Training in the correct techniques to perform the various maneuvers
Sources
Common questions
A torn ligament does not heal on its own due to insufficient blood supply, and surgical treatment is often done in athletes to rebuild the anterior cruciate ligament which is necessary to perform sports movements.
Using rehabilitation and physical therapy, and in certain cases of injury, the torn ligament and knee may stabilize after three months, but it will not heal completely without surgery.
In the absence of treatment, the injury may turn into a chronic condition, where the affected knee becomes constantly less stable, and abnormal slippage may damage the knee cartilage, and may lead to osteoarthritis at a young age.
This depends on the severity of the condition. In mild to moderate cases, after the pain, swelling and other accompanying symptoms have passed, and in the absence of another knee injury, it is possible to walk in a straight line and even go up and down the stairs.