Knee stiffness is a common condition in which the movement of the knee joint is restricted as a result of several factors, such as arthritis, with age, which affects daily activities and a person’s lifestyle.
Knee stiffness affects all ages and genders, but it is common among the elderly and athletes who practice sports that require repetitive knee movements, in addition to those who suffer from inflammatory conditions in the joints.
The danger of knee stiffness lies in the possibility of joint damage (in the case of osteoarthritis), which requires a knee joint replacement. Learn with us about the causes of knee stiffness and ways to treat it.
Overview of knee stiffness
Knee Stiffness or knee stiffness is a condition in which the range of motion of the knee joint becomes limited, which leads to difficulty fully bending the knee and thus difficulty walking and performing daily activities.
Knee stiffness can occur at any age and in everyone, but it is more common in the following cases:
- Elderly people: As they age, the cartilage in the knee may wear down, leading to the possibility of them developing osteoarthritis, which causes knee stiffness.
- Athletes: especially sports activities that involve repetitive knee movements, such as running or jumping, as they are more susceptible to stiffness as a result of overuse of the knee joint or due to repeated injuries to which they are exposed.
- Lack of physical activity: Knee joint stiffness can occur due to lack of physical activity and sitting for long periods, which leads to weak muscles around the knee joint
- Knee stiffness after surgery: Knee stiffness is common after knee surgery as a result of several factors, including swelling, muscle weakness, and scar formation.
Causes of knee stiffness
There are many reasons that may lead to knee stiffness and the inability to bend it, including: Knee stiffness the following:
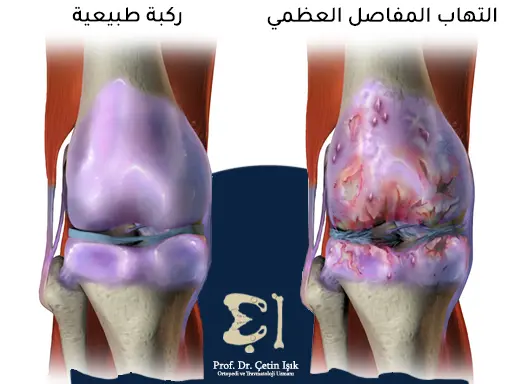
- Osteoarthritis (Osteoarthritis): It is the most common cause of knee stiffness, especially in the elderly. Inflammation occurs due to erosion of the knee cartilage.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the joints, including the knees, and leads to stiffness and swelling of the knee joint.
- Articular cartilage damage: Articular cartilage damage occurs when the knee is pressed or rotated excessively, which leads to the knee becoming stiff and swollen as a result of the injury.
- Ligament damage: It can cause ligament damage; Such as anterior cruciate ligament injury; Knee stiffness
- Knee tendinitis: These are the structures that connect muscles to bones. The cause of knee stiffness may be the occurrence of tendinitis in cases of overuse of the knee
- Knee bursitisIt is a small fluid-filled sac that protects the knee joint. When inflamed, it can cause stiffness and pain.
- Gout: It is a type of arthritis in which uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints (such as the knees), leading to sudden, severe pain, swelling, and stiffness.
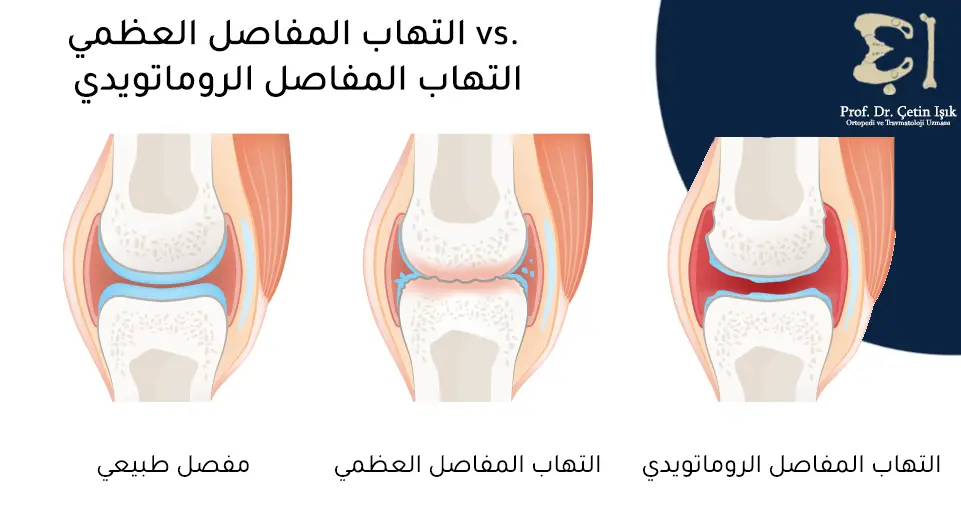
Symptoms of knee stiffness
Symptoms vary Knee stiffness Depending on the underlying cause of atheroma, common symptoms include:
- Difficulty bending the knee completely
- Feeling pain or discomfort when moving the knee
- Swelling around the knee joint
- Determines the range of motion of the knee
- Knee joint weakness
- A popping sound when moving the knee
- Heat or redness in the knee joint
Diagnosis of knee stiffness
Examinations and tests are usually performed to diagnose the underlying cause of knee stiffness. This is done by conducting a clinical examination of the knee to evaluate its range of motion and reviewing the patient’s medical history.
Blood tests may be done to check for inflammation, and imaging tests such as X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be ordered to examine the structures in the knee joint.
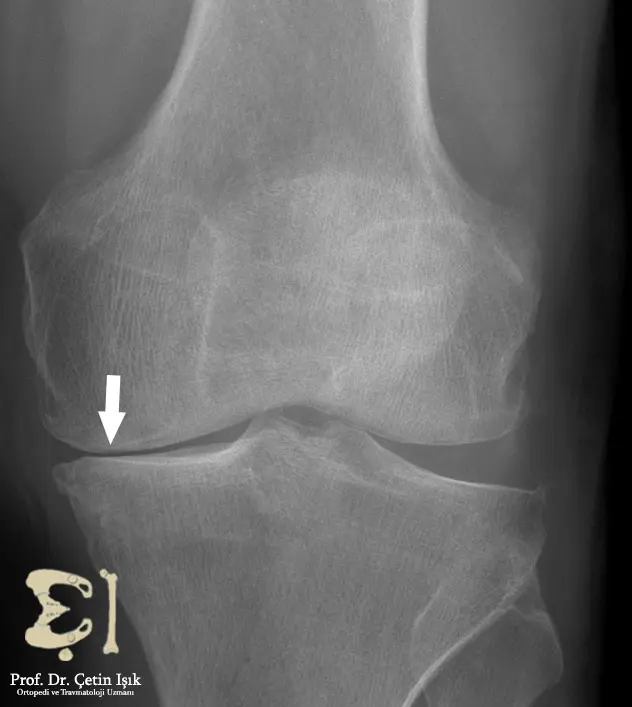
Treatment of knee stiffness
Treatment of knee stiffness depends on treating the cause of the stiffness, and conservative measures are usually sufficient for treatment, but in some cases other, more invasive treatment methods may be used.
Conservative (home) treatment
Conservative (home) treatment includes some options that the patient can do at home to manage knee joint stiffness, including:
- Rest: The knee should be rested and activities that aggravate stiffness should be avoided
- Hot or cold compresses: Compresses can relieve inflammation and pain and are useful in cases of chronic pain
- Wear a brace to protect the knee joint and reduce pressure on it
Medical therapy
Drug treatment can be relied upon to manage knee joint stiffness in general, or in particular if the cause of the stiffness is known and specific medication for the disease is taken. Drug treatment options include:
- Non-prescription pain relievers, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen; To reduce pain and discomfort in the knee joint
- Corticosteroids: These can effectively relieve symptoms such as joint pain and stiffness
- Drugs Rheumatoid Arthritis (Rheumatic): These are disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biological drugs
Physical therapy (knee stiffness exercises)
Your physical therapist may develop a specific program of exercises for you to reduce pain and inflammation and speed up the healing process. Knee stiffness exercises include:
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening the muscles around the knee can relieve pressure on the joint, such as leg raises
- Range of motion exercises: Range of motion and stretching exercises keep the joint moving, such as heel slide exercises
- Balance exercises: These exercises increase the strength of the muscles around the knee, in addition to reducing the risk of falling, which causes damage to the joint. Examples include standing on one leg.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment can be resorted to if previous treatment methods fail to manage knee joint stiffness. The surgical treatment performed varies depending on the cause of the stiffness. Surgical treatment options include: Knee arthroscopyKnee joint replacement and ligament reconstruction.
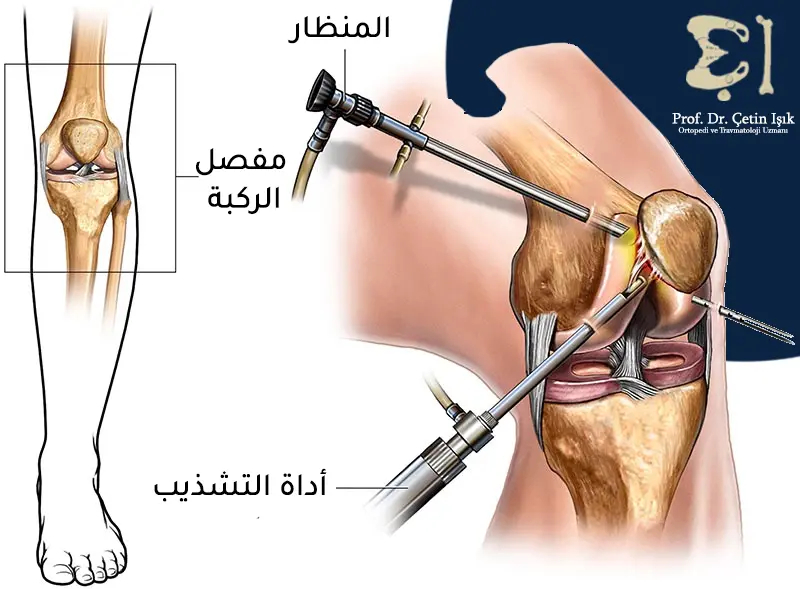
Complications of knee stiffness
Complications of knee stiffness vary depending on the cause of the stiffness, including:
- Muscle weakness: Lack of movement and use of the knee joint may lead to muscle weakness and atrophy
- Joint damage: If the condition is neglected and the cause leading to stiffness is not treated
- Chronic pain: Knee stiffness may cause chronic pain, which affects a person’s lifestyle
- Secondary complications: The patient may change his way of walking or position due to knee stiffness, causing back or hip pain
Preventing knee stiffness
Knee stiffness can be prevented by managing the underlying causes of the stiffness and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Prevention tips include:
- Exercising regularly: to maintain the strength and flexibility of the knee, in addition to the necessity of warming up before doing any exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can cause additional pressure on the knee joint, so you must follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Avoid overuse of the joint and repetitive movements: Overuse of the knee joint may cause fatigue and stiffness of the joint, so activities must be diversified and rest periods should be taken.
- Treating injuries early: You must obtain immediate medical care when suffering a knee injury to prevent knee stiffness and its complications
Knee stiffness is a common condition in which the movement of the knee joint is limited, leading to the patient feeling pain and difficulty moving the knee. Knee stiffness may worsen and cause joint damage and chronic pain that affects a person’s life and daily activities.
Sources:
Common questions
It is a condition in which there is restriction and difficulty in moving the knee due to several reasons, including arthritis and lack of physical activity.
Symptoms of stiffness include difficulty bending the knee, discomfort, limited knee range of motion, and a popping sound when moving the knee.
Knee stiffness can be treated at home by following home treatment methods, which include rest and using cold and hot compresses.
How to treat knee stiffness varies depending on the cause of the stiffness. Usually, conservative measures are sufficient to manage the stiffness (rest), but in some cases other more effective treatment methods may be used, such as drug therapy (pain relievers) and physical therapy (knee stiffness exercises), and rarely Resorting to surgical treatment if previous treatments fail (knee arthroscopy - knee joint replacement - ligament reconstruction).