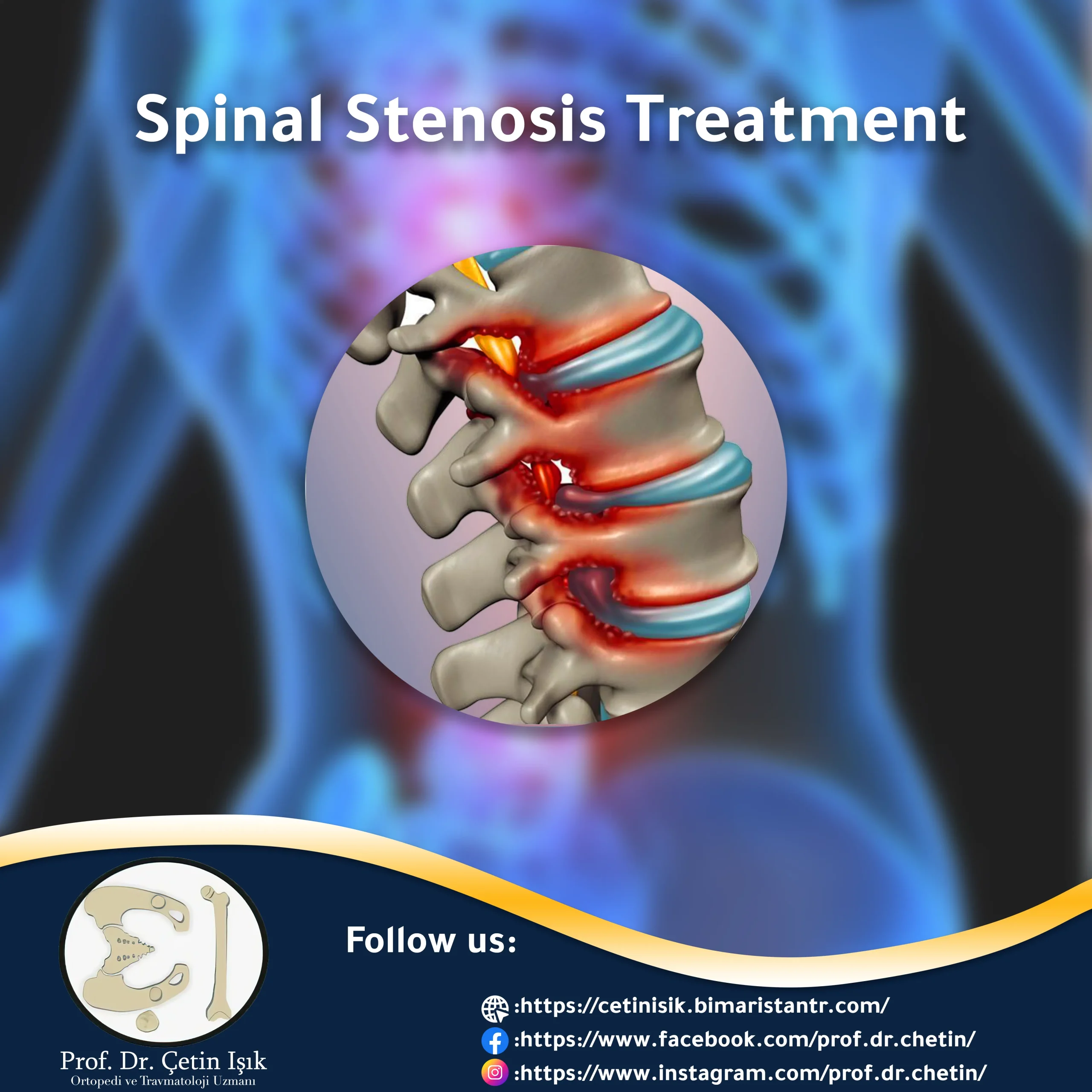
ما هو تضيق القناة الشوكية؟
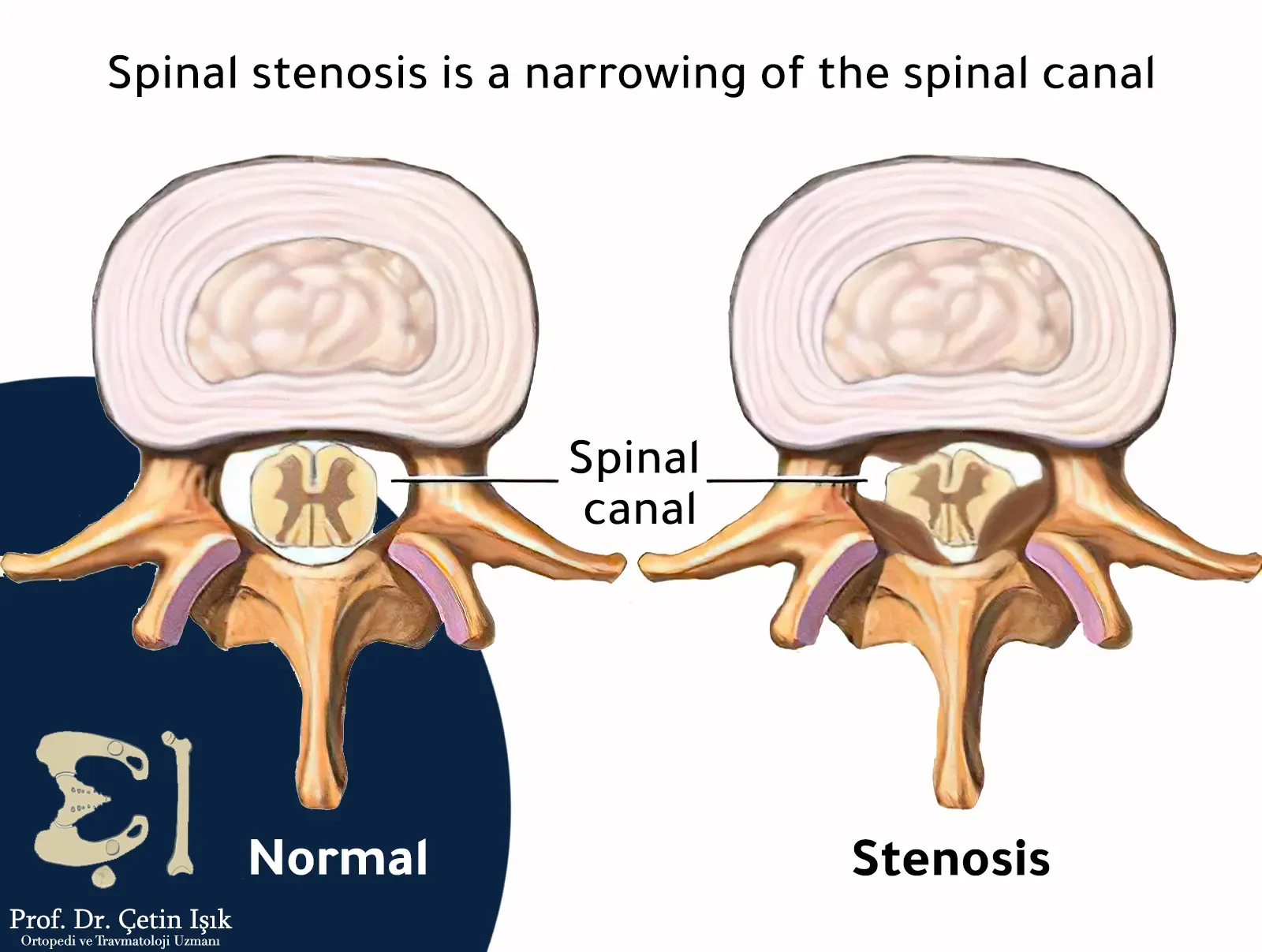
Spinal stenosis (Spinal Stenosis) هو حالة مرضية تحدث عندما تضيق المساحة داخل العمود الفقري، مما يؤدي إلى الضغط على النخاع الشوكي أو جذور الأعصاب. غالبًا ما يظهر في الفقرات القطنية (أسفل الظهر) أو العنقية (الرقبة)، ويُسبب آلامًا وتنميلًا وضعفًا في الأطراف، خصوصًا أثناء المشي أو الوقوف لفترات طويلة.
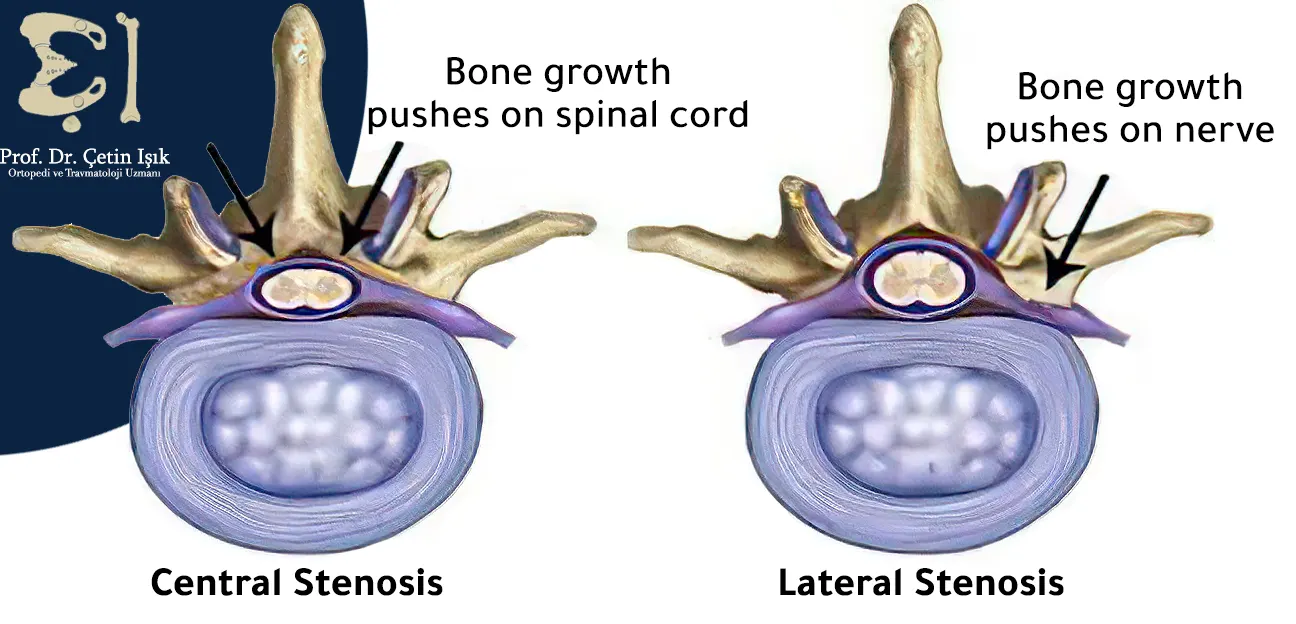
Causes of spinal stenosis
- التغيرات التنكسية المرتبطة بالتقدم في العمر (مثل تآكل الغضاريف)
- Slipped disc (الديسك)
- النمو الزائد للعظام (النتوءات العظمية)
- السماكة الزائدة في الأربطة (تؤدي إلى تضييق القناة)
- الكسور أو إصابات العمود الفقري
- أسباب خلقية (تشوهات منذ الولادة)
Symptoms of spinal stenosis
| الموضع | الأعراض الشائعة |
|---|---|
| الرقبة (عنقي) | ألم في الرقبة، تنميل أو ضعف في الذراعين، فقدان التوازن |
| lower back | ألم في الظهر، ثقل وتنميل في الساقين، صعوبة في المشي |
| عام | تفاقم الأعراض مع الوقوف أو المشي، تحسنها عند الانحناء للأمام |
تشخيص تضيق القناة الشوكية في إسطنبول
في إسطنبول، يُستخدم مزيج من الفحص السريري والتصوير الطبي المتطور لتحديد درجة التضيق بدقة:
- الرنين المغناطيسي (MRI): يُظهر التضيقات بدقة عالية.
- الأشعة المقطعية (CT): لتحديد التغيرات العظمية.
- X ray: لفحص تراصف الفقرات والنتوءات العظمية.
- تخطيط الأعصاب (EMG): لتقييم تأثر الأعصاب.
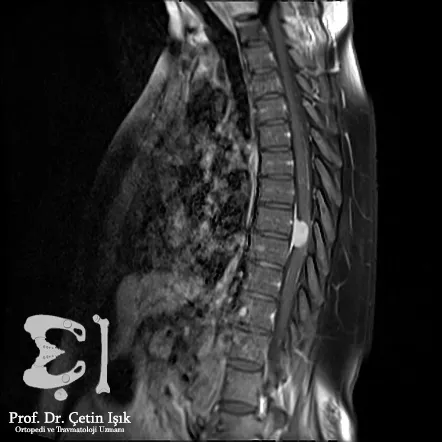
خيارات علاج تضيق القناة الشوكية في إسطنبول
1. العلاج التحفظي (غير الجراحي)
| الطريقة | التفاصيل |
|---|---|
| Physical therapy | تمارين لتقوية العضلات وتحسين المرونة وتخفيف الضغط |
| أدوية مضادة للالتهاب | لتقليل التورم وتخفيف الألم |
| حقن العمود الفقري | مثل حقن الكورتيزون لتقليل الالتهاب مؤقتًا |
| تعديل نمط الحياة | فقدان الوزن، تحسين وضعية الجسم، استخدام داعمات خاصة |
يُناسب الحالات الخفيفة إلى المتوسطة والتي لا تهدد الوظائف العصبية.
2. العلاج الجراحي
إذا لم تُجدِ العلاجات التحفظية نفعًا، يُوصى بالتدخل الجراحي لتوسيع القناة الشوكية وتخفيف الضغط العصبي.
أشهر أنواع العمليات في إسطنبول:
| نوع العملية | الشرح |
|---|---|
| استئصال الصفيحة الفقرية (Laminectomy) | إزالة جزء من العظم لفتح القناة الشوكية |
| التحرير المجهري للأعصاب | باستخدام المنظار الجراحي عبر شق صغير |
| دمج الفقرات (Spinal Fusion) | لتثبيت الفقرات بعد إزالة الضغط، ويُستخدم غالبًا في حالات عدم الثبات |
| جراحة المنظار (Endoscopic surgery) | طفيفة التوغل، نتائج سريعة، وألم أقل بعد العملية |
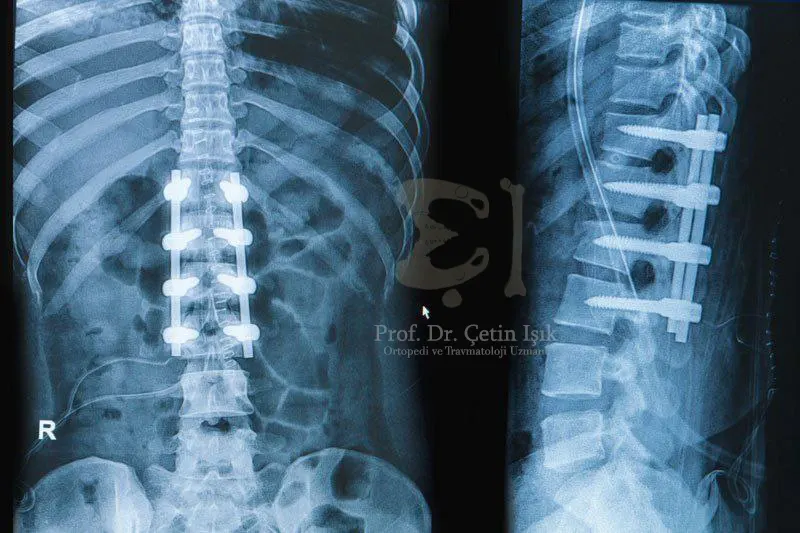
مميزات علاج تضيق القناة الشوكية في إسطنبول
- أطباء أعصاب وجراحة عمود فقري بخبرة أوروبية.
- تقنيات جراحية حديثة تشمل المنظار والليزر.
- تكلفة منخفضة نسبيًا دون المساس بجودة العلاج.
- مستشفيات حاصلة على اعتماد JCI (اللجنة الدولية المشتركة).
- خدمات مخصصة للمرضى الدوليين تشمل الترجمة، المواصلات، والإقامة.
تكلفة علاج تضيق القناة الشوكية في إسطنبول
| نوع العلاج | التكلفة التقريبية (دولار أمريكي) |
|---|---|
| العلاج الطبيعي (10 جلسات) | 400 – 700 |
| الحقن فوق الجافية | 600 – 1,000 |
| جراحة بالمنظار لتوسيع القناة | 4,000 – 6,500 |
| جراحة استئصال الصفيحة | 5,000 – 8,000 |
| جراحة دمج الفقرات المعقدة | 8,000 – 12,000 |
تختلف التكاليف حسب عدد الفقرات المصابة، نوع التقنية، ومدة الإقامة.
مقارنة الأسعار عالميًا
| الدولة | تكلفة الجراحة بالمتوسط (دولار أمريكي) |
|---|---|
| تركيا (إسطنبول) | 4,000 – 8,000 |
| ألمانيا | 12,000 – 18,000 |
| الولايات المتحدة | 20,000 – 45,000 |
| الإمارات | 10,000 – 20,000 |
المدة المتوقعة للعلاج والإقامة
| المرحلة | المدة |
|---|---|
| التقييم والتصوير | 1 – 2 يوم |
| الإجراء الجراحي (إن وُجد) | يوم واحد |
| الإقامة في المستشفى | 2 – 5 أيام |
| فترة التعافي الفندقي | 4 – 7 أيام |
| العودة للحياة اليومية | خلال 2 – 4 أسابيع |
| العودة للنشاط البدني الكامل | خلال 2 – 3 أشهر |
أسئلة شائعة
هل يمكن علاج تضيق القناة الشوكية بدون جراحة؟
نعم، العديد من الحالات تستجيب للعلاج التحفظي مثل العلاج الطبيعي والحقن، خصوصًا في المراحل المبكرة.
هل الجراحة آمنة؟
في المراكز المتخصصة في إسطنبول، تُجرى الجراحات تحت إشراف فرق طبية متكاملة باستخدام أنظمة مراقبة دقيقة، ما يقلل من المخاطر ويزيد من نسبة النجاح.
هل يمكنني السفر بعد الجراحة؟
نعم، معظم المرضى الدوليين يمكنهم السفر بعد أسبوع إلى 10 أيام من العملية، بعد التأكد من استقرار حالتهم.
هل يتكرر التضيق بعد العملية؟
نادرًا ما يتكرر التضيق بعد الجراحة، خاصة إذا تم الالتزام ببرنامج التأهيل والعلاج الطبيعي.
خلاصة
إذا كنت تعاني من آلام مزمنة في الظهر أو الأرجل بسبب تضيق القناة الشوكية، فإن إسطنبول توفر لك حلولًا علاجية متقدمة تجمع بين الخبرة الطبية العالية andالتكلفة المقبولة. سواء اخترت العلاج التحفظي أو الجراحي، ستحصل على رعاية متكاملة في بيئة طبية حديثة، وبدعم من فرق متخصصة في جراحة العمود الفقري.
Spinal stenosis can occur in anyone, but it is more common in people 50 years of age or older.
Sources:
Common questions
The skill of the surgeon, the extent of spinal stenosis, and the patient's general health are all factors that affect the success of surgical treatment, but the results of spinal stenosis surgery are often good, with 80-90% patients recovering from their pain after surgery.
Like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks of serious complications, such as:
▪︎ infection.
▪︎ Allergic reaction.
▪︎ Nerve or spinal cord damage.
▪︎ Not relieving pain.
▪︎ The need for alternative surgery.
Full recovery after spinal stenosis surgery and return to daily activities usually takes about three months, and possibly longer for spinal fusion, this determines the complexity of the surgery and the efficiency of rehabilitation afterwards.