A marrow transplant is used to replace damaged stem cells in the bone tissue to recreate blood normally. Bone marrow transplant is used to treat many diseases.
A bone marrow transplant Marrow transplant You need healthy stem cells, which may be from the same patient or from another patient, and this process is used to treat many diseases such as cancer and anemia, and bone marrow transplantation is often resorted to when other treatments fail and when the disease is life-threatening, because it carries Many risks and complications, when transplanting marrow, there must be a match between the donor and the recipient, so some tests must be performed before the operation.
In this article, we will present what is a bone marrow transplant? What are the most important types, and how is the bone marrow transplant performed? The most important risks and complications after the operation.
What is a bone marrow transplant?
The bone marrow is a spongy tissue that produces stem cells, which are immature cells that grow into one of the main types of blood cells, such as red blood cells that carry oxygen to all parts of the body, white blood cells that help fight infection, or platelets that stop bleeding.
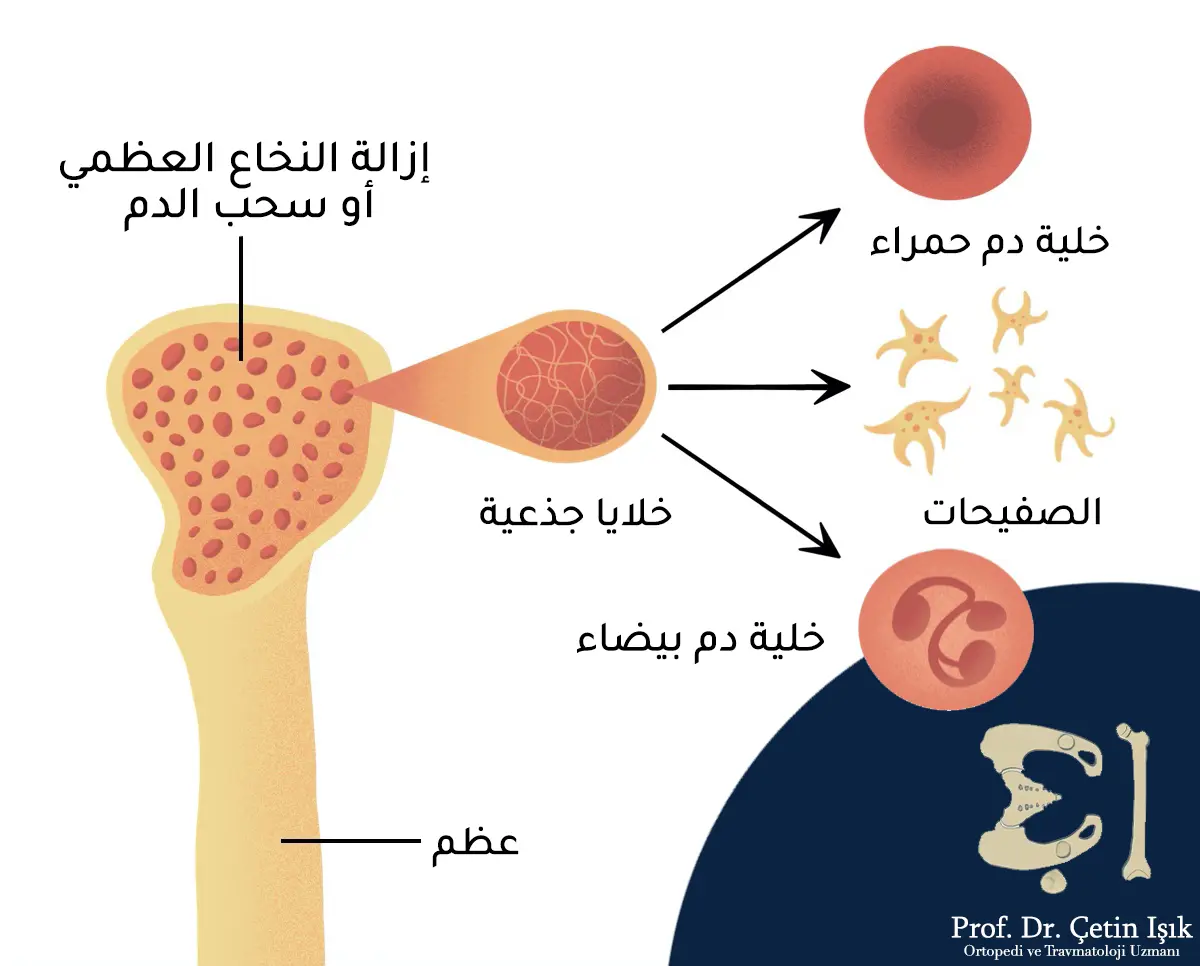
Bone marrow transplant It is a process in which damaged cells are removed from the bone marrow and replaced with healthy stem cells that are obtained either from the same patient or from another patient, depending on the condition of the patient and the type of operation used in the treatment. Bone marrow transplantation is used to treat many cancers and diseases. Marrow transplantation may be used for children. in order to treat Bone hardening for example.
Types of bone marrow transplant
There are several types of bone marrow transplantation, classified according to the person who provides the stem cells. Types of bone marrow transplants include:
Autologous bone marrow transplant
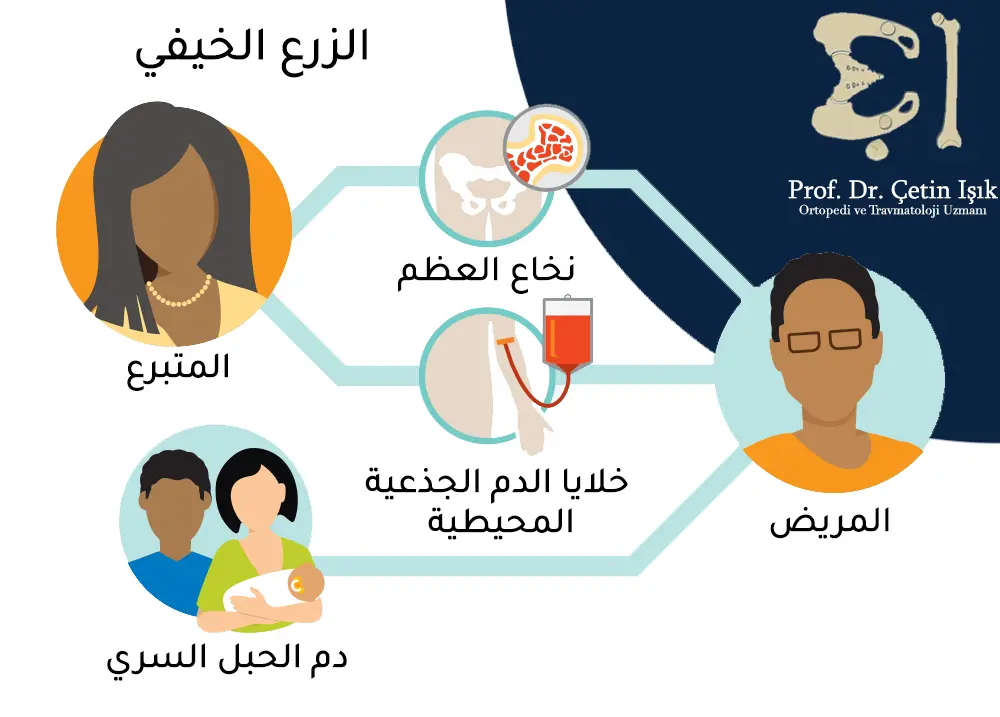
In autologous marrow transplantation, the donor is the patient himself, as the stem cells are withdrawn from the patient, either by collecting them from the bone marrow or by apheresis, then they are frozen and returned to the same patient after intensive treatment.
Allogeneic bone marrow transplant
In this type of transplant, there is a genetic match between the donor and the patient. The donor from whom the stem cells are taken is genetically identical to the patient and is usually a brother or sister. The donor may be one of the parents, and here the match will be haploid, or it may not be between the patient and the donor, i.e. They are related, but there is a genetic match between them.
Umbilical cord blood culture
Stem cells are obtained from the umbilical cord immediately after birth and then frozen until the patient needs a bone marrow transplant. Stem cells taken from the umbilical cord are better and more effective than cells taken from the bone marrow of an adult or a child.
When do we resort to a bone marrow transplant?
Bone marrow transplantation is usually done after other treatments have failed, and a marrow donor must be available before bone marrow transplantation. The most important cases in which we resort to bone marrow transplantation are:
- Damage to the bone marrow and its inability to produce healthy blood cells
- One reason for a bone marrow transplant may be to replace damaged blood cells after aggressive treatment for cancer
- Bone marrow transplants for cancer patients, too, may be used Bone marrow transplant In the treatment of many diseases, the most important of which are leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, as well as in the treatment of thalassemia and sickle cell anemia.
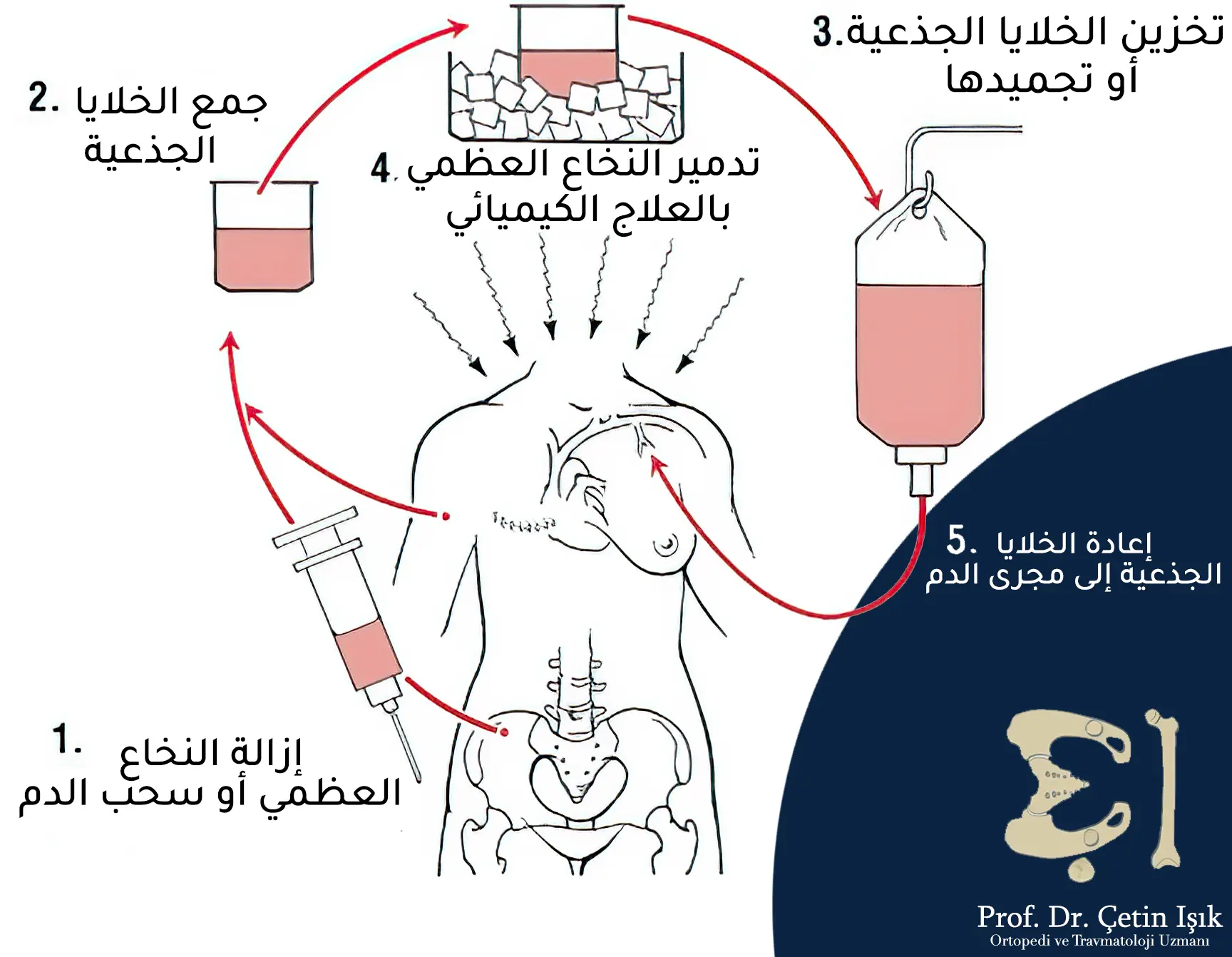
How is a bone marrow transplant?
A donor must be found if the transplant is allogenic rather than autologous before starting the steps of a bone marrow transplant, even if it is a method Bone marrow transplant The most important steps of a bone marrow transplant are:
- First, stem cells must be collected, whether from the same patient or from another donor, depending on the type of bone marrow transplant. This stage takes several days, then the collected stem cells are stored until needed.
- Secondly, pre-transplant treatment in order to prepare the body to receive blood stem cells, which may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy as needed, and this stage takes about a week.
- Third, transplanting new stem cells to replace damaged cells, where stem cells are pumped into the bloodstream by catheter, and this stage often takes less than an hour, depending on the case.
- Fourth, the recovery period after a bone marrow transplant, where the patient is monitored intensively by the doctor in order to treat some side effects, and he may recommend taking some anti-inflammatory drugs.
To find out the cost of a bone marrow transplant and the best bone marrow transplant hospital, contact us to book your appointment and we will tell you all the details related to the costs of treatment and accommodation in Turkey.
We conclude that marrow transplantation is one of the common operations in children, which results in the replacement of damaged blood-producing stem cells with other undamaged stem cells, and there are many ways in which bone marrow transplantation is performed. The method of bone marrow transplantation is chosen according to the condition of each patient.
Sources:
Common questions
The success rate of bone marrow transplantation differs from one patient to another, depending on the reason for bone marrow transplantation and the degree of match between the patient and the donor. When there is a link between the patient and the donor, the survival rate after bone marrow transplantation for patients with acute leukemia ranges from 55% to 68%.
The bone marrow transplant takes about an hour or two under general anesthesia in the operating room, without the patient feeling any pain.
There are some risks after a bone marrow transplant that may threaten the patient's life. The bone marrow transplant may be considered dangerous for some patients, as the patient may be exposed to attack symptoms after the marrow transplant.
When the bone marrow transplant fails, the patient will not recover from the disease he suffers from, and the blood components will remain deficient, and the medical staff will perform the transplant again.
Bone marrow transplantation for cancer patients may be a cure for some types of cancer, but not all, such as leukemia or lymphoma.
There are some symptoms that donors may suffer from, such as headache, bone and muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and exposure to infections, and this is the danger of bone marrow transplantation for the donor.
When making the donation, the doctor will anesthetize the donor with general or local anesthesia in the hospital so that he does not feel any pain.
There are many risks that may occur due to bone marrow transfer, which are many infections in the patient’s body, as well as a disease that the body attacks the transplanted stem cells, the emergence of new cancers, and death.
Bone marrow transplantation is often successful in treating certain diseases such as leukemias, lymphomas, aplastic anemia, and immunodeficiency disorders.