Shoulder calcification disease is an acute or chronic painful condition due to the presence of calcified deposits in the rotator cuff. It is treated with medication, physiotherapy, and in some cases, surgical treatment.
What is shoulder calcification?
The rotator cuff is made up of several tendons that connect the muscles around the shoulder to the upper arm (humerus), helping to stabilize the shoulder joint and move the arm within a normal range.
Calcific tendinitis occurs when calcium deposits accumulate in the tendons and muscles, as these deposits become inflamed and cause severe pain that may last for months.
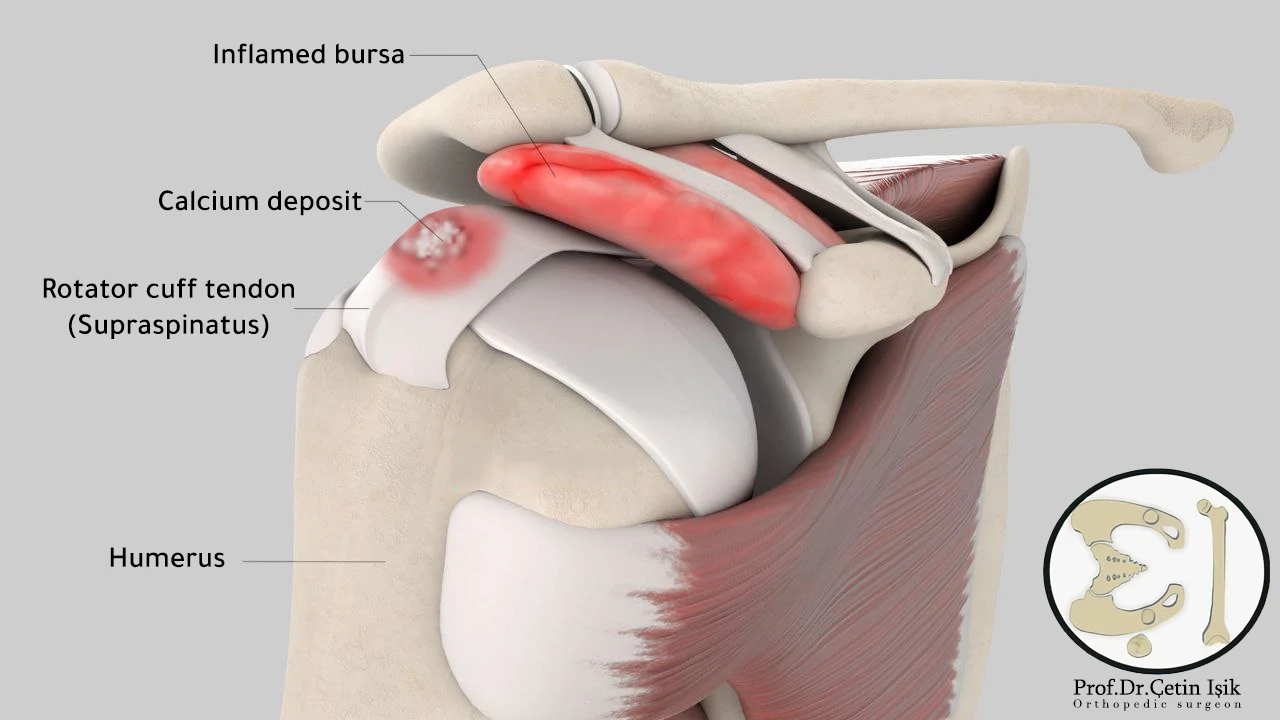
Calcific tendinitis can occur anywhere in the skeleton, such as the hip joint or the knee joint, but it is more common in the shoulder joint.
Risk factors for calcified shoulder disease
Shoulder calcification disease affects people between the ages of 40 and 60 years, and women are more likely to get it than men, and it is usually more common in the right shoulder than in the left.
The buildup of calcium deposits may be associated with one of the following factors:
- aging
- Tendon damage
- Hypoxia of the tendons
- heredity
- Inflammatory mediators secreted by the body in case of inflammation
- diabetic
- Abnormal activity of the thyroid gland
Causes of shoulder calcification disease
Doctors believe that the exact cause of shoulder calcification development is not fully known, as the mechanisms involved in tendon calcification are still not completely clear.
This condition usually occurs over time as a result of keeping the shoulder joint in one position for a long time, as in the case of sleeping on the shoulder every night or participating in various activities that require raising the hand above the head, as in athletes; This is why the disease is also referred to as: swimmer's shoulder or tennis shoulder.
Stages of shoulder calcification disease
Calcification of the shoulder develops slowly in three stages, namely:
- Pre-calcification: During this initial phase, changes develop at the cellular level, and movement causes pain and becomes limited in scope.
- Calcification: Calcium is released outside the cells to form deposits on the rotator cuff tendon, so that the body begins to absorb it after a while. This stage can cause a feeling of discomfort.
- Post calcification: In this procedure, calcareous deposits are replaced with healthy tissue, and range of motion begins to improve.
Shoulder calcification symptoms
Symptoms of shoulder spondylolisthesis tend to get worse slowly. Initial symptoms can be relieved with rest, but later the pain becomes severe and may interfere with sleep.
The symptoms of the disease vary, due to the duration of the joint injury, as they include the following:
- Sudden pain and swelling in the front of the shoulder and the side of the arm
- Severe pain caused by raising or lowering the arm
- A crackling sound when moving the arm
- Didn't it reach behind the back
- Loss of movement and strength in the affected arm
In the event that you feel any of the symptoms of shoulder calcification, you can: Contact us To take a medical consultation with Dr
Diagnosis of shoulder calcification disease
The doctor takes the patient's medical history and health history in case of medical problems and predispositions, and then conducts a physical examination of the affected area to find out the location of the pain and test the strength of the joint through light pressure and moving the shoulder.
The patient's neck can also be examined to check for conditions such as a slipped disc or arthritis that can cause symptoms similar to scapular spondylosis.
Finally; The doctor orders imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis of shoulder calcification and rule out any other causes of the pain, such as:
X-rays: which usually show calcium deposits in the rotator cuff, but the doctor must take x-rays in different cycles to avoid bone overlaying the deposits and making them less visible.
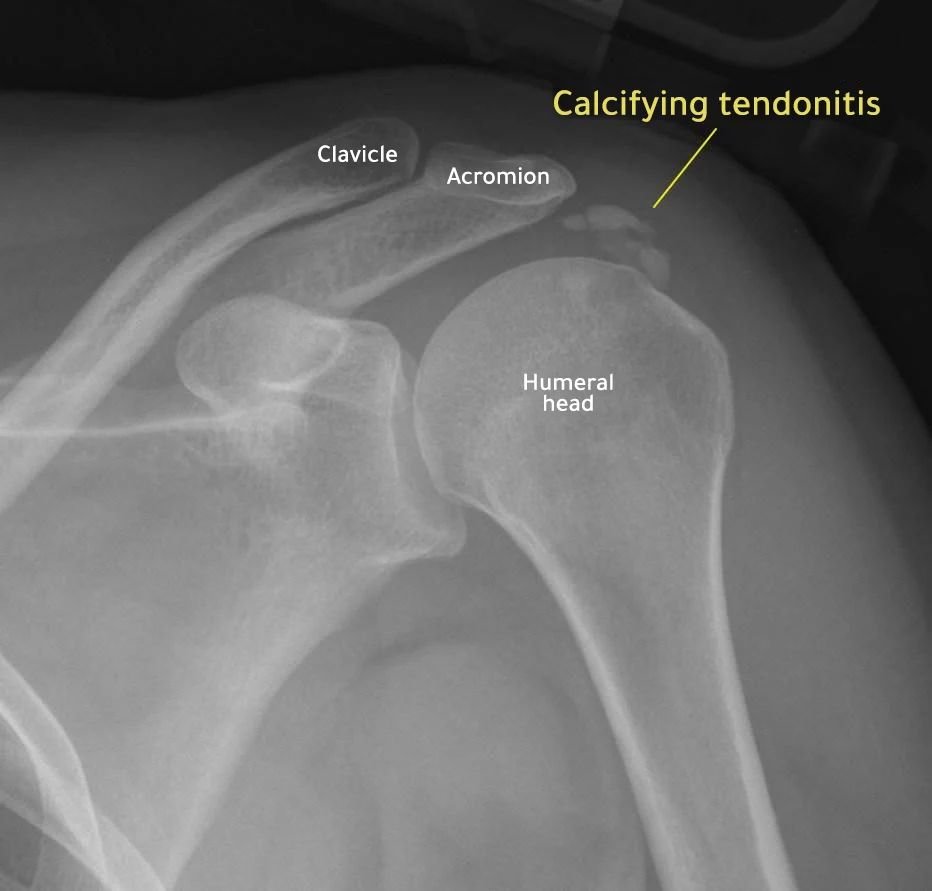
Ultrasound and MRI: to detect signs Inflammation in the shoulder joint Or in the event of a tendon rupture.
Shoulder calcification treatment
Initial treatment for shoulder spondylosis aims to control shoulder joint pain and reduce swelling to promote healing. This can be done by:
- Avoid activities that cause pain
- Put cold compresses on the surface of the injury area three to four times a day
- taking pain-relieving medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which include ibuprofen and naproxen
In the event that the pain persists and the symptoms do not improve, a set of effective measures can be used in the treatment of calcific tendinitis:
Physical therapy:
Physical therapy includes stretching and stretching exercises to help return to normal range of motion and relieve pain.
The specialist therapist can add exercises to the patient's schedule that increase the strength of the muscles around the shoulder once the symptoms are controlled.
Herbal shoulder treatment:
It is considered a natural method with very few side effects for treatment Shoulder pain Light, and these herbs include: turmeric, ginger, black sesame seeds and olive oil
Steroid injection:
If previous treatments fail, the doctor injects a steroid into the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle to reduce inflammation and swelling.
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy ESWT:
It is performed by means of a small device that provides mechanical shocks to the patient’s shoulder near the place where calcium deposits accumulate. These shocks break down the deposits. The more frequent the shocks, the more effective they are. It can be painful, but the doctor can adjust the level of frequency to suit the patient’s tolerance.
Treatment is carried out once a week for 3 weeks.
Radial Shockwave Therapy RSWT:
It is very similar to the previous procedure in that it delivers low-to-moderate energy shocks to the area of deposition in the tendon tissues and around the shoulder.
Treatment of calcification of the shoulder by pricking the skin with needles:
It is a more invasive procedure. First, the doctor applies a local anesthetic to the area before using needles to make holes in the skin.
It then removes the sediment through these holes using ultrasound waves to guide it towards the correct area.
Surgical treatment of shoulder calcification
Most people can treat calcific tendinitis or shoulder calcification without surgery, however 10% patients required the surgical option.
There are two types of surgery in which deposits are removed:
- Open shoulder surgery: In rare cases, open surgery becomes necessary. The surgeon accesses the calcium deposits by cutting through the muscles and other surrounding tissues. He cuts the tendon itself to remove the deposits. Then the surgeon suctions the area to remove calcium crystals that can irritate the tissues. Finally, suturing is done. skin and muscle together.
- Shoulder arthroscopy: In it, a small camera is used that guides the surgeon precisely to the location of calcareous accumulations.
Most of the time, recovery after shoulder tendon calcification surgery takes about six weeks. The patient may need to wear a brace to prevent the shoulder from moving too much.
Sources:
Common questions
Shoulder calcification is one of the painful bone diseases, as shoulder calcification causes excruciating pain if the calcium deposits increase in size or become inflamed, and hinders the daily activities of the injured person, such as wearing clothes, for example.
There are many treatment options in the event that a person has calciform tendonitis, such as: taking painkillers, taking adequate rest, adhering to physical therapy, steroid injections and shock wave therapy, and surgery can be resorted to as a last resort.
Shoulder calcification refers to inflammation within the tendon of the rotator cuff. Frozen shoulder is a condition characterized by pain and stiffness. Sometimes calcific tendinitis is associated with immobilization of the shoulder.