التهاب أوتار اليد هو حالة شائعة تسبب ألمًا وضعفًا في حركة اليد أو الأصابع. وغالبًا ما تصيب الأشخاص الذين يستخدمون أيديهم في الأعمال المتكررة أو الذين يتعرضون لإجهاد مستمر في المفاصل.
في هذا المقال، سنتعرف بالتفصيل على أسباب التهاب أوتار اليد، أهم الأعراض، وكيفية تشخيصه، وخيارات العلاج المتاحة من الراحة والعلاج الطبيعي إلى الأدوية والتدخل الجراحي.
ما هو التهاب أوتار اليد؟
Tendons هي أنسجة قوية تربط العضلات بالعظام، وتساعد على تحريك المفاصل. وعندما تلتهب هذه الأوتار نتيجة لإجهاد أو إصابة، تحدث حالة تُعرف بـ التهاب الأوتار (Tendinitis).
أكثر أوتار اليد تعرضًا للالتهاب:
- وتر الإبهام (De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis).
- أوتار الرسغ (المثنية أو الباسطة).
- أوتار الأصابع (مثل التهاب الزُليل).
Causes of hand tendonitis
| السبب | الشرح |
|---|---|
| الحركات المتكررة | مثل الطباعة، استخدام الهاتف، رفع الأثقال، أو الأعمال اليدوية |
| إصابات مباشرة | مثل الرضوض أو الكسور السابقة في اليد |
| وضعية غير صحيحة | عند استخدام الكيبورد أو الماوس لفترات طويلة |
| أمراض مزمنة | مثل السكري، التهاب المفاصل الروماتويدي، والنقرس |
| the age | تزداد نسبة الإصابة مع التقدم في السن بسبب قلة مرونة الأوتار |
| Pregnancy | خاصة في حالة “دي كيرفان” (De Quervain)، بسبب احتباس السوائل والتغيرات الهرمونية |
Symptoms of hand tendonitis
| العرض | الوصف |
|---|---|
| ألم في اليد أو المعصم | خاصة عند تحريك الإصبع أو المفصل المصاب |
| تورم موضعي | فوق منطقة الوتر الملتهب |
| تيبس أو صعوبة في الحركة | خصوصًا عند الاستيقاظ صباحًا |
| شعور بفرقعة أو طقطقة | مع حركة الإصبع، كما في “الزناد” (Trigger Finger) |
| احمرار أو دفء | في الحالات الالتهابية الحادة |
| ضعف في القبضة | وصعوبة في الإمساك بالأشياء الثقيلة أو الدقيقة |
أنواع شائعة من التهاب أوتار اليد
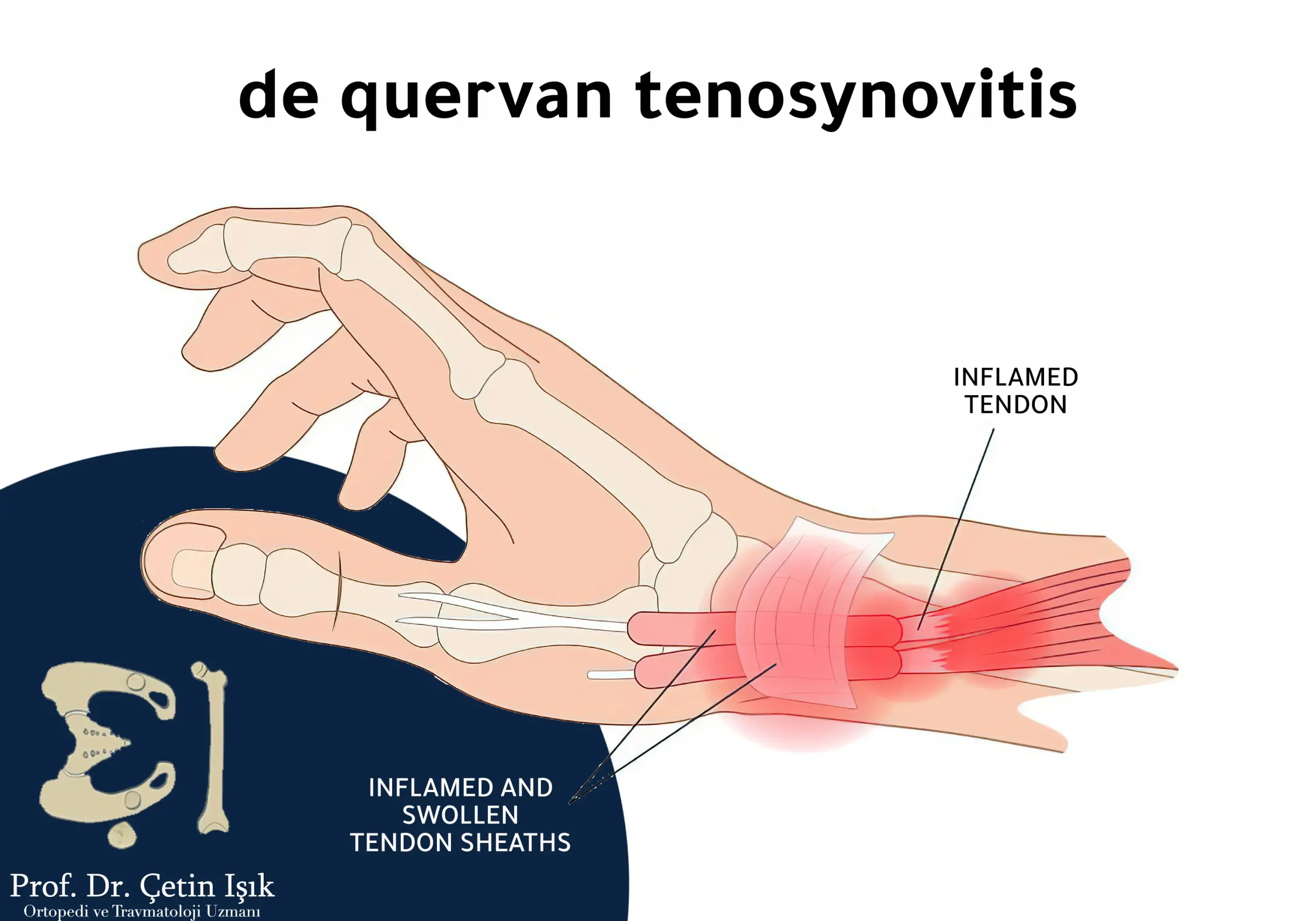
1. التهاب وتر دي كيرفان (De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis)
- يصيب أوتار الإبهام عند قاعدة الرسغ.
- يسبب ألمًا عند رفع الطفل، فتح البرطمانات، أو استخدام الهاتف.
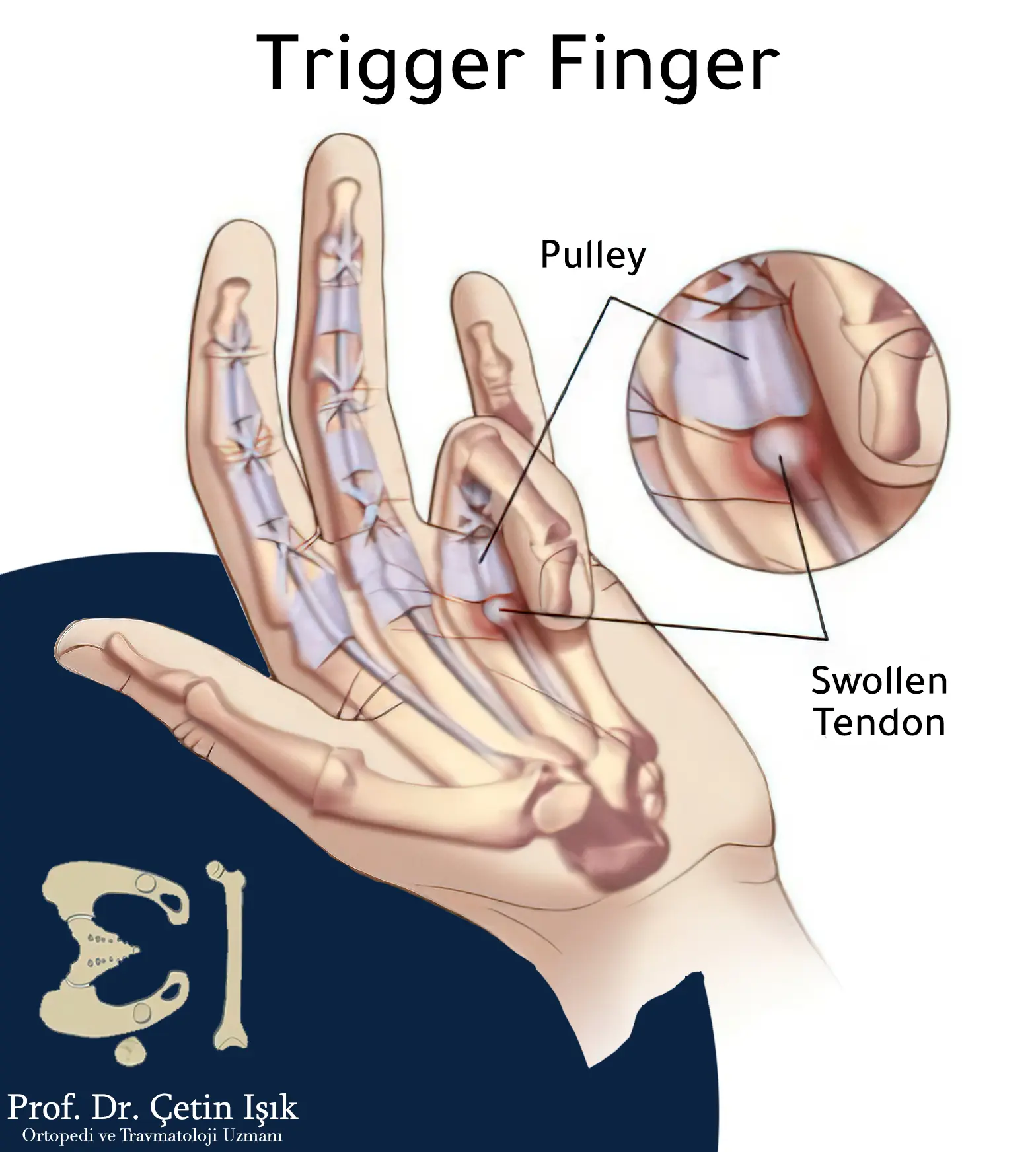
2. إصبع الزناد (Trigger Finger)
- يحدث عندما يلتهب وتر أحد الأصابع، فيُحبس داخل غمده ويُحدث طقطقة عند الثني أو البسط.
3. التهاب أوتار الرسغ المثنية أو الباسطة
- يسبب ألمًا على الوجه الراحي أو الظهري للرسغ.
- شائع لدى من يستخدمون الأجهزة لفترات طويلة.
Diagnosis of hand tendinitis
1. Clinical examination
- يطلب الطبيب من المريض تحريك اليد أو الإصبع لتحديد موقع الألم والتيبس.
- اختبار Finkelstein يُستخدم لتشخيص De Quervain.
2. الأشعة فوق الصوتية (Ultrasound)
- تُظهر الالتهاب والتورم حول الأوتار بدقة.
3. الرنين المغناطيسي (MRI)
- يُستخدم عند الشك في تمزق أوتار أو وجود أمراض مصاحبة.
Hand tendonitis treatment
أولًا: العلاج التحفظي (المرحلة الأولى)
| الخيار | الشرح |
|---|---|
| Rest | تجنب الحركات المتكررة أو المجهدة |
| الكمادات الباردة | لتخفيف التورم خلال الأيام الأولى |
| Medications | مضادات الالتهاب مثل الإيبوبروفين أو ديكلوفيناك |
| الجبائر (Splint) | لتثبيت المفصل وتقليل الضغط على الوتر |
| Physical therapy | يشمل تمارين التمدد، تقوية العضلات، واستخدام موجات فوق صوتية |
ثانيًا: حقن الستيرويد
- تُستخدم في الحالات التي لا تستجيب للعلاج الدوائي.
- تخفف الالتهاب بسرعة، خاصة في حالة إصبع الزناد أو De Quervain.
- لا يُنصح بتكرارها كثيرًا لتجنّب ضعف الوتر.
ثالثًا: التدخل الجراحي
يُوصى به فقط في الحالات التالية:
- عدم الاستجابة للعلاج بعد 3–6 أشهر.
- وجود تليفات أو انحباس كامل للأوتار.
- الألم الشديد المستمر الذي يعيق الحياة اليومية.
الهدف من الجراحة:
- تحرير الوتر من الأنسجة المحيطة أو إزالة التليف.
- العملية بسيطة وتُجرى غالبًا تحت تخدير موضعي، مع تعافٍ سريع.
كم يستغرق الشفاء من التهاب أوتار اليد؟
| شدة الحالة | مدة التعافي |
|---|---|
| خفيف إلى متوسط | 2–6 أسابيع |
| مزمن أو مقاوم | 2–3 أشهر أو أكثر |
| after surgery | التحسن يبدأ خلال أيام، والتعافي الكامل خلال 4–6 أسابيع |
الوقاية من التهاب أوتار اليد
خذ فترات راحة منتظمة أثناء استخدام اليدين.
استخدم الوضعية الصحيحة عند الطباعة أو استخدام الهاتف.
قم بتمارين إطالة اليد والأصابع بانتظام.
تجنب حمل الأشياء الثقيلة بطريقة خاطئة.
ارتدِ داعم للرسغ إذا كنت تستخدم يدك لفترات طويلة.
متى يجب زيارة الطبيب فورًا؟
إذا لاحظت:
- ألم شديد لا يخف بالمسكنات.
- تورم مستمر مع احمرار أو سخونة.
- فقدان القدرة على تحريك الإصبع أو اليد.
- فرقعة مؤلمة عند تحريك الإصبع.
Sources:
Common questions
Tendonitis in the hands can be cured by a simple home treatment that includes rest and cold compresses. If the inflammation does not improve and its problems increase, the doctor prescribes various pain relievers such as steroid injections. As for management by surgical treatment, they are in the more complicated cases.
A tendon or many tendons may become inflamed. The assessment of the seriousness of this inflammation is up to the doctor, but most injuries are minor.
Symptoms of tendon inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and hearing a bone crack with the inability to move the hand or fingers in the wrist or thumb area, help to identify and diagnose the injury.
Massage can relieve symptoms and pain, give relief to the injured, and help speed up the treatment of hand tendonitis.