A ganglion cyst in the hand is a round, fluid-filled mass that can cause pain and difficulty in some movements depending on its size and location. Treatment varies from observation to surgery.
What is a ganglion cyst in the hand?
The extent to which the hand and wrist interact depends on the integrity of the bones, joints and related ligaments and tendons, as any injury to these components can affect the functions of the upper extremity and thus the quality of life of the patient.
A ganglion cyst of the hand or synovial cyst is a small, fluid-filled mass under the surface of the skin that forms around joints and tendon sheaths as a result of tendon irritation. It is usually round or oval and may be soft or hard. The cyst ranges in size from a pea to a golf ball.
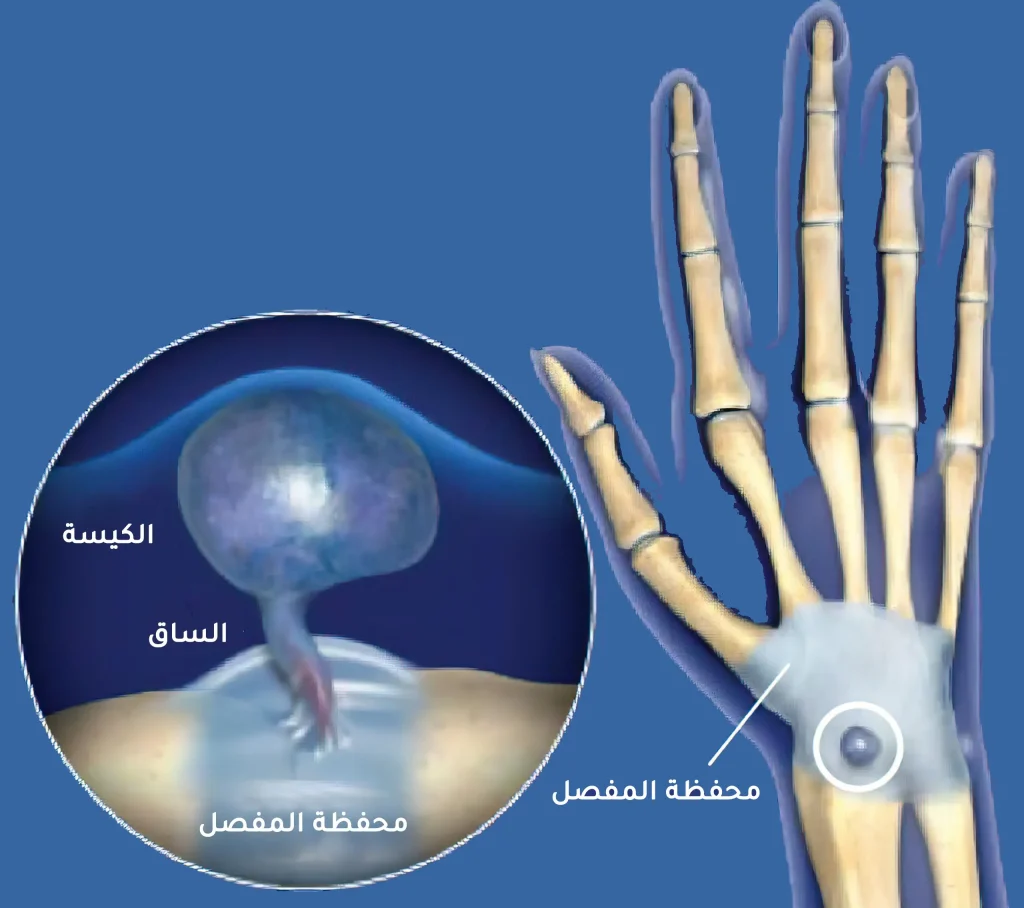
Ganglion cysts occur in 60% through 70% cases at the back of the wrist or at the front at the base of the thumb.
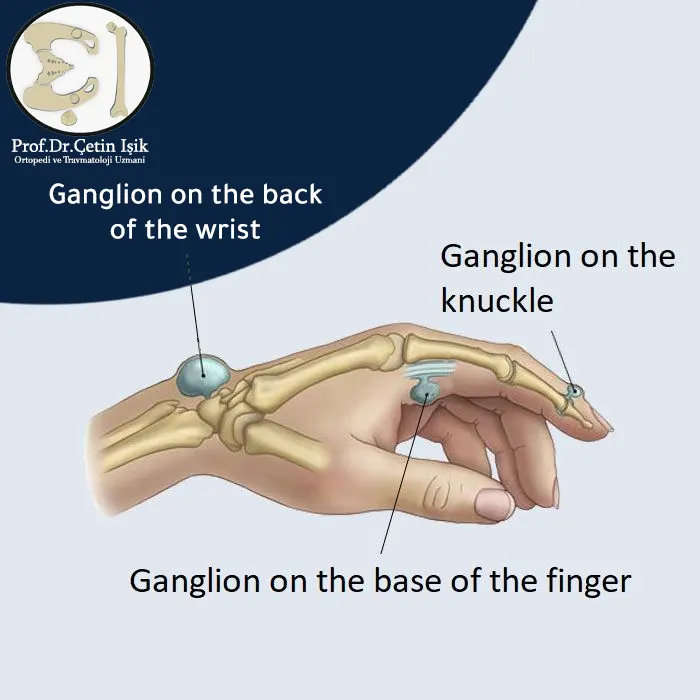
Many people develop ganglion cysts, as they are the most common benign (non-cancerous) mass that develops in soft tissues.
Risk factors for ganglion cysts of the hand
Anyone can develop ganglion cysts, but certain factors may increase the chances of infection. Such as:
- Gender: Women are affected by ganglion cysts three times as often as men
- Age: The cyst appears most often in people between the ages of 20 and 50.
- Previous injury: Joint and tendon injuries such as tendinitis due to overuse increase the chances of a ganglion cyst forming at the site of the injury.
- Hand arthritisIn most people with chronic arthritis, the cyst is found in the hands near the fingertips (the joint near the nail).
Causes of ganglion cysts in the hand
Doctors have not yet identified an exact cause for the development of a ganglion cyst. Some theories indicate that it may occur after an injury to one of the joints of the hands and leakage of synovial fluid from the joint capsule through the tissues, causing swelling and swelling in the joint or tendon of the hand.
Symptoms of ganglion cysts in the hand
Ganglion cysts share symptoms with other types of problems such as carpal tunnel syndrome and arthritis, so it is important to know the signs that ensure wrist pain is caused by a ganglion cyst in order to start appropriate treatment.
- A visible lump on the wrist: It is the most common sign of ganglion cyst formation, as the cysts usually look like a spherical or oval-shaped cyst filled with fluid just below the surface of the skin. The cysts usually increase in size when using the hands with repetitive movements.
- Wrist pain: Ganglion cysts may or may not be painful, depending on the compression of the nerve adjacent to them. In this case, tingling and numbness can be felt in one or both hands.
- Inflammation in the area of the cyst: The mass effect of the swelling, if enlarged, may cause inflammation at the site of its development.
- Wrist movement at risk: A ganglion cyst can also interfere with the movement of the wrist joint, if the cyst is pressing on a nerve or joint tissue, as this causes difficulty in performing certain tasks such as holding a spoon or a pen.
Diagnosis of ganglion cysts of the hand
First, the doctor asks the patient about his medical history and the duration of the cyst, and then begins to visually examine the nodular cyst to verify the appearance and location of the mass, and gently press on it to ensure the presence of accompanying pain.
The doctor may highlight it to detect translucency, if present, as this helps distinguish between a solid tumor and a fluid-filled cyst.
Finally, in some cases, the doctor may resort to taking a biopsy from inside the lump by removing a sample from it.
In rare cases, X-rays are taken to investigate further the cause of the symptoms.
The doctor may order an MRI or ultrasound, in the event that the ganglion cysts are very small and do not form a clear protrusion but nevertheless cause pain, in which case it is called the ganglion cyst.
Hand ganglion cyst treatment
A ganglion cyst of the hand usually does not require treatment as long as it does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient. In 58% cases, the cyst resolves on its own over time.
Treatment options for ganglion cysts range from conservative management, which is the most common, to surgical intervention.
The different types of non-surgical ganglion cyst treatment include:
Medications:
Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen, naproxen, or ibuprofen can help relieve mild pain associated with certain activities and reduce swelling.
Warm compresses:
Regular use of warm compresses may increase blood flow to the hand and promote fluid drainage. However, hot compresses will not prevent cyst growth.
Braces:
A splint or brace is used to immobilize the injured area of the hand joint and prevent movement throughout the recovery phase, as it can be worn for several days or weeks.
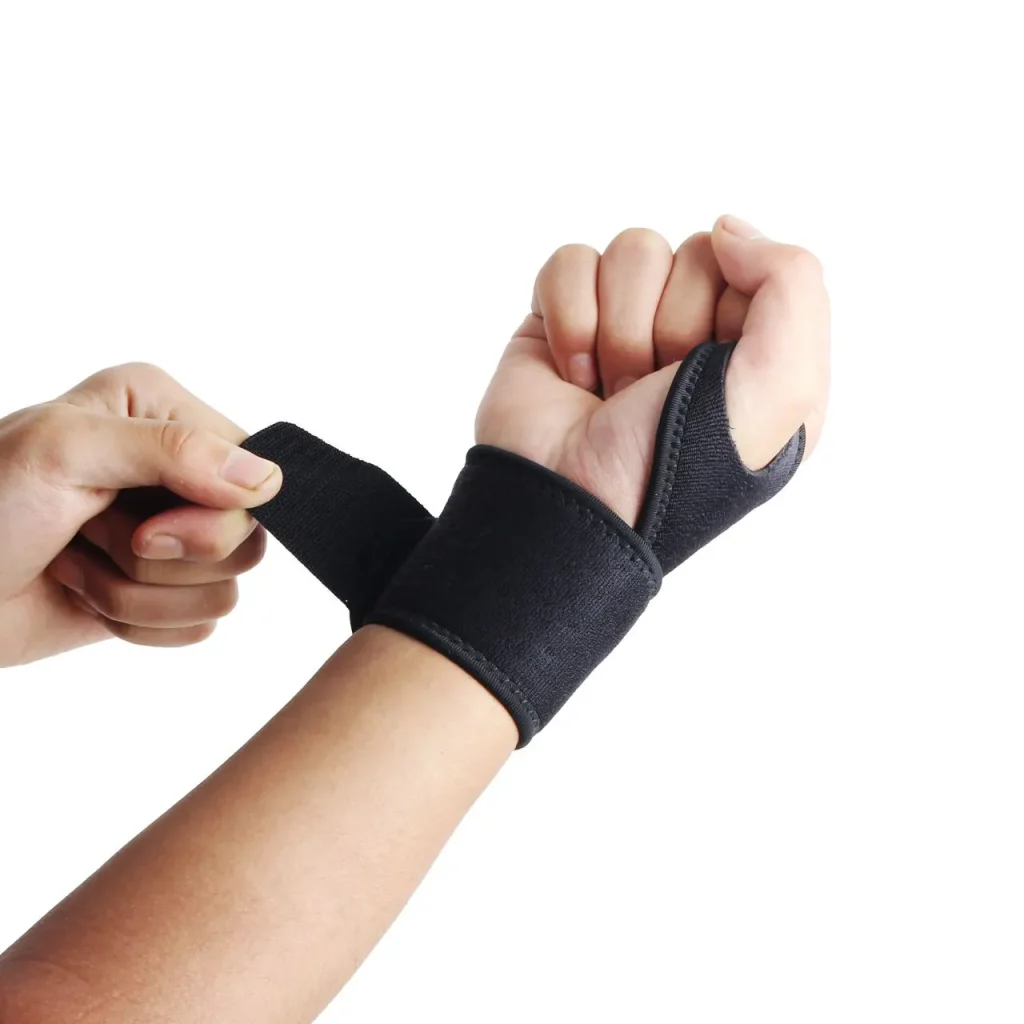

Ganglion cyst resorption:
It involves removing fluid from a ganglion cyst with a needle with or without ultrasound guidance while numbing the area around the cyst with a local anesthetic.
The liquid may be too thick to fill the syringe; Pressure can then be applied to the cyst to force the fluid out into the surrounding tissues of the skin.
Recurrence is common with this procedure because the underlying structure of the ganglion cyst remains attached to the joint, and it can be performed multiple times.
Surgical treatment of ganglion cyst:
If conservative measures do not relieve the pain, the doctor may resort to surgical removal of the cyst. Surgical options include two types of removal:
Laparoscopic resection:
It is a minimally invasive surgical technique, where the surgeon through a very small incision and with a small camera removes the cyst by cutting the tibia or tibia.
Open resection:
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis and under general anesthesia, in which the surgeon makes an incision at the top of the cyst, and during this minimally invasive procedure, the cyst and joint capsule are removed.
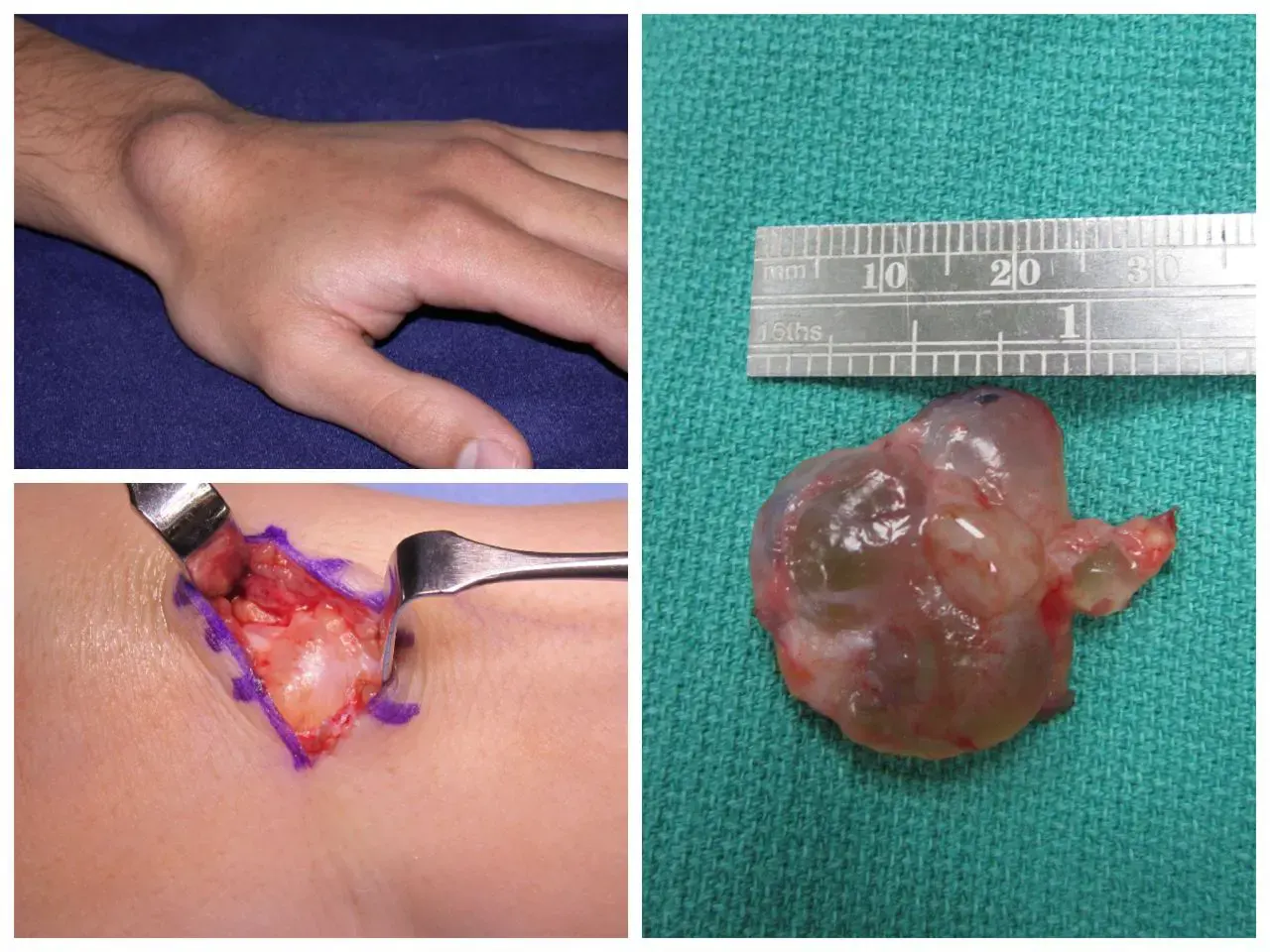
The patient feels better in the first few days, and it takes about two to six weeks for complete recovery and full reuse of the wrist joint.
Even after complete excision of a ganglion cyst; There is a small chance of cyst recurrence and recurrence estimated at 5% to 15%.
you may Contact us If you have any questions about the symptoms and treatment of a ganglion cyst in the hand.
Sources:
Common questions
In general, you do not need to worry about them, as they are non-cancerous lumps that develop mostly on the back of the hand at the wrist joint or the base of the fingers and do not spread to other parts around it. It is also common that they may occur in the ankles and feet. The main problem lies when they increase in size significantly. Motor function may be impaired.
Patients suffer from ganglion cysts in different ways. They may be firm to the touch or have a soft, jelly-like texture that moves easily under the skin of the body, which is more common.
Gently massaging the ganglion cyst has been shown to have benefits as part of the fluid within the cyst leaks out and from it appears in a smaller size.
Ganglion cysts are non-cancerous masses that often develop along the tendons of the ankles and feet or the hand and wrist, and they are often harmless, but if the cyst appears uncomfortable or there is accompanying pain; Treatment options can be used.
The size of the cyst varies, and the size often increases when the joint formed on it is moved repeatedly, whether at the forearm or wrist.