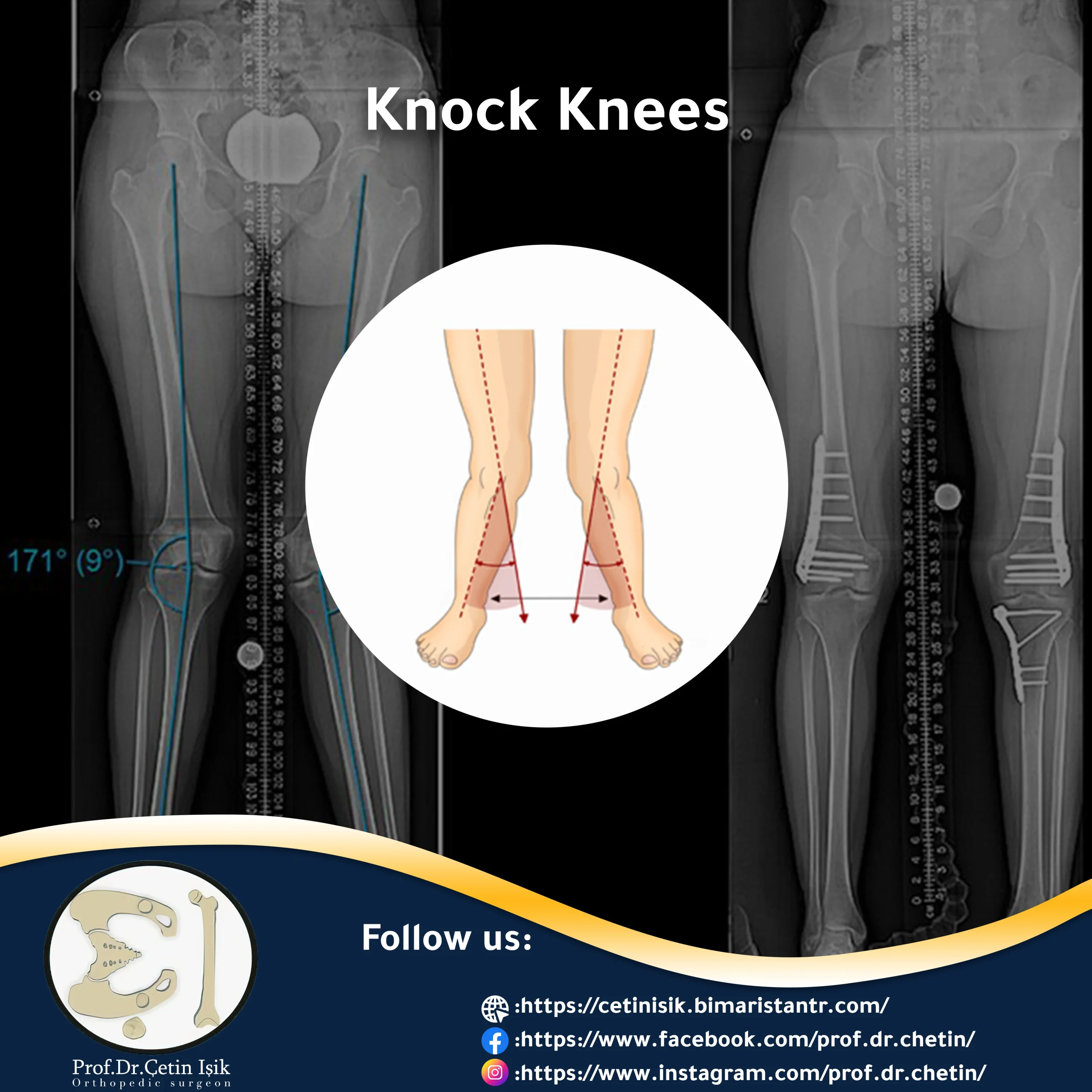
Knee knock is a common medical condition in children where the knees tilt inward. Treatment options for relieving symptoms range from exercise, physiotherapy and even surgery.
75% children between the ages of 3 to 5 years suffer from hallux valgus knee problem as part of their normal development, which may correct on its own before the age of seven years or may continue after adulthood and cause symptoms that affect the quality of life, continue with us in this article to know The most prominent causes and symptoms of hallux valgus and conservative and surgical treatment methods.
What is the knock knee ?
knee varus or Scoliosis Medically known as the knee joint genu valgum It is a condition in which the knees bend towards each other when a person stands, and in the most severe cases, the knees can touch without the ankles converging, as a distance of 8 cm is formed between the ankles of the injured person.
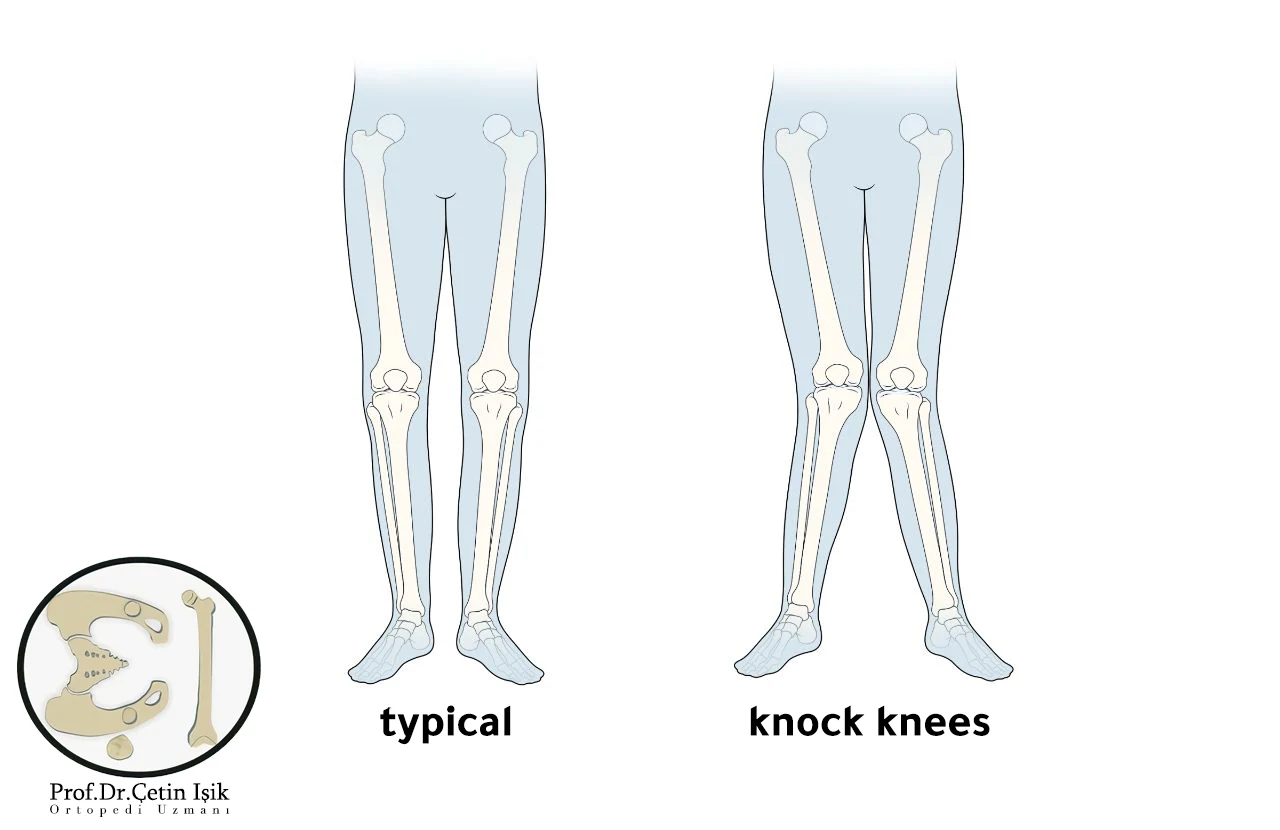
Knock knee is more common in children, and it may appear in adolescents or adults, especially women, as a result of knee disease such as: Osteoporosis or Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Knee development
From birth to infancy, arching of the legs is common as the knees begin to touch each other at the age of 2-3 years, and sticking knees are more common at the age of four.
In most cases, by the time a child reaches the age of seven or eight, the knees return to a straightened position.
Causes of knock knee
Doctors haven't identified any specific cause of knock knees, but there are many possible causes, including metabolic bone disorders and genetic disorders, as it turns out that this condition can run in families.
Factors that increase the risk of knock knee include:
- Skeletal dysplasia of the knee
- Bone deformation due to Rickets caused by a deficiency of vitamin D
- An injury or infection to the leg or knee
- Overweight and obesity, which increases pressure on the knees
- Arthritis, especially in the knee
- Lack of calcium
- Lysosomal storage diseases such as Morquio syndrome
Symptoms and signs of knock knee
In case The knee varus In children, we notice the following symptoms:
- The knees touch while standing with the leg outstretched, while the ankles are wide apart and the distance between them is at least 7 cm
- There is usually no pain
- Knock Knee can be associated with an arched leg
If genu valgum continues to worsen over time after childhood, it may cause additional symptoms such as:
- knee pain
- Stiff joints
- Hip, foot and ankle pain due to ligament and muscle strain
- It affects the feet with lameness and difficulty walking
- Imbalance, if the injury is in only one knee
If you have any of the previous symptoms; You can seek medical advice from Competent He can guide you to the best treatment.
Diagnosing the knock knee
The doctor first takes the detailed medical history of the patient, if the patient is a child, the trajectory of the growth of his legs is followed, and then he begins a physical examination for him.
In the event of pain in the leg or knee, the doctor asks the patient to describe its location, intensity, and frequency.
The doctor also makes sure with a physical examination that:
- Knee alignment when standing
- Having lameness or difficulty walking
- The difference in the length of the legs
In some cases, the doctor may order an MRI or X-ray to examine the bone structure and detect the underlying problem causing the sticky knees.
Knock Knee treatment
Treatment for hallux valgus depends on the cause and severity of symptoms. If the injury is due to rickets, it is likely that the doctor will prescribe it Vitamin D and calcium supplements to help restore normal levels, and powerful non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to relieve joint pain.
Non-surgical treatments for hallux valgus
A typical treatment plan for knock knee and bow legs includes one or more of the following:
Weight loss
Obesity puts additional pressure on the knees, which exacerbates the condition, so it is necessary to follow an integrated diet until the weight reaches a healthy mass index.
Doing exercise
A physiotherapist can assess a patient's gait and suggest an exercise program designed to strengthen the thigh, leg, and hip muscles, which includes two types of exercises:
- Gentle stretching or Pilates exercises on the knee can help relieve spasms and symptoms
- Simple resistance exercises such as raising the legs while sitting or lying down, and as the exercise routine progresses, weights are added to the legs to make it more effective, and squats that stretch the muscles and improve joint mobility
Orthopedic appliances
If the length of the legs is not equal in the hereditary kneecap, wearing shoes with heels on the shorter side helps in adjusting their length and straightening the patient's gait.
For children whose knee has not been corrected by the age of eight, it contributes knee brace Or the splint to guide bone growth to ensure proper alignment.
Treatment of knock knee by surgery
Surgery is the last resort in the rare cases in which normal development does not correct a child's knee, or in adults with knee pain that conservative measures have not helped.
There are two main surgical options for treating knee luxation:
Guided growth surgery
It is an option to correct the knees by slowing down the growth of the curved side of the bone.
During this procedure, the surgeon implants small metal devices on the inner side of the knee near the growth plates around the knees. The outer side continues to grow, making the legs straighter.
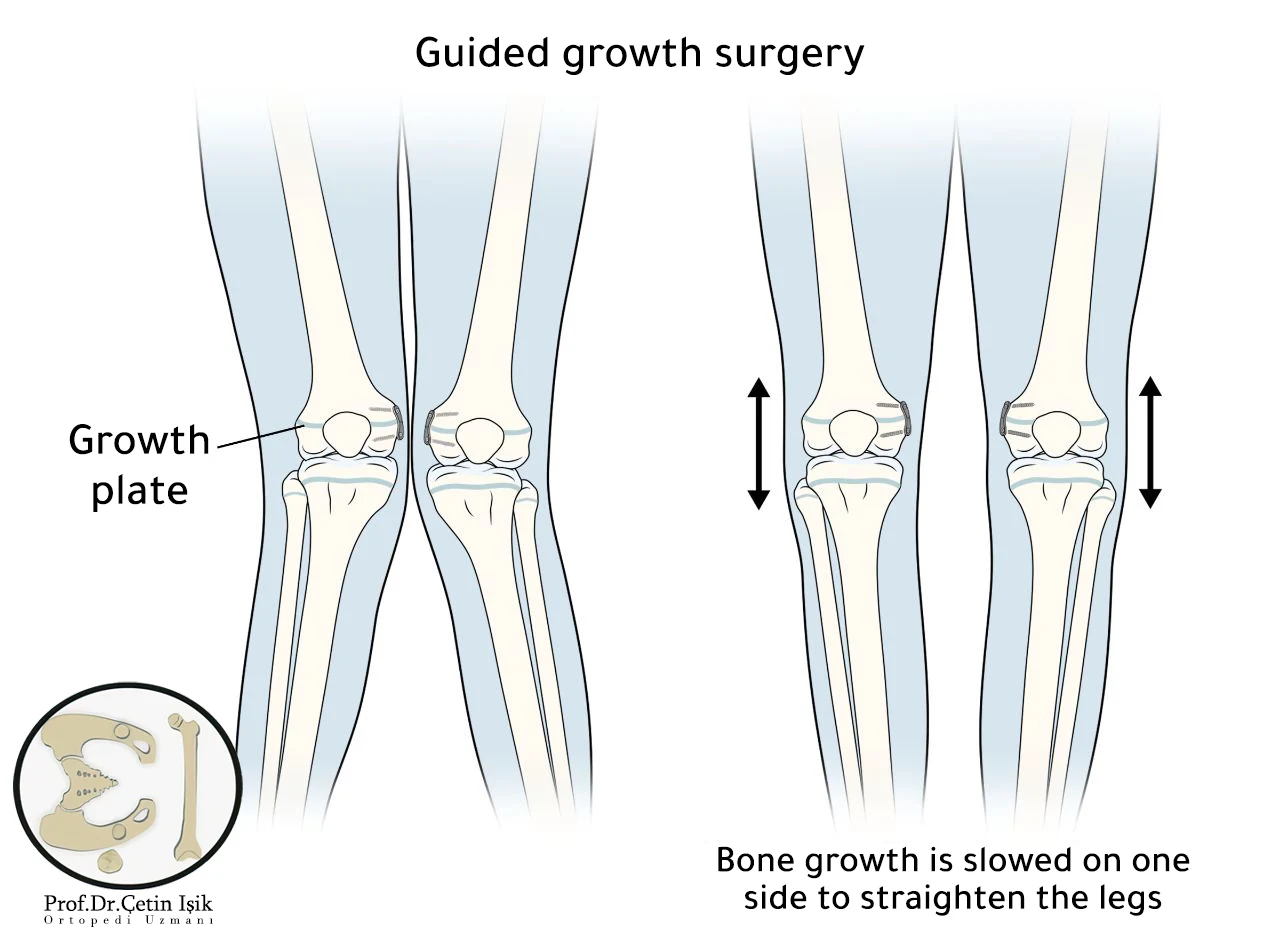
This operation is performed when the child approaches puberty before the adolescent growth spurt, usually around 11 years for girls and 13 years for boys.
Guided growth surgery is an outpatient procedure, so that children can bear weight on their legs immediately and return to their various activities within a few weeks.
Osteotomy surgery
Osteotomy surgery is an ideal option for the treatment of knock knee in adults, as the knee does not improve on its own after puberty, as it works to correct severe knee deformities.
The goal of this surgery is to straighten the legs by changing the angle of the bone. The surgeon does this by cutting and reshaping the bones above or below the knee and fixing them with metal plates.
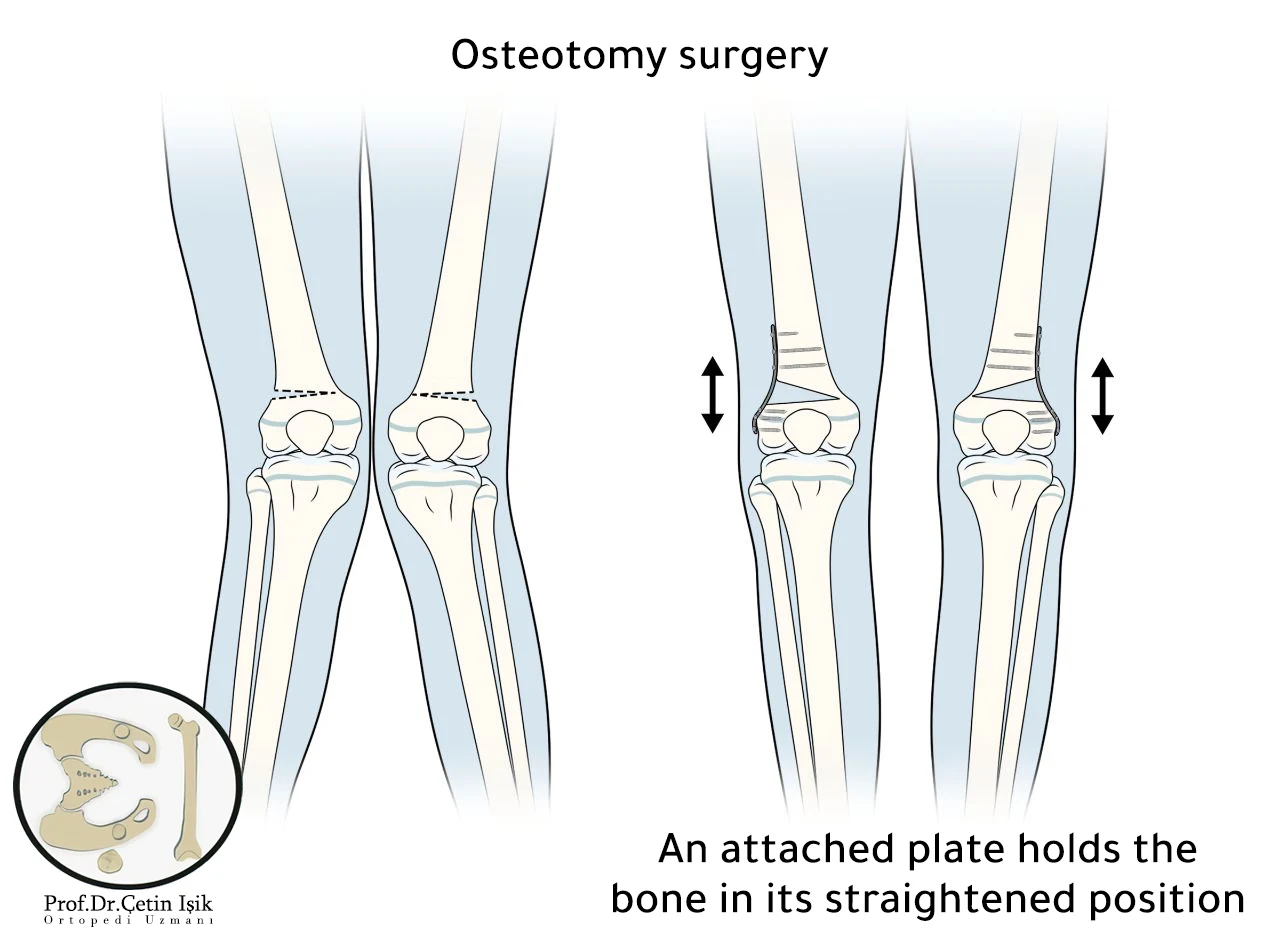
The patient needs to stay in the hospital for a few days after the osteotomy surgery.
Patients are usually advised to start physical therapy after the operation, under the supervision of a specialized trainer, to restore muscle strength, as well as to use crutches while walking. The return to full activity takes place six months after the procedure.
In the end, there is no need to worry about the condition of the knock knee, as the vast majority of people who suffer from it improve without surgical treatment and have very positive results in the long term. Conservative measures and surgical procedures are completely safe by preventing the development of the knee joint problem or alleviating its symptoms, and children's bones usually heal faster and more reliable than adults.
Sources:
Common questions
Knock knee occurs as a normal part of the process of development and growth in children, so it often means a child of primary school age from his knees.
The treatment of knock knee inward includes resolving the main problem if it exists, and also practicing stretching exercises such as Pilates and resistance to correct the knees and relieving pain or wearing orthotic devices, and in the event that conservative measures fail, it is possible to resort to orthopedic surgery for adults and directed growth surgery for children, especially before puberty .
The hip muscles, hamstrings, and quadriceps femoris are essential to support your knees. If any of these muscles are weak or overly tight, a sticky knee can result. Quadriceps and hip strengthening exercises often help support the knee joint and treat knock knee or vagus leg.
Genetic conditions such as skeletal dysplasia or the presence of metabolic problems such as rickets can cause genu valgum. The prevalence of valgus knee in the same family is also noted, which supports the contribution of genetic factors.