The treatment of rickets is very important, because of its great role in improving the quality of life of children, as most patients improve after treatment, allowing them to continue their lives normally.
What is rickets?
Rickets, or so-called rickets disease, is a skeletal disorder that affects the bones in children, caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, calcium and phosphate, which are essential nutrients for the proper growth and development of bones in children.
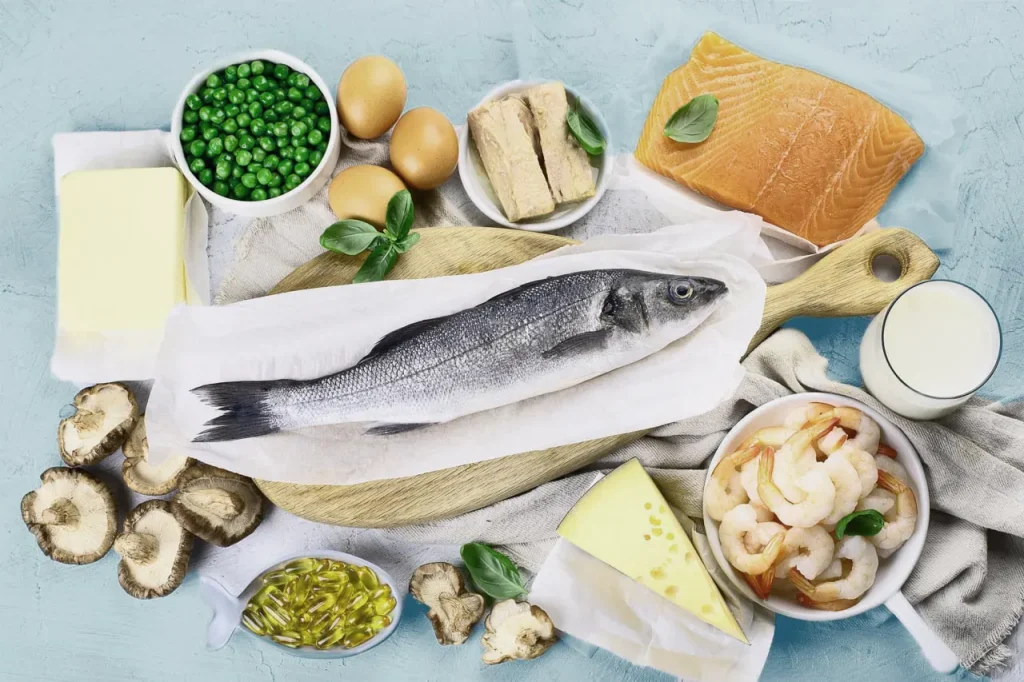
Vitamin D is an important vitamin that helps the body absorb calcium and phosphate from the intestines, and it is obtained from various sources, such as milk, eggs and fish, and the body can form this vitamin when exposed to sufficient sunlight.
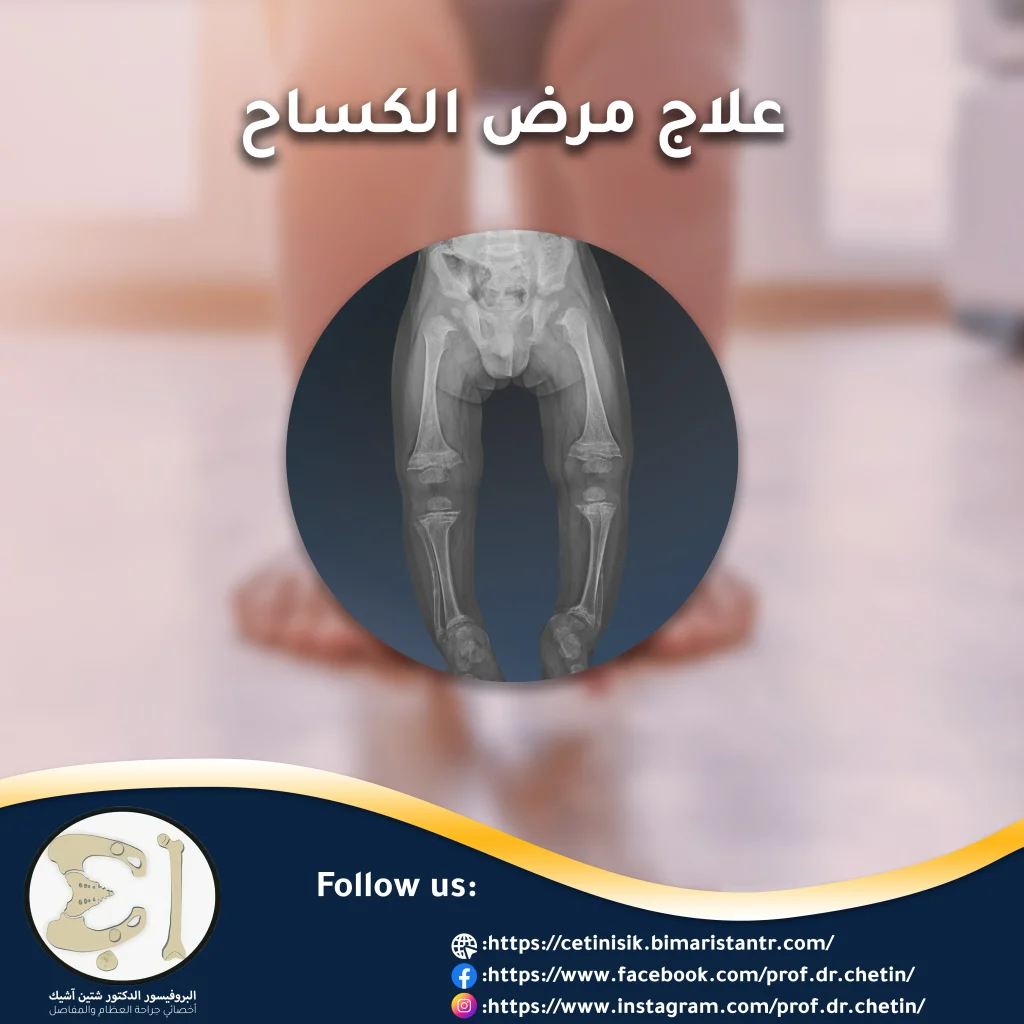
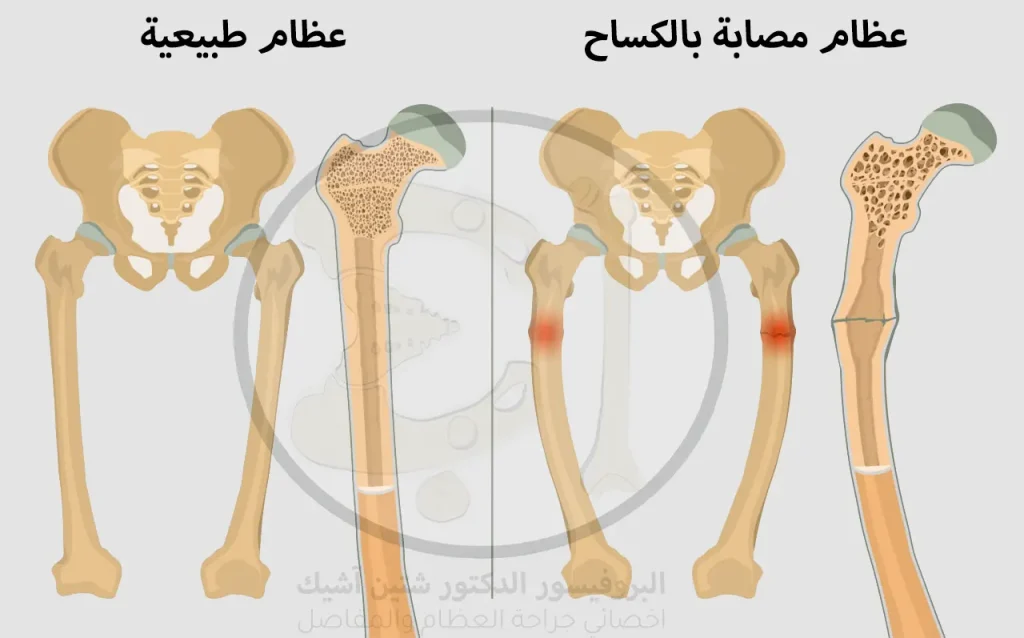
Rickets causes stunted growth, soft and weak bones in children, which makes them twist or bend and break more easily, and in severe cases of rickets, children develop structural deformities, so the treatment of rickets is of great importance in the child.
Causes of rickets
A child's bones grow when new bone is formed in the area of the growth plate or what is known as the epiphyseal plate, which is located near the end of the long bones, and this bone growth needs phosphorous and calcium, which bind to the bones to become strong and durable.
When a deficiency in vitamin D occurs in the body, the body suffers from difficulty in maintaining adequate levels of calcium and phosphorous, and this incites the body to secrete hormones that cause the release of these minerals from the bones, making them soft, weak and easy to break in young people with this disease.
A deficiency in the manufacture of this vitamin results in people who are usually not exposed to the sun sufficiently, such as those who live in areas with little exposure to the sun, or people who work indoors during daylight hours, or are obliged to stay indoors, which causes a decrease in the manufacturing rate This natural vitamin.
A deficiency can be formed due to insufficient nutrition or diet, such as people who suffer from lactose intolerance, or people who do not drink milk products or who follow a vegetarian diet and do not take what the human body needs of this vitamin, which leads to rickets for nutritional reason as a result of this deficiency.
Rickets may develop in newborns who depend on breastfeeding milk without other nutritional supplements, since breastfeeding milk does not contain high amounts of vitamin D necessary for the growth of the child. Dark-skinned children.
In less common cases, rickets may occur due to a genetic condition, some genetic disorders that cause poor absorption of calcium, phosphorous and vitamin D in a child, which predisposes to rickets and osteomalacia.
And no matter the cause of rickets, it is necessary to treat rickets and osteomalacia in children and adults.
Symptoms of rickets
Common symptoms in children with rickets and osteomalacia include:
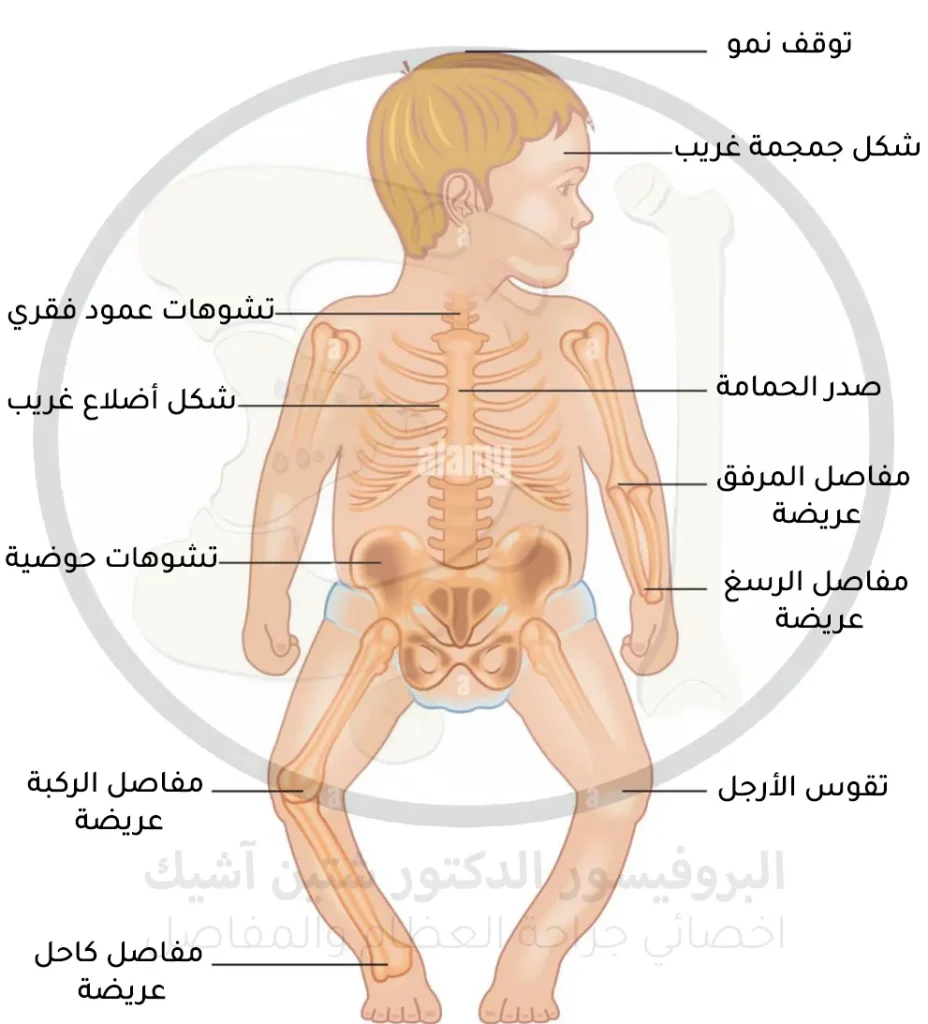
- Skeletal deformities such as the curvature of the bones in the legs of the child, his skull is soft, deformities in the pelvis, the pigeon's chest as a result of the protrusion of the sternum, and in rare cases, symptoms of spinal curvature appear.
- Symptoms of thickening and swelling in the ankle, wrist and knee joints, because the ends of the bones are larger than normal.
- Dental abnormalities in children such as delayed eruption of teeth in the mouth, holes in the enamel of the tooth, abscesses and an increase in the number of dental caves.
- Symptoms of pain and tenderness in the bones affected by rickets in children, where the child may refuse to walk or tire quickly, and the child's gait may seem strange and swaying.
- Symptoms of delayed crawling and walking, and stunted growth where the child is shorter than his peers.
- Symptoms of muscle cramps and tremors as a result of calcium deficiency, numbness in hands and feet.
- The bones of the injured are fragile and more prone to fractures.
Therefore, when you notice the appearance of one of the symptoms or signs of rickets in children, you must hurry to see a doctor in order to diagnose and treat rickets as soon as possible. If your child has symptoms of rickets, or you have any questions about the topic, you can Contact us and doctor Çetin Işık will answer you for all your inquiries.
Diagnosis of rickets in Turkey
There are several ways to diagnose the problem of rickets. This is usually done through a physical examination performed by the doctor. The goal of this examination is to detect tenderness or pain in the child's bones by applying gentle pressure on them.
The doctor may then order several tests to confirm the diagnosis of rickets, including blood tests, including:
- Serum calcium
- Serum alkaline phosphatase
- Serum Phosphate
- Arterial blood gases
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Urine calcium level
A radiograph of the bone is also usually ordered to detect any skeletal abnormalities, and in rare cases of rickets a bone biopsy is ordered.
Genetic analyzes may be required for hereditary rickets, and after detection and confirmation of the diagnosis, rickets will be treated in an appropriate manner.
Rickets treatment
Treatment of rickets aims to relieve symptoms and treat the cause of this injury in order to prevent the disease from recurring and returning. Therefore, the doctor depends on the accurate detection and diagnosis of rickets in order to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Rickets, and especially the one caused by nutritional deficiency, is considered a curable and treatable disease when it is detected early at a young age, and the treatment method depends on the severity of the condition.
The treatment of rickets focuses on compensating for the deficiency in the amount of vitamin D that results in softness, defects and curvature of the bones in children, and compensation for the deficiency and decrease in the amount of lost body minerals such as calcium and phosphate, through appropriate nutritional foods that contain additional amounts of calcium and vitamin D. Which improves rickets and relieves its symptoms.

The treatment is also based on increasing the exposure of the rickets patient to the sun, so that the body can then make vitamin D naturally.
Or the doctor may prescribe a rickets patient with calcium and vitamin D-replacement drugs to treat rickets, but the amount recommended by the doctor, which varies according to the size of the child, must be adhered to, as the increase in calcium and vitamin D may be dangerous.
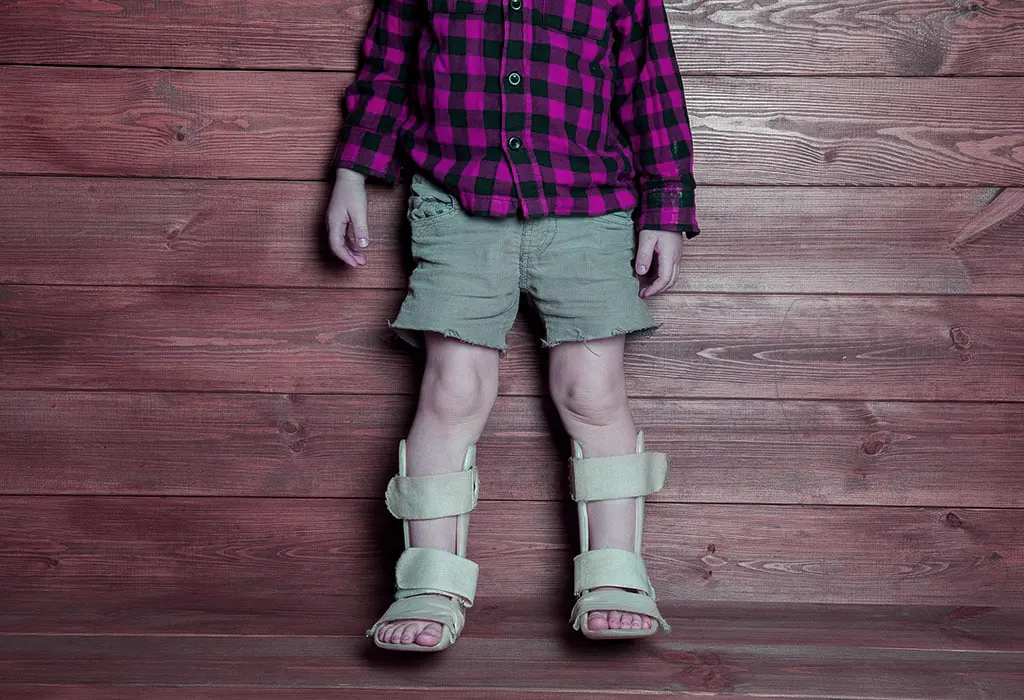
And if there are structural abnormalities caused by rickets, the treatment in children with rickets may be added to the wearing of a belt to correct the position of the bones and fix them correctly during their growth, and in severe cases the affected child may need corrective surgery in order to treat rickets.

In hereditary rickets, treatment is based on a combination of phosphate supplements and high doses of a special type of vitamin D for the treatment of rickets and osteomalacia in affected children.
And when there are diseases that cause rickets and osteomalacia, then these causes must be treated in order to treat rickets.
Rickets prevention
There are several steps that help prevent children from rickets and avoid a deficiency in vitamin D, which causes soft bones, including:
- Calcium-rich foods: such as dairy products, cereals, nuts, seeds, and green vegetables.
- Sun exposure: The body naturally makes vitamin D when exposed to the sun.
- Eating foods that contain vitamin D in abundance: There are several types of fish that contain vitamin D in abundance, in addition to foods that are supported with large quantities of vitamin D such as milk, orange juice and cereals.
As for genetic diseases that affect children and cause rickets, these diseases are difficult to avoid.
Sources:
Common questions
Treatment is carried out within weeks or months in the case of nutritional rickets, until the bones return to their normal position and complete growth properly.
Vitamin D and calcium deficiency is the main cause of rickets, because of their great role in the growth and strengthening of bones.
If rickets is left untreated, this may lead to negative effects on the bones, as the child stops growing and develops various deformities. In severe cases of untreated rickets, the patient may suffer epileptic seizures and heart attacks that lead to death.
Fish and fish oils are among the richest sources of vitamin D, and it is also found, but in smaller quantities, in egg yolks and cheese.