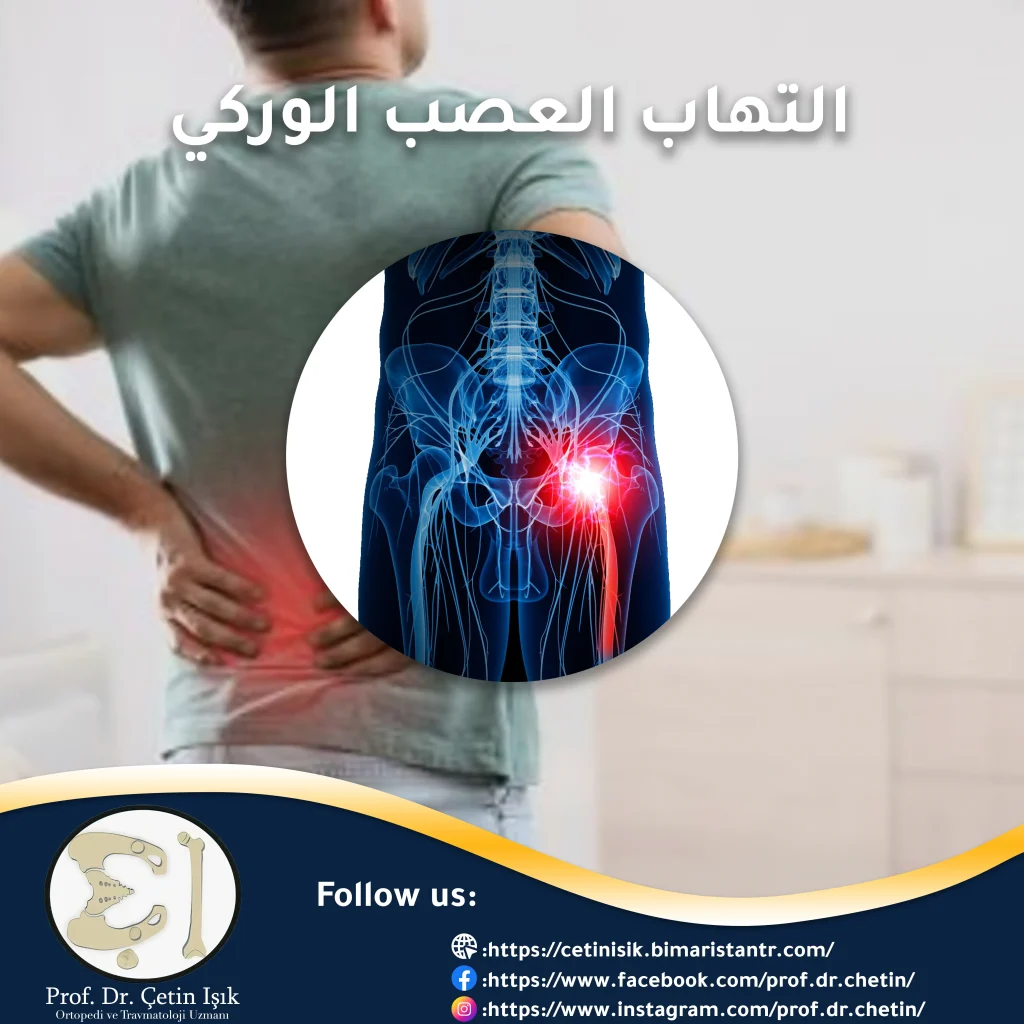
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve (sciatica) is irritation of the nerve as a result of its compression, which leads to feeling pain that spreads along the path of the nerve from the lower back to the legs, which restricts the patient’s movement.
The danger of inflammation of the sciatic nerve lies in the possibility of chronic weakness in the leg muscles, causing foot drop. Let us learn together about inflammation of the sciatic nerve and its risks.
What is sciatica?
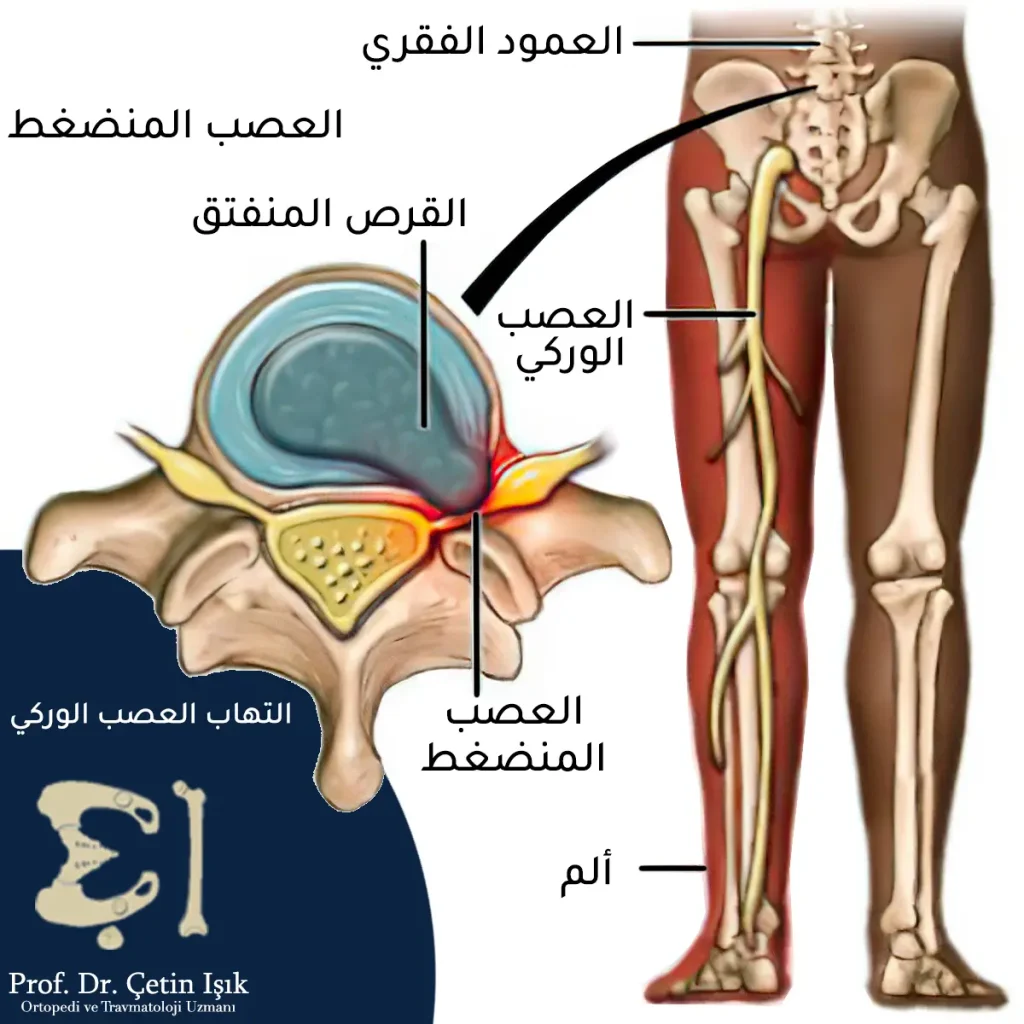
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, or so-called sciatica, is an irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve, which leads to pain, numbness, and numbness along the path of the nerve, starting from the lower back and possibly reaching the leg.
The sciatic nerve is the longest and thickest nerve in the human body. The lower back is formed from the nerve roots of the lumbosacral column and extends to the leg.
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve can occur at all ages and in both sexes, but there are some factors that contribute to its occurrence, called risk factors for sciatica, and they include the following:
- Age: The risk of sciatica neuritis increases with age due to the increase in degenerative diseases with age, which leads to pressure on the nerve.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise and sitting for long periods can contribute to muscle weakness, which increases pressure on the spine
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional pressure on the spine
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, hormonal changes and weight gain may cause pressure on the spine
Causes of sciatica
There are many causes that lead to nerve irritation and inflammation, including the following:
- Herniated disc: A herniated disc causes pressure on the adjacent nerve roots that form the sciatic nerve
- Spinal stenosis: occurs with age and leads to pressure on the nerve roots. Including the sciatic nerve
- Degenerative disc disease: The discs between the vertebrae can degenerate with age, losing their flexibility and shock absorption, and may put pressure on the nerve roots.
- Spondylolisthesis: It is a slippage of one of the vertebrae forward or backward, which leads to pressure on the nerve roots
- Trauma: Any direct trauma to the spine can affect the sciatic nerve, such as fractures and dislocations
- Tumors and cysts: Tumors and cysts can press on nerve roots, causing nerve inflammation
Read more about: Spinal stenosis treatment
Symptoms of sciatica
He can pretend Sciatica Many symptoms include:
- Pain: It is the most common symptom of inflammation of the sciatic nerve. It often begins in the lower back and then spreads down the back of the thigh and leg, and sometimes to the foot. Its intensity can range from mild to severe pain, and the pain is described as burning or similar to the pain of an electric shock.
- Numbness and tingling: The patient may not feel any sensations in the lower back and leg because sensory signals do not reach the brain due to inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
- Muscle weakness: Weakness occurs in the muscles innervated by the sciatic nerve, which leads to difficulty controlling the affected leg, and this affects the patient’s activities such as walking and climbing stairs.
- Difficulty sitting or standing: Patients with sciatica often have difficulty sitting or standing, but changing position can provide temporary relief for the patient.
- Worsening of symptoms with certain activities: Some activities can cause worsening of symptoms, such as bending over, sneezing, and coughing. Because these activities may cause additional pressure on the nerve.
- Urinary or fecal incontinence: This is the involuntary passage of urine or feces due to poor bladder and bowel control as a result of nerve injury.
Diagnosis of sciatica
Diagnosis usually begins with a comprehensive physical examination and review of the patient's medical history. The doctor may perform a physical test to determine the location and cause of nerve irritation, for example the straight leg raise test (raising the leg and knee straight to elicit symptoms of the sciatic nerve).
Additional tests may also be ordered to help confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause of sciatica. These tests include:
- X-RAY: This may help rule out other causes of back pain, such as: Spinal fracture And structural distortions
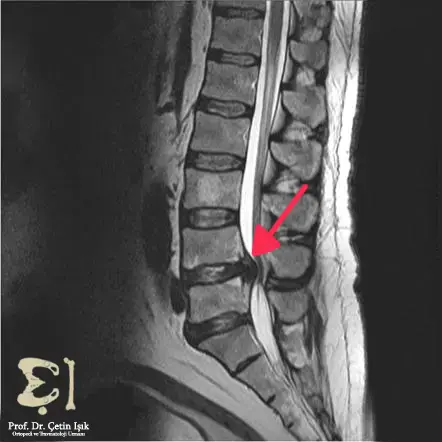
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): gives a detailed picture of the spine and surrounding structures and diagnoses some diseases such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
- Computed tomography (CT-scan): It also gives detailed images of the spine, especially in cases where it is not possible to perform an MRI.
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NSC): These tests can evaluate electrical activity and function of muscles and nerves, and determine the presence of nerve damage or pressure
Treatment of sciatic nerve inflammation
Treatment for sciatica aims to relieve pain and inflammation and treat the underlying cause. Treatment options can vary depending on the severity and duration of symptoms and the cause of inflammation. How to get rid of sciatic nerve pain includes home, medication, natural and surgical treatment.
Home (self) treatment
Sciatica pain can be relieved and mild cases of the disease can be managed through home (self) treatment. Options for treating sciatica at home include:
- Rest and take non-prescription pain relievers such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Heat or cold therapy: Applying hot or cold compresses to the affected area can reduce inflammation and pain
Medical therapy
Medications may be used to treat sciatica if self-treatment is not sufficient to manage sciatica pain. Medications used include the following:
- Epidural corticosteroid injections in cases of severe or persistent pain. The steroid reaches the space around the affected nerve and reduces inflammation and pain.
- Muscle relaxants and tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline)
Physical therapy (exercises to treat sciatica)
A personalized exercise program is developed for the patient by your physical therapist to improve flexibility and strengthen muscles, in addition to improving any poor posture. Sciatic nerve exercises include stretching exercises and some routine exercises.
Stretching exercises aim to relieve the pain of sciatica through stretching exercises for the lower back. Physical therapy can also include some techniques such as ultrasound therapy or electrical stimulation to relieve pain and speed up the healing process.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment can be resorted to when conservative treatment fails and when the inflammation is severe and affects the patient's activities. There are many surgical options that can be performed depending on the cause. These options include resection of a herniated disc, laminectomy, and vertebral fusion.
Discectomy
Part or all of the herniated disc is removed Treatment of herniated disc Which puts pressure on the sciatic nerve, and this operation has two methods. In the first method, the open disc is removed by making an incision in the back and removing the herniated disc. In the second method, the microscopic disc is removed through a small incision and using an endoscope, which reduces damage to the surrounding tissues.
Laminectomy
This surgery is used in cases of spinal stenosis; Part of the vertebra (lamina) is removed in order to expand the spinal canal and relieve pressure on the nerves.
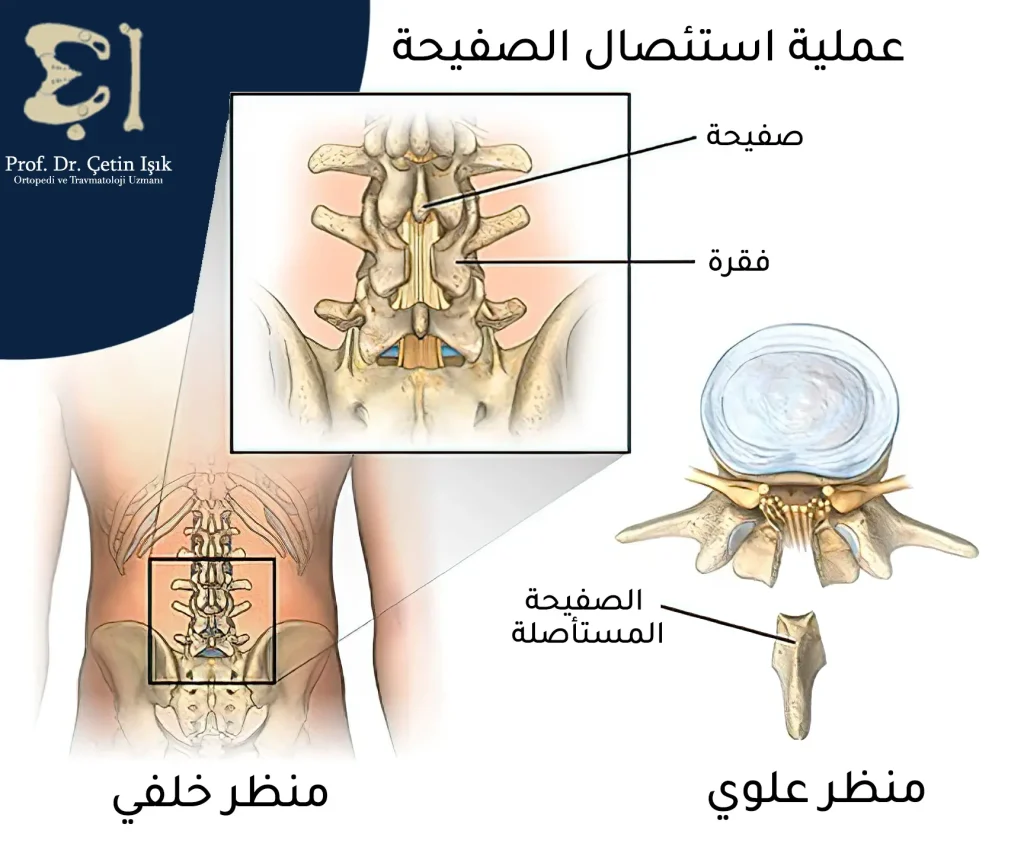
merge paragraphs (Install the paragraphsSpinal fusion
This operation can be performed in the event that the spine is unstable and puts pressure on the nerves, where two or more vertebrae are fused together using bone or metal grafts to stabilize the spine and relieve pressure on the nerves.
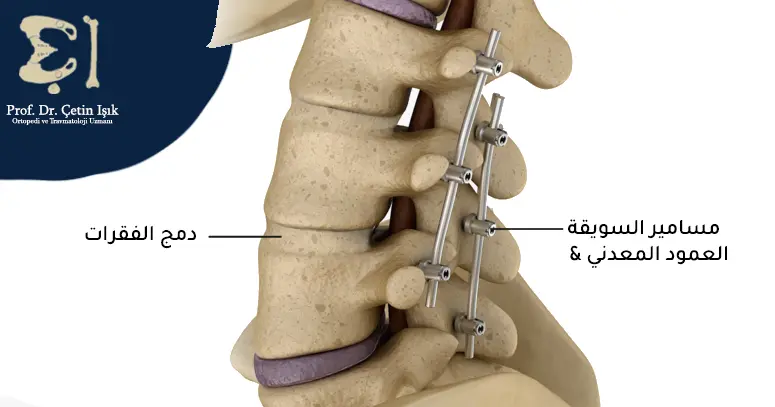
Treatment of sciatic nerve inflammation with herbs
There is usually little resort to treating sciatica with herbs due to the lack of scientific studies indicating the possibility of using herbs in treatment. However, some herbs that have anti-inflammatory properties can be used after consulting a doctor.
Herbs that can be used include turmeric (contains anti-inflammatory curcumin) and ginger (gingerol).
Complications of sciatica
Most cases of hip neuritis improve with appropriate treatment over time, but some complications can occur as a result of neglect or poor management. These risks include:
- Chronic pain: Chronic pain results from neglecting the condition and not treating it, and this affects the patient’s quality of life and daily activity
- Nerve damage: Prolonged pressure on nerves can damage them, causing muscle atrophy Its weakness and, consequently, permanent weakness in the leg or foot on the affected side
- Restriction of movement: Pain and discomfort limit movement and activity, resulting in general physical weakness
- Loss of bladder and bowel control: In rare cases, severe pressure on the sciatic nerve may cause loss of bladder and bowel control (urinary or fecal incontinence).
Prevention of sciatica
Sciatica can be prevented by protecting the back by following the following tips:
- Maintain good back posture
- Do not sit or stand for a long time
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Do regular exercise
التهاب العصب الوركي هو حدوث تهيج العصب مما يؤدي إلى حدوث ألم في أسفل الظهر ينتشر على مسار العصب، وغالباً ما تتحسن معظم الحالات بالعلاج المناسب بمرور الوقت، لكن قد يؤدي إهمال المرض إلى حدوث بعض المضاعفات التي قد تؤثر على حياة المريض
Sources:
Common questions
The sciatic nerve is the longest and thickest nerve in the human body. It forms in the lower back from the nerve roots of the lumbosacral column and extends to the leg.
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve can be eliminated by following up on the condition and treating it through home, medication, natural or surgical treatment, depending on the condition and the most appropriate treatment method.
Symptoms of sciatica include pain that begins in the lower back and spreads along the path of the nerve, in addition to numbness or numbness, muscle weakness, and difficulty sitting or standing.
Sciatica can be cured by properly monitoring and treating the disease.
Walking is beneficial for inflammation of the sciatic nerve, to improve fitness and reduce muscle weakness that may result from inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Sciatica can be treated at home in mild cases by resting, taking pain relievers, and using hot and cold compresses.