Treatment of meniscus rupture depends mainly on relieving symptoms through conservative treatment.
Overview of the meniscal cartilages of the knee
The meniscus are fibrous cartilaginous structures with an elongated wedge shape located between the femur and shinbone. The medial meniscus is U-shaped and covers about 60% of the articular surface, while the lateral meniscus is C-shaped and is smaller.
The articular knee cartilage tissue contains protein fibers of collagen, which gives the cartilage flexibility and durability at the same time, and these fibers have a certain direction to distribute weight uniformly along the surface of the knee.

The condition of these fibers is what will determine whether or not there is a need to treat a meniscus tear, and the perfusion of the knee and articular tissue is of great importance, as the cartilage is divided into two main parts:
- The red area of the knee cartilage: 25% is made of cartilage and has abundant blood vessels so that damage is reversible and rupturing is not that serious and can be managed.
- The white area of the knee cartilage: Inside the joint, and a simple rupture in it can cause major problems because it is almost empty of blood vessels, as it bears high pressure, but it usually requires quick intervention to relieve pain and also to avoid losing cartilage tissue.
The medial meniscus
When compared to its lateral counterpart, the medial or proximal cartilage is characterized by being more concave, and covers a smaller surface, which means that it is able to withstand higher pressure, and the incidence of injuries is higher due to a few factors, the most important of which is the greater attachment of cartilage to bone surfaces and its being subject to frequent inflammation, especially for athletes and people who has a highly active lifestyle like military officers and professional trainers.
Meniscus rupture
The meniscal tear is the most common injury in the knee joint ever, and it was believed in the past that the meniscal cartilages were of no importance and had no specific use and were completely removed in clinics and hospitals when injuries and harm occurred.
Recently, knee and meniscal cartilage surgeries depend mainly on the amount of healthy cartilage tissue, as the more cartilage was preserved within the operation, the better the surgical results.
Degrees of meniscus tear
The cartilages are approached and managed by treating the meniscus rupture after determining the degree of rupture in it, as the doctor cannot apply any treatment before knowing this degree. There are five degrees of meniscus rupture, which are:
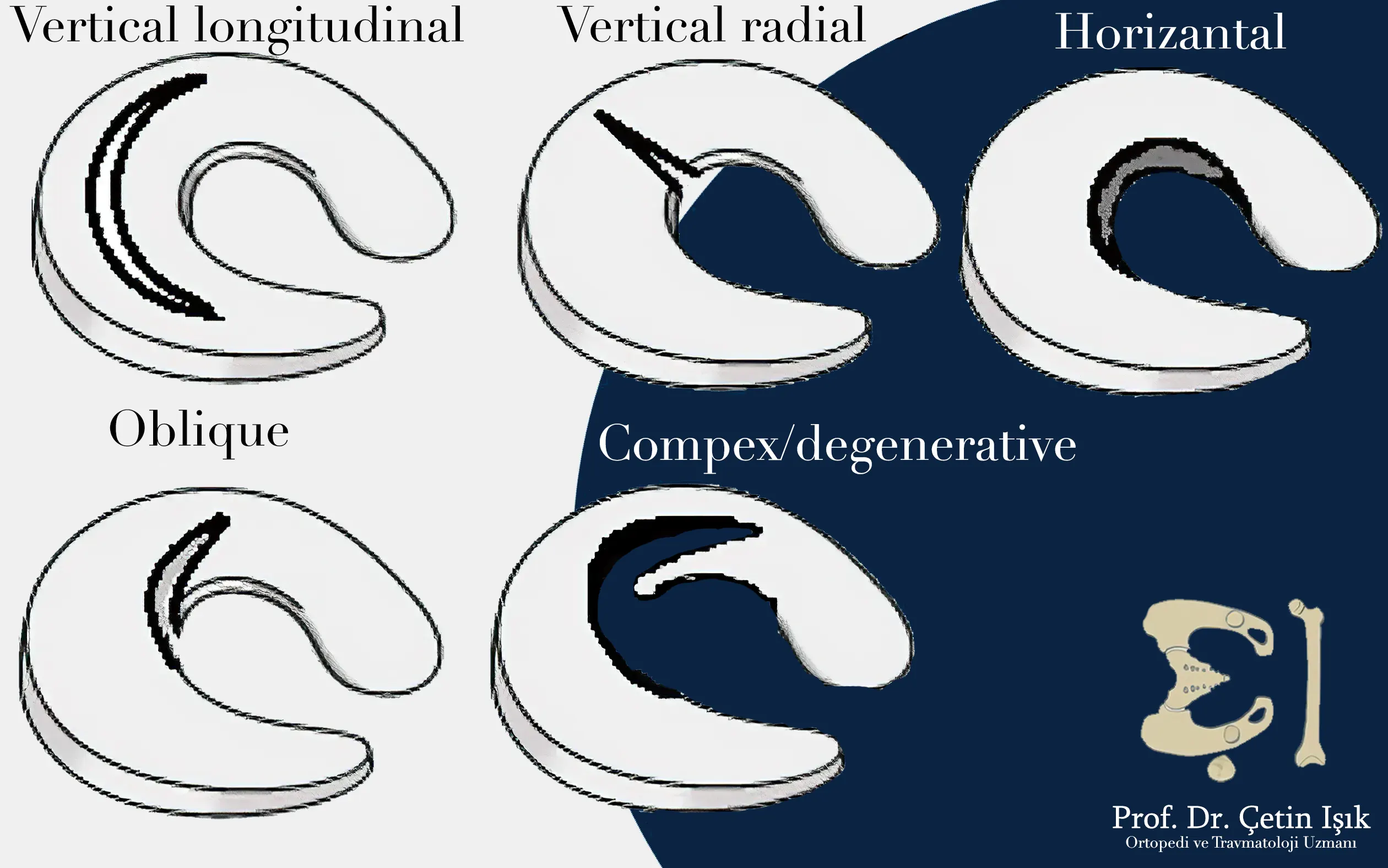
- Elongated vertical tear: It is a common injury and may be asymptomatic, so there is no need for surgery to treat the tear. Sometimes, especially in sports injuries, it causes crackling and pain in the knee when it is moved.
- Transverse vertical tear: Tears affect the ability of the cartilage to carry the weight of the body and cause severe pain. Unfortunately, their treatment is difficult due to the difficulty of diagnosing the damage and the involvement of many factors in its occurrence.
- Horizontal tear: It is easy to diagnose by performing magnetic resonance imaging, as the cartilage is divided into two parts, upper and lower, and the joint in it is more stable, but it is possible for the knee to rupture sharply and form meniscal cysts, and therefore the problem must be quickly diagnosed and treated.
- Oblique tear: The main issue with this type of tear is that it also needs to be partially or completely removed quickly before the cartilage breaks when you bend your knee.
- Complex rupture: More common in the elderly and frequently encountered by orthopedists, is when there is more than one type of tear in the joint cartilage of patients.
Meniscus tear symptoms
The most common symptoms of a torn meniscus include:
- Chronic pain, which is related to the way the knee is positioned and moved.
- Swelling is one of the most common problems seen and can vary depending on the patient's condition, but it is an early symptom.
- Difficulty to move the knee after the injury.
- Difficulty bending and extending the knee while walking.
- The knee's unexplained tendency to freeze, especially when resting.
In the beginning, a meniscus tear may give only mild symptoms for a long time, but once the meniscus is exposed to repeated inflammation, your knee will hurt very much.
To diagnose a meniscus tear, doctors recommend taking an x-ray after examining your knee carefully. Symptoms may be the result of bone fractures and other problems. In the end, the resonance image provides the most reliable imaging to diagnose and it's the the standard of care in this aspect.
Pharmacological treatment of meniscus rupture
The treatment options for a meniscus tear in specialised modern centers into three main types:
- Non-surgical method: It is more common in those with mild inflammation, as symptoms improve with exercise and some medications.
- Chondectomy: Surgical treatment is applied to patients who have symptoms and cannot undergo cartilage repair and treat the problem conservatively.
- Cartilage repair: For the treatment of young people who complain of a peripheral lateral tear, it is done by arthroscopy.
As for the medications used in the treatment of meniscus ruptures, traditional painkillers such as NSAIDs are prescribed, such as ibuprofen in addition to paracetamol. There are some special analgesics that require a prescription, especially when the meniscus rupture pain is severe and chronic.
Steroids or cortisone can be injected into the joint, and although it is not the final treatment, it relieves symptoms significantly, and sometimes the benefit lasts for a long time on these injections.
There is a modern technique based on the injection of special biological factors derived from the blood and bone marrow that the doctor may recommend such treatment after the failure of conventional methods.
Meniscus physical therapy
It is possible to help some methods that adopt the treatment of meniscus rupture in a conservative and natural way, especially in young patients who have joint pain that has lasted for a long time and may be caused by a meniscus tear.
Non-Surgical treatment for knee cartilage rupture
After giving medications that relieve meniscus inflammation, and the patient can then walk normally and bend his knee, physical therapy is used to restore the strength and flexibility of the meniscus to what it was.
Of course, there is a training regimen for each individual patient, but the focus is generally on the muscles of the thighs and calves for complete and correct joint flexion and extension.
Physiotherapy after a meniscus tear often lasts four to eight weeks, and if necessary, this treatment may take several months.
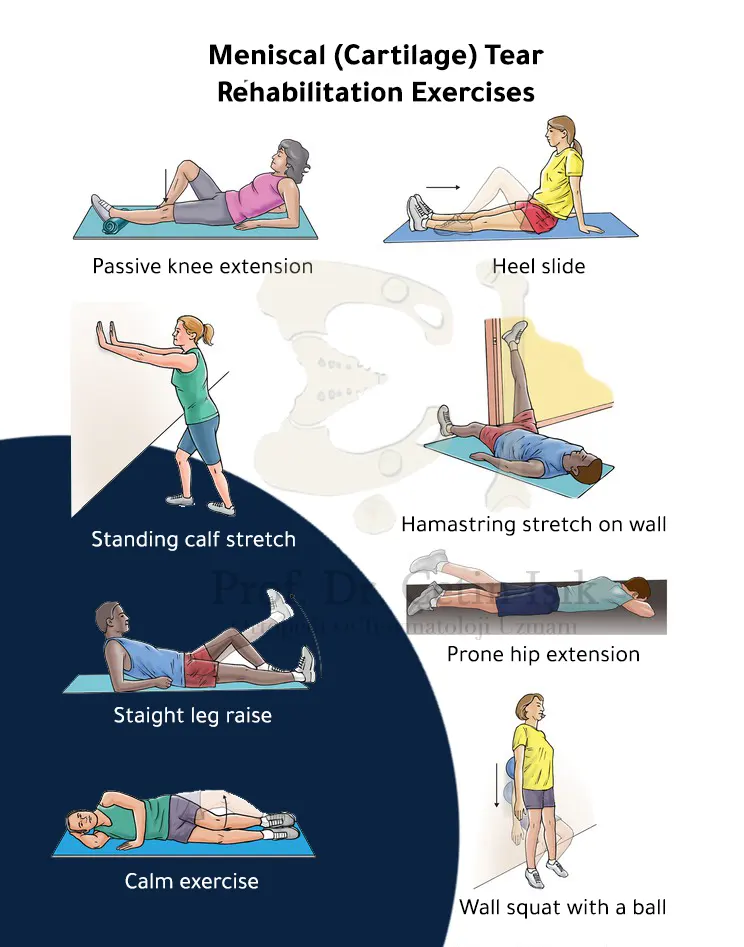
Meniscus tear exercises
There are specific exercises that are practiced in physiotherapy after a meniscus tear, the most important of which are:
- Passive knee extension.
- knee stretch
- Pull the heel of the foot.
Herbal treatment of knee cartilage rupture
In addition to physical therapy, some foods and dietary supplements contain antioxidants that can speed up the healing process, such as:
- Turmeric
- Fish oil
- Glucosamine
- Chondroitin sulfate
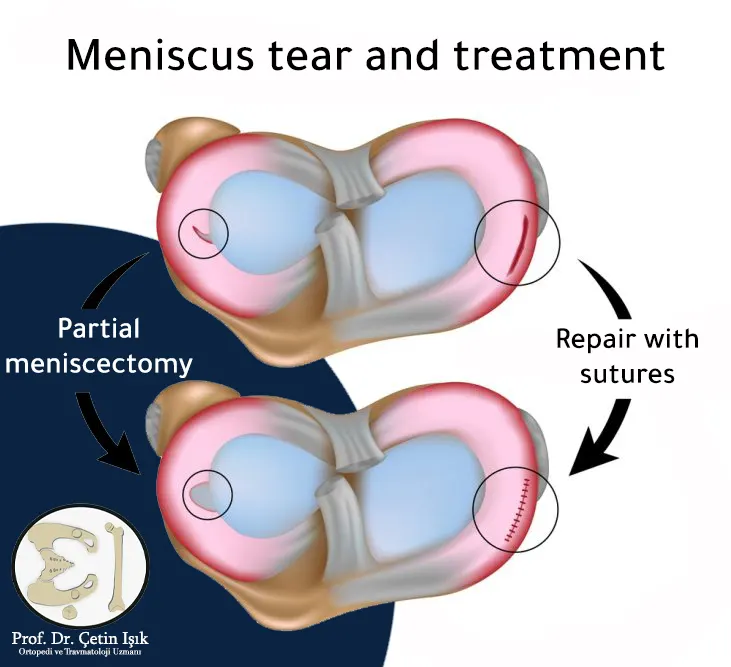
Surgical treatment of meniscus rupture
As mentioned previously, the surgical treatment for meniscus rupture and its management is divided into two main types of operations:
- Chondectomy: There are two types of resection, partial and total, both of which aim to relieve symptoms and preserve healthy cartilage tissue.
- Cartilage repair: It has fewer side effects than resection. The popularity of this operation has increased a lot after recognizing the importance of the meniscal cartilage. The success of the treatment here depends on the existence of a specialised surgeon and a good blood supply for the cartilage.
Results of knee cartilage rupture treatment
As a result, we can conclude that non-surgical conservative treatment for meniscus rupture is an excellent short-term solution, but when osteoarthritis is present, it's better to consult a specialist orthopedic surgeon as that may be more effective for treating white central area tears in particular.
Meniscus tear repair is currently the most common procedure and should be considered first in the treatment of most cases.
Possible side effects of meniscus tear treatment
The perfect treatment without any side effects may not be possible sometimes, and that hugely depends on the patient's age, the type of treatment and the extent of the patient's commitment to it.
The most common complications and problems include:
- Bleeding after meniscus surgery.
- Nerve damage and numbness in the foot.
- Osteoarthritis after a long period of up to twenty years.
- The need for re-operation.
Sources:
Common questions
Pain, swelling, and difficulty moving normally.
First, medications and physical therapy are given, and after the failure of these methods, surgery is resorted to repairing or removing the meniscus tear.
It is certainly possible for the cartilage to repair itself and there is no need for treatment in this case, but there are severe cases of rupture that require medical intervention.
The cruciate ligament is a group of fibers that keep the knee together and prevent it from dislocating, while the meniscus is a cartilaginous disc that facilitates the movement of the kneecap and acts as a shock absorber.
It takes at least six months, and the duration of treatment for a meniscus rupture may take up to a year or more.