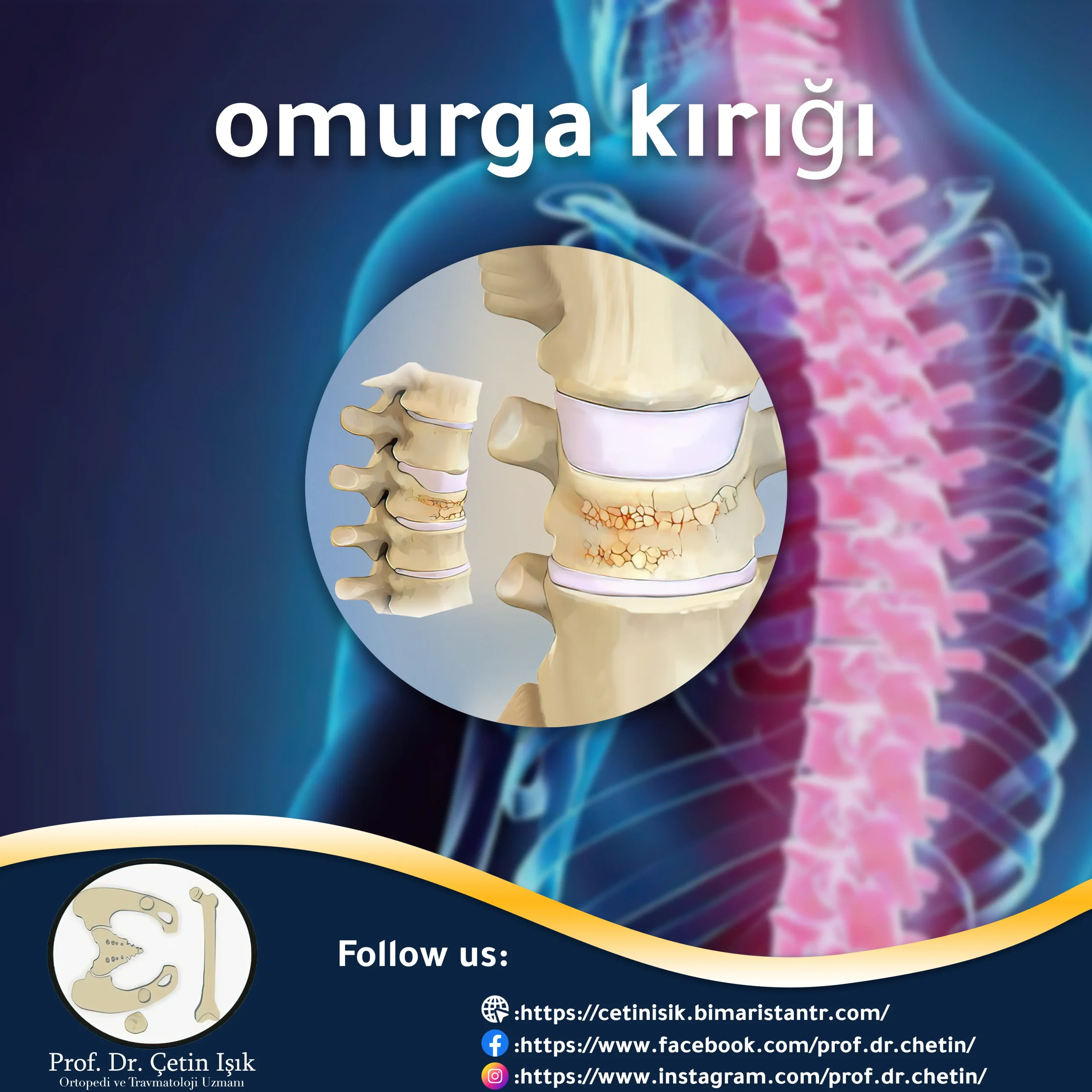
A spinal fracture is a serious injury that causes damage or fracture of the vertebrae. It usually occurs as a result of injury or severe pressure on the spine and requires immediate treatment.
Although a spinal fracture is a rare injury; however, it may lead to serious health complications for the patient, such as pressure on the spinal cord and peripheral nerves, which can lead to weak muscles in the body and then paralysis. Hence the importance of treating severe vertebrae fractures seriously and in coordination with a qualified medical team. Continue with us in this article. To learn about the fracture of the spine, its types, the most important symptoms and causes of fracture, and the conservative and surgical treatment methods used in its management.
Profile of a vertebral fracture
A spinal fracture is a fracture of one or more vertebrae along the spine. The severity of the fractures varies depending on the cause. Injuries resulting from trauma, car accidents, or falling from a height cause large fractures that require emergency treatment, while underlying chronic diseases in the elderly such as osteoporosis Or tumors fractions of light impact.
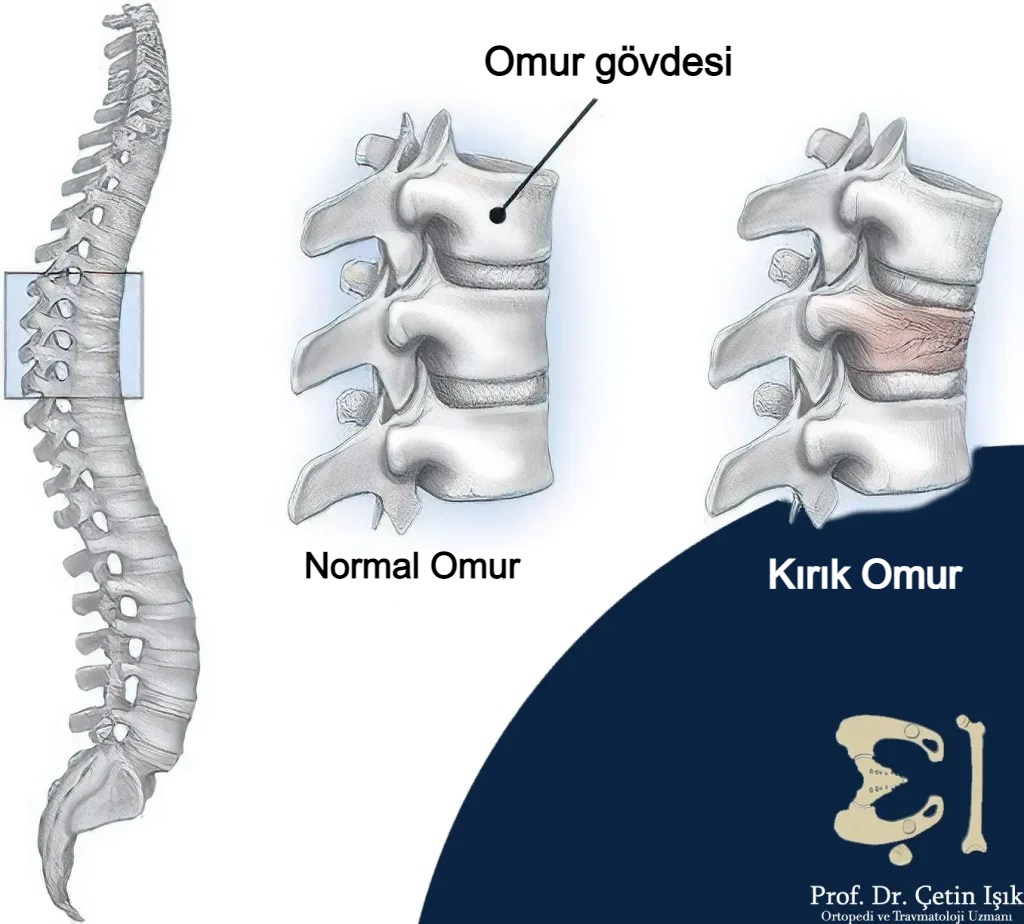
The spine consists of 33 vertebrae and fractures can occur anywhere along its length. 15% occurs in the neck region, while 64% occurs in the lumbar spine.
Types of spine fractures
There are three main classifications of spinal fractures; Which:
- Compression fractures: the vertebrae are thin and weak containing small cracks, and it is common in patients who suffer from osteoporosis, lack of bone tissue, bone cancer, or those who undergo chemotherapy or radiation
- Explosive fractures: They occur when the vertebrae are crushed by forces such as car accidents, falls from a great height, and landing on the feet, usually in multiple places, resulting in movement of bone pieces in the spinal cord or surrounding soft tissues. It is one of the most difficult types to treat because of the great damage it causes.
- Bending fractures: They occur when the body of the injured person is pushed forward suddenly, such as when standing suddenly, or a person is exposed to a car accident, during which a vertebra or a group of vertebrae may break, depending on the degree of strength. It usually affects the middle or back region of the vertebra.
Fractures can also be classified into stable and unstable, depending on whether or not the vertebrae deviate from their normal alignment.
Risk factors that increase the chances of vertebral fractures
Anyone can suffer from spinal fractures, but women and people over 50 years of age are most at risk.
In addition to Osteoporosis Certain health conditions or taking certain medications may increase the risk of spinal fractures, including:
- Cancer (especially if the patient is receiving chemotherapy or radiotherapy)
- Taking corticosteroids for a long time
- bone infections ( Osteomyelitis)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Anorexia nervosa
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Kidney patients
- smoking
- Alcoholism
Causes of vertebral fracture
include causes Fractures of the vertebrae of the spine the following:
- Osteoporosis: The risk of many types of fractures increases due to the loss of bone density and strength over time
- Trauma: A sudden, strong force can create pressure that exceeds the flexibility of the spine, causing a spinal fracture.
- Spinal tumors: Most spinal tumors arise from metastasis from other regions (metastatic tumor).
Symptoms of a vertebral fracture
Symptoms of a vertebral fracture vary according to the severity of the injury, its location, and the type of fracture. They include the following:
- Back pain, which is the most common symptom of vertebral fracture and worsens with movement
- Swelling
- Posture changes
- Irregular muscle spasms
- Tingling or numbness
- Short stature
- Urinary incontinence and loss of bowel control
Diagnosing a vertebral fracture
In the event of a severe trauma or accident, the patient is evaluated by emergency physicians.
A doctor first diagnoses spinal fractures with a physical exam and imaging tests.
During the physical exam, painful areas are checked and changes in column shape, posture, and proper alignment are detected.
Radiographic tests to diagnose vertebral fractures include:
- X-ray: It is one of the confirmed tests for diagnosing spinal fractures
- Computed tomography: to assess the extent of damage to the bone and surrounding tissues in the event of planning surgery
- Magnetic resonance imaging: It is important to determine whether or not the spinal cord is at risk due to vertebral column fractures
The DEXA bone density test can also detect osteoporosis and determine its degree in patients.
Spinal fracture treatment
The course of treatment of spinal fractures varies depending on several factors. The most important of which are the type of fracture, its severity, and the patient's health condition.
Most spinal fractures do not require surgery and can heal over time with conservative treatment measures, which include the following:
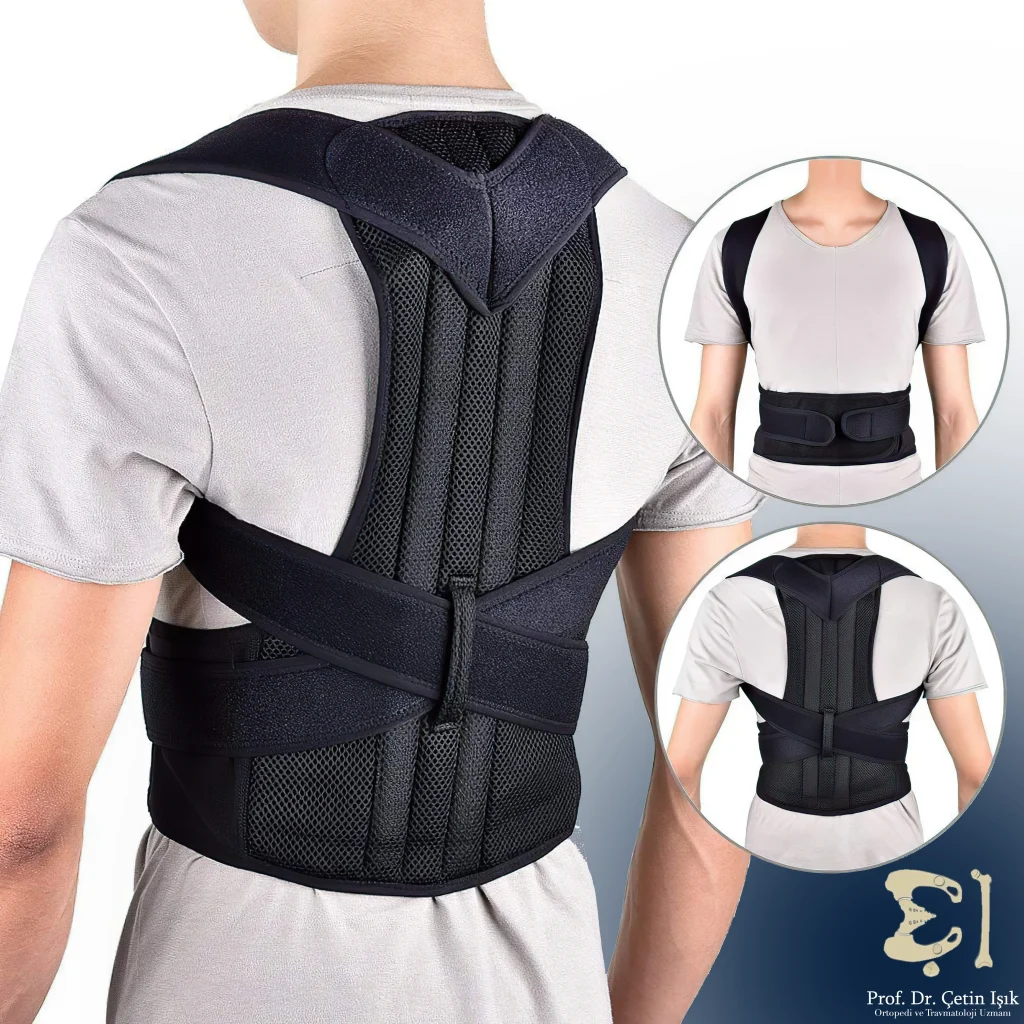
- Wearing a brace: A back brace helps stabilize the vertebrae of the spine in the correct alignment. Most patients need to wear the brace for about a few months.
- Take pain-relieving medications: such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve fracture symptoms
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening the back muscles can reduce bone erosion and the risk of fractures. You can follow up with a specialized physical therapist or do the appropriate exercises at home.
- Management of osteoporosis: In the event that the patient has fragility, he must take osteoporosis medications prescribed by the specialist or calcium supplements that do not require a prescription.

Surgical treatment of spine fractures
The patient needs to undergo surgery to treat the vertebrae fracture if the symptoms of the fracture persist after several months of adhering to conservative measures, or if the fracture is so severe that the spinal cord is damaged.
kyphoplasty of the spine
It is the most common surgical procedure that is performed to repair spinal fractures, during which the surgeon injects the broken vertebrae with liquid medical cement to strengthen them, after inserting a small balloon into the column and inflating it to push the bones into their correct place and restore the space that existed before the fracture.
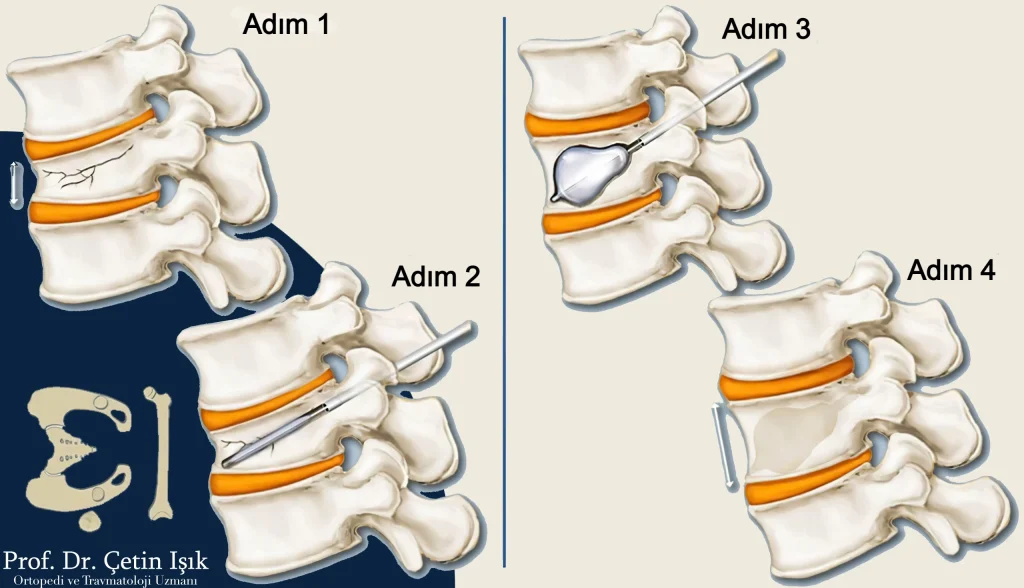
kyphoplasty is an outpatient procedure where the patient can go home the same day.
Laminectomy
This operation is common in unstable burst vertebrae fractures that cause nerve injury, in which the surgeon removes the bony arch that forms the back of the spinal canal to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and then fixes the vertebral bones back to their position using implants such as screws.
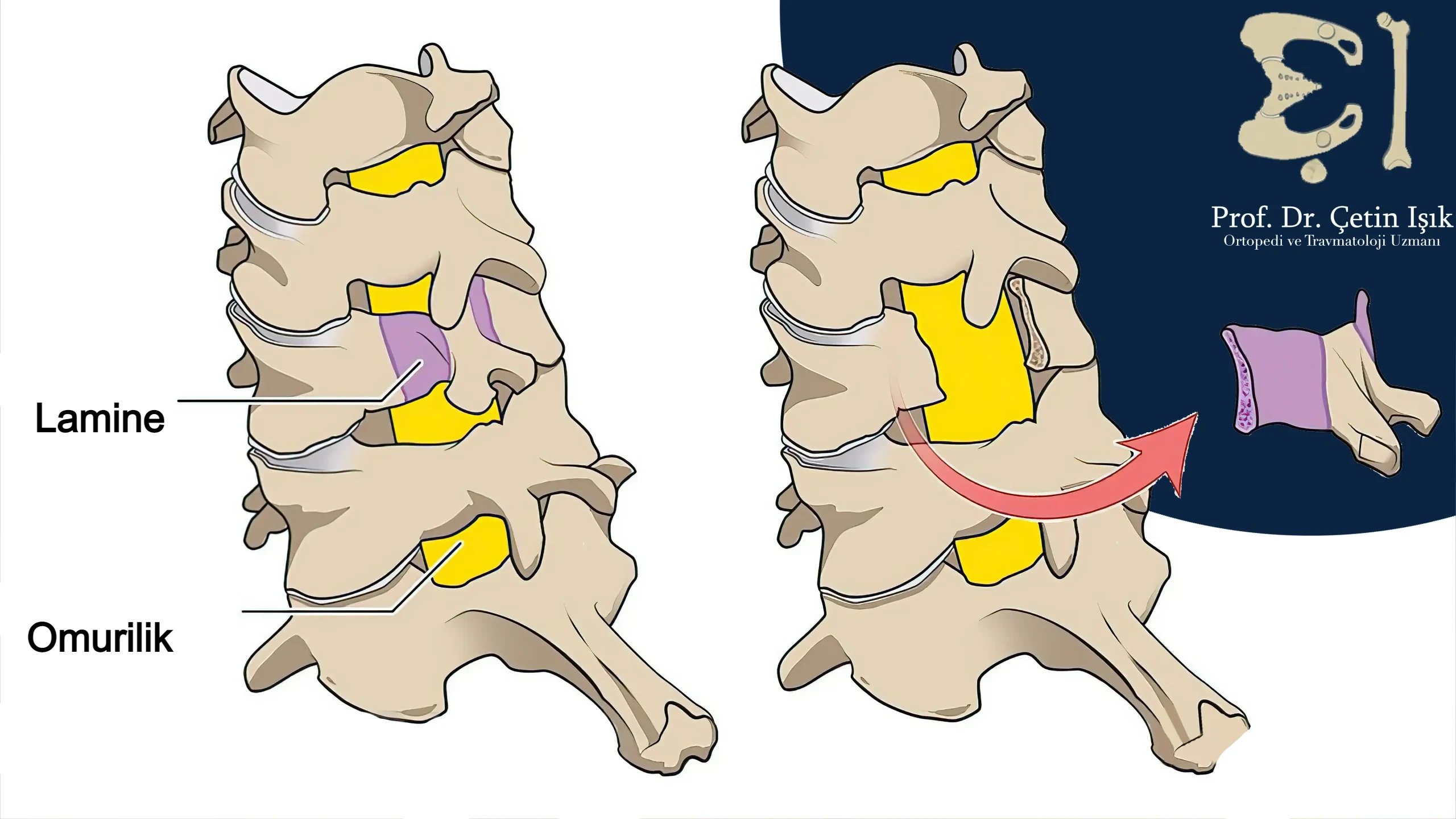
After the treatment of the fracture of the vertebrae of the column, the patient often needs to recover and rehabilitate directly to restore the mobility and strength of the spine. These measures include exercise, physiotherapy, and respiratory exercises.
Prevention of vertebral fracture
It is possible to reduce the risk of a spinal fracture by following important general safety instructions, such as:
- Wear a seat belt while driving to avoid traffic accident injuries
- Use a cane or crutch if you have difficulty walking
- Safely use appropriate sports tools and equipment during sports to prevent falls and maintain stability
- Follow a healthy diet and exercise regime as well that help maintain bone health and prevent osteoporosis, such as food rich in vitamins, especially D and C, and calcium.
Finally, spinal fractures are among the important injuries that require care depending on their severity, as the fracture symptoms can be controlled by taking pain relievers and wearing the appropriate brace in the case of mild fractures. Some patients may need surgery for severe fractures.
Sources:
Common questions
In cases of severe, untreated spinal fractures, health problems that end in paralysis can develop as a result of damage to one of the nerves of the spinal canal.
Any surgery may involve risks such as infection, bleeding and pain. Rarely, surgery may damage nerves, causing numbness or weakness in the back or other areas.
Most fractures heal within three months if they do not need surgery, but in the event of undergoing fracture repair surgery, a spinal fracture may take six months to a year to heal.
During the period of spontaneous fracture healing, it may not return to its normal position, but rather to its shape after compression, so it forms like a hump, or short stature occurs as a result of the curved spine.
Most vertebral fractures can be healed with rest and medication, however severe and unstable fractures may require surgery to reposition the bones.
The most important symptom in the event of a spinal fracture is the pain of the vertebrae. However, the fracture can occur without detection if it is due to a chronic underlying condition, as in a compression fracture.