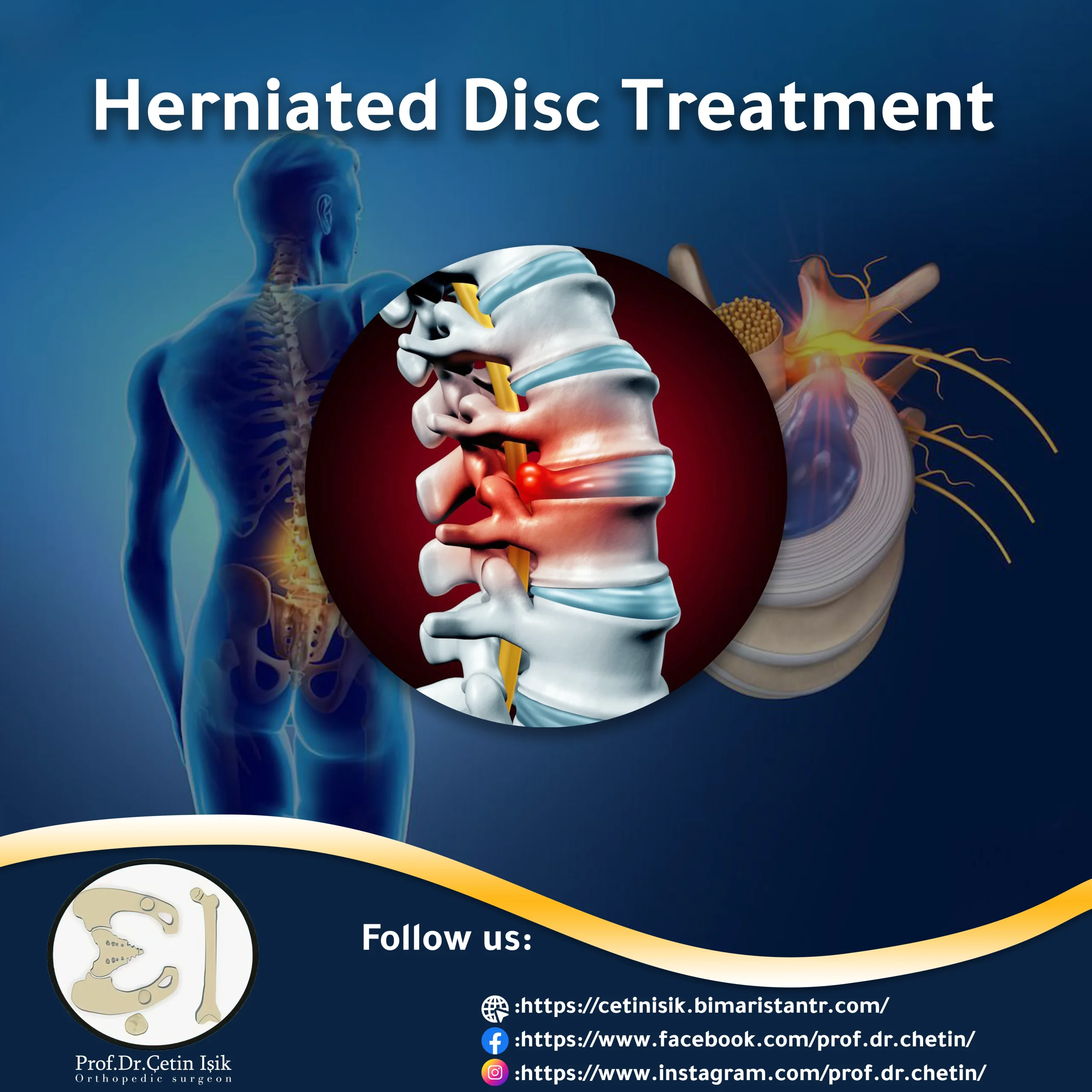
Treatment of a herniated disc in Istanbul is divided between conservative management and surgical treatment, and doctors have sought to develop surgical techniques due to the prevalence of the disease and the pain it causes in the neck and lower back.
What is the treatment for herniated disc?
To understand the treatment methods, we have to go through the herniated disc mechanism, its symptoms, and the components of the spine.
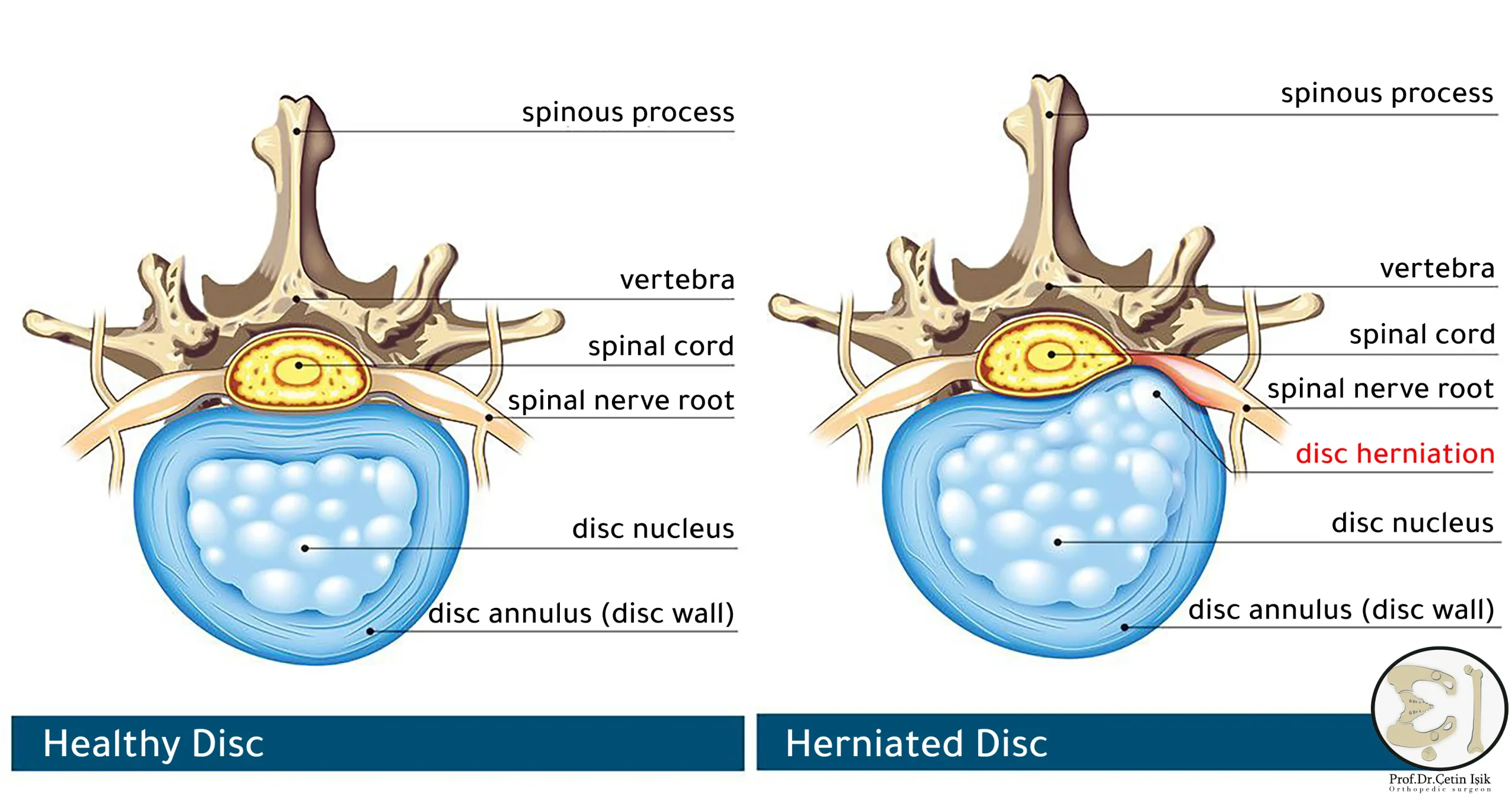
The spine is made up of 33 bones called vertebrae, between which there is spongy connective tissue surrounded by a rough annular membrane resembling soft rubbery cushions called intervertebral discs.
It prevents the bones from rubbing against each other, fixes the vertebrae in place and protects the nerves as they pass through the spinal cord, and by working with the ligaments and lateral joints, it allows to maintain the natural curvature of the spine.
The spine is affected by a slipped disc or herniation of the nucleus pulposus due to a rupture or injury of the ring surrounding the nucleus of the disc and part of it pushes into the spinal canal.
This displacement results in compression of the accompanying spinal nerve, causing severe pain along its path, hence the importance of treating a herniated disc.
It can occur anywhere along the spine, but herniated discs are most common in the lower back or neck and rarely in the middle of the back.
Herniated disc risk factors
It can happen to anyone, but injuries are most common between the ages of 35 and 50, and in 2% people develop a herniated disc.
There are several factors that contribute to this, including:
- Smoking: It is one of the most important influencing factors, as smoking can lead to the disintegration of the outer ring and the nucleus of the cartilage core.
- Obesity and overweight: the owner of the lumbar disc herniation.
- Carrying heavy weights: puts pressure on the bones in the lower back.
- Sitting and standing for long periods in the same position, such as dentists.
- Heredity: It has been found that the presence of people with disc disease in family members increases the risk as well.
- Men are twice as likely to be affected by women.
- Repeated bending and twisting movements.
Causes of herniated disc
A herniated disc forms when the outer ring becomes weak or torn and a protrusion of disc content occurs between the vertebrae of the spine.
This can be done for several reasons:
- Aging (aging): Because the cartilage material gradually dries up with age, making the disc more prone to rupture even with slight strain or flexion of the body.
- Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle: contribute to the weakness of the muscles and ligaments supporting the cartilage.
- Severe injury put a lot of pressure on The disc and spineon.
- Accidents such as falling from a height or a car accident.
Stages of herniated disc
A herniated disc goes through four stages of deterioration for several years before reaching its final state:
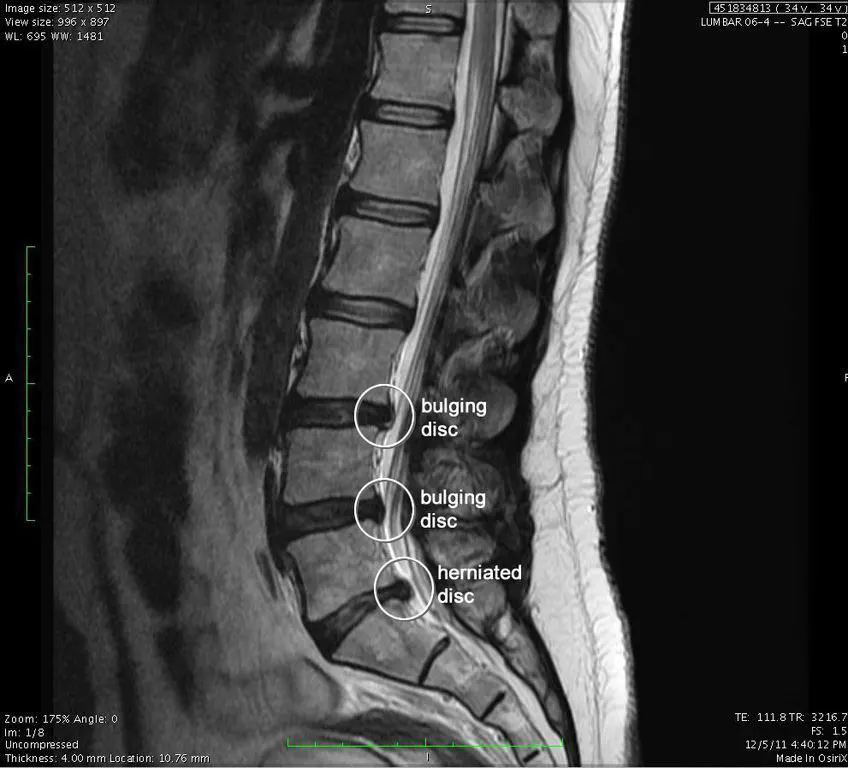
- bulging disc: At first there is weakness in the outer layer and bulging out, but without rupturing the fibrous ring of cartilage.
- disc kernal protrusion: At this point, the nucleus pulposus is pushed outward further into the annulus, which means that the disc appears drooping and prominent.
- Herniated disc (extrusion): The outer layer of the disc ruptures at this point, and a large portion of the nucleus spills beyond the annulus cartilage, but remains within the cartilage.
- Prolapse of the nucleus pulposus of the disc (incarceration): The nucleus completely separates from the main mass, causing severe pain by pressing on the adjacent nerve within the spine.

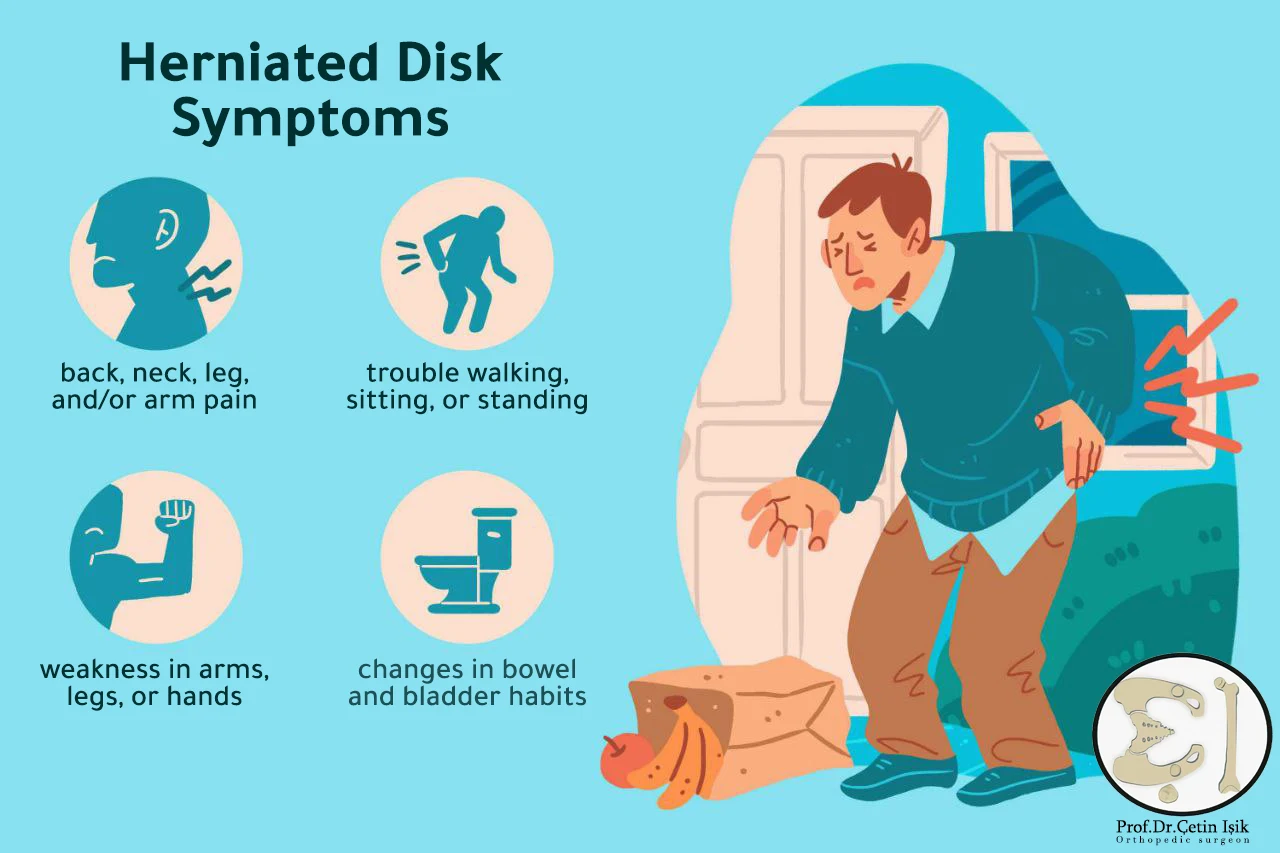
Symptoms of a herniated disc
The exit of a section of the nucleus pulposus of the cartilaginous disc stimulates the release of chemical agents that irritate the nerves surrounding the vertebra, causing inflammation in the area and severe pain; Common symptoms of a herniated disc also include:
- Numbness or tingling: It occurs when pressure is applied to the spinal cord or the nerves leaving it, and the sensation may travel along the nerve path to the leg or arms, often on one side of the body.
- Muscle weakness: Over time, the muscle connected to the compressed nerve may atrophy, which can cause stumbling when walking.
- the pain: It usually occurs in the lower back or neck and may extend to the arms or leg, and is characterized by being sharp and burning.
- Bowel or bladder control problemsIn the case of a severe and untreated herniated disc in the lumbar region.
Cervical herniated disc
The pain is localized in the shoulders, arms and neck bones, and symptoms such as tingling and arm tingling, stiffness in the neck vertebrae and the accompanying difficulty in sleeping, and chronic headaches occur as a result of pressure on the nerves of the head.
Lumbar herniated disc (lower back)
The normal lumbar spine is considered the most mobile, and because of this, this region is most affected by degenerative conditions and post-slip spinal stenosis.
Pain when a herniated lumbar disc spreads to the buttocks, thighs, and legs. Pain that travels along the sciatic nerve is known as SciaticaIt usually occurs due to compression of the fifth lumbar or first sacral nerve.
Most cases of lumbar herniated disc are located between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae L4-L5.
Herniated disc in the middle of the back
Less common pain localized in the back may travel around the rib cage to the front of the body.
Diagnosis of herniated disc
The doctor can diagnose a herniated disc by physical examination of the patient, by checking: intensity of reflexes, location of pain, muscle strength, nerve response, range of motion, ability to walk.
To confirm the diagnosis before treatment, we resort to radiography:
- X-ray: Helps rule out other causes of back or neck pain.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): It is the most common and accurate investigation, so it is reliable in diagnosing a herniated disc.
- Myelogram: To detect the location of the spinal canal stenosis and the location of the slipped disc.
Complications of herniated disc
Complications of a herniated disc include chronic back pain or permanent nerve damage in severe hernias for many years without treatment.
In rare cases, a herniated disc can compress an entire group of nerves. This condition is referred to as:
Cauda equina syndrome, the main symptoms are: severe lower back pain and difficulty urinating, and it is a problem that requires emergency surgical treatment.
Methods of treating herniated disc (disc) in Turkey
The options available for the treatment of herniated discs vary, according to: the degree of herniated disc, the age of the patient, the accompanying symptoms, the presence of chronic diseases and the patient’s general health status.
Herniated disc treatment includes conservative or surgical management. Surgery may lead to rapid recovery of symptomatic herniated disc, but the results are also similar with conservative treatment one year after herniated disc surgery.
In most cases, doctors adopt non-surgical measures first to treat a herniated disc and relieve symptoms. The patient may need one or more of these treatments:
Medications:
- NSAIDs: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen and naproxen can help in cases where the pain is mild.
- Opioid analgesics: Sometimes used to relieve severe pain, they are prescribed for the shortest possible period, taking into account their side effects.
- muscle relaxants;
- Nerve pain relievers: If symptoms persist over time, the doctor may resort to anticonvulsant drugs such as gabapentin and duloxetine.
Physical therapy:
It is not recommended to start physical therapy until symptoms of a herniated disc have persisted for at least three weeks.
However, it is a common method, where a physical therapist helps teach the patient proper spinal alignment, how to move safely, range of motion, and flexibility.
The components of physical therapy may include a group of exercises that the patient does at home to stretch and strengthen the abdominal muscles which are necessary to support the lower back, and it will be under the supervision of the therapist. The results of adhering to it usually appear after several weeks of practice.
When resting, heat and cold compresses can be used alternately on the vertebrae where the pain is located, which speeds up the process of treating a herniated disc.
Many patients also find significant improvement in practicing yoga exercises that gently stretch the neck, back, hips, joints and hamstrings and reduce muscle fatigue.
Injection:
Herniated disc is treated with epidural and spinal corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling and inflammation caused by slipped disc and relieve back pain. This measure is known as a nerve block.
This injection is done under the guidance of medical imaging so that the surgeon can insert the needle and safely inject the material into the exact location.
Most doctors agree that epidural injections can be helpful during an acute attack of back pain or sciatica.
This injection provides sufficient pain relief to allow the patient to progress in the rehabilitation physiotherapy program.
The main disadvantages of injection herniated discs are that they are not always effective, and if effective they tend to be temporary, ranging from a week to a year.
surgery:
Surgical intervention is considered the last resort in the treatment of a herniated disc when other treatment methods have failed after trying for 6 to 12 weeks and when the patient is neurologically impaired, early intervention in these cases is best in order to maximize the possibility of neurological recovery.
The doctor uses minimally invasive surgical methods whenever possible, by making very small incisions so that the herniated disc can heal faster and return to life activities as soon as possible after surgery.
Among the surgical methods used in the treatment of a herniated disc:
Laparoscopic discectomy surgery: This technique, which is considered the least invasive method of treating slipped discs, requires making the smallest incision (7 mm). The specially trained surgeon uses a thin endoscope that is inserted into the incision and X-rayed is guided into the herniated disc. This is done without cutting the muscle, making This method of treating herniated disc is essentially painless, and the patient can return home on the same day of the procedure.
Nucleotomy: To treat a herniated disc, the nucleus pulposus of the disc is removed by suction or by laser.
Laminectomy surgery: It is a thin plate that forms the back of the vertebra, a hole can be made in it to reduce pressure on the spinal nerve or to completely remove it.
Spinal fusion (spinal fusion): In this surgical procedure, the doctor attaches two or more vertebrae together. The surgeon works through small incisions and uses screws to unite the two vertebrae while avoiding injury to the nearby soft nerve tissue. Spinal fusion reduces the movement of the spine in the treated area of the slipped disease, but this treatment technique is very effective in treating Herniated disc and pain relief.
Disc Replacement Surgery: The slipped disc is replaced with an artificial one that is able to perform the function of the healthy disc after locating the slipped disc. The implant is only done in the case of treating a herniated disc of a single damaged disc, and he also does not suffer from osteoporosis or arthritis diseases.
In case you encounter any problem and seek the correct medical advice to treat a herniated disc case Contact with usAnd the doctor will answer you Çetin Işık will answer you for all your inquiries.
Prevention of herniated disc
To reduce the risk of spinal injury and avoid herniated disc recurrence:
- Maintaining the body in the correct position.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects.
- stop smoking.
- Sit properly with regular breaks to move around.
- Exercising regularly to strengthen the abdominal and back muscles.
Sources:
Common questions
With proper treatment of a slipped disc, which is usually a combination of pain relievers and conservative physiotherapy without surgery, the symptoms of a slipped disc may resolve within 4-6 weeks.
It is a common, non-life-threatening condition, but it can sometimes cause permanent nerve damage if left untreated.
Daily walking is an excellent way to exercise with a herniated disc, without putting pressure on the spine and causing painful symptoms, starting with 5-10 minutes a day with an increase in the duration to reach 40 minutes.
Deep tissue massage is an ideal option in the case of a herniated disc, using the appropriate amount of pressure to relieve tension and deep muscle spasms that develop to prevent muscle movement in the affected area, it is an adjunct option to treat a herniated disc.
The preferred sleeping position for a herniated disc patient is lying on the back, thus keeping the vertebrae neutral, thus reducing the chance of pressure on the nerve, and for more comfort, pillows can be used under the knees and lower back.
The cost of treating a herniated disc varies depending on the number of affected vertebrae and the treatment method used, whether by injection, laser, or minimally invasive surgical intervention. But in general, the cost ranges between 2 and 5 thousand US dollars.