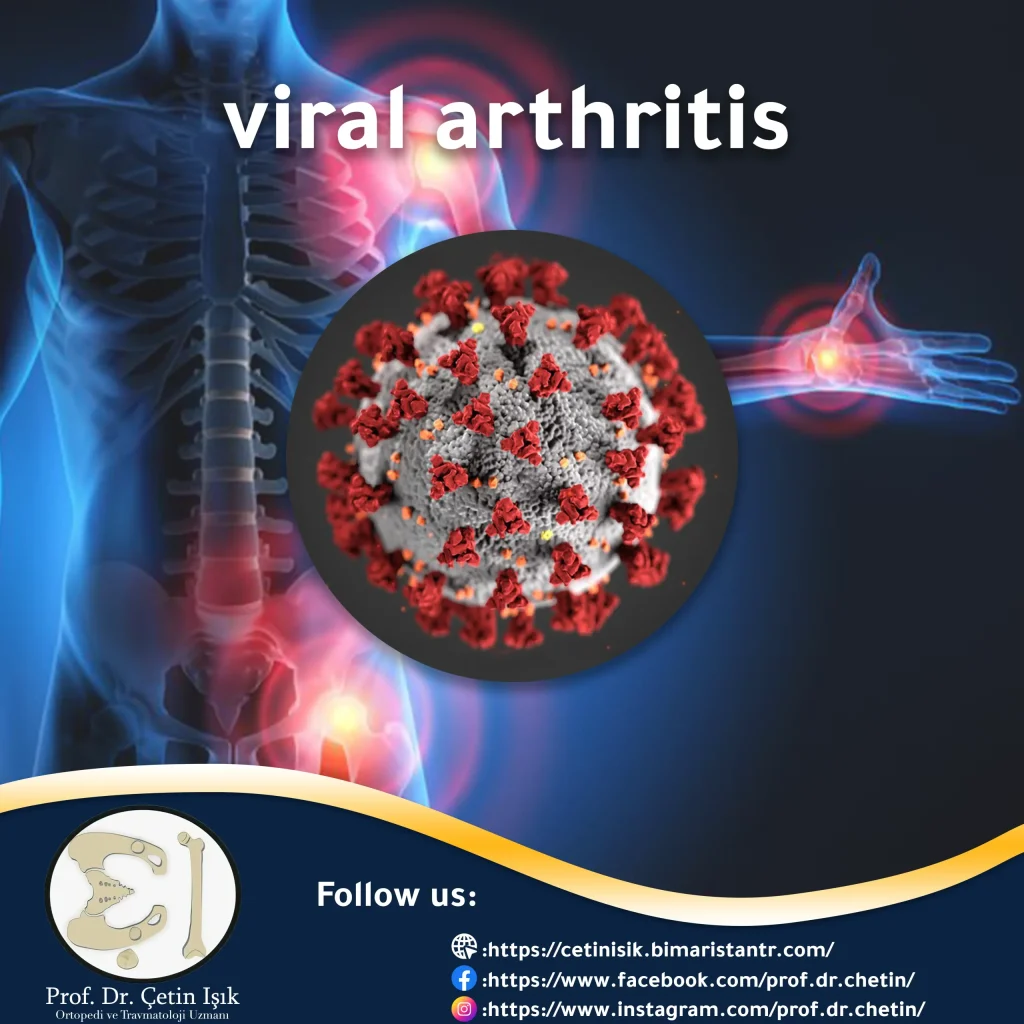
Viral arthritis is an acute inflammatory condition of one or more joints following a viral disease that can affect anyone of any age and is associated with other non-articulatory symptoms.
Many viruses can cause this type of arthritis, but is viral arthritis a severe condition? And indicate the poor health of the patient. And abnormal reproduction of viruses in the body? Follow us to learn more about its symptoms and management.
Profile of viral arthritis
Viral arthritis is a type of infectious arthritis that may result from exposure to any type of germ, virus, or fungus.
Viral arthritis accounts for about 1% of all acute arthritis but is most common in adults in virus-endemic areas, affecting adults more than children.
Viral arthritis occurs quickly and lasts for hours or days, as there is swelling with inflammation in the joints of the affected body, and it is not a chronic disease.
Pathogenesis of viral arthritis
Viruses can predispose to disease or infection and contribute to conditions in the skeletal system. The occurrence of viral infections is related to factors related to the patient, such as age, gender, and the natural immunity of the person, and other factors related to the virus include the extent of the virus’s reproduction in addition to the ability to persist in human tissues and the possibility of causing damage to them and the effect Human immunogenic antigens on the virus.
Activation of the body's immunity against the virus leads to the deposition of immune complexes in the viral sites so that they can be deposited in the joints, which are the meeting place of two bones or the meeting of bone with cartilage or a connection between two cartilages, and this deposition leads to the emergence of symptoms of viral arthritis.
Viruses that cause viral arthritis
Several types of viruses can cause arthritis, including:
- Parvovirus 19: The most common arthritis virus, transmitted through the respiratory and blood systems.
- Viral hepatitis types AB C.
- Rubella virus: It is transmitted by the nasopharyngeal route.
- Corona virus Covid 19.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Virus (AIDS) is transmitted through the blood or infection through the sexual route.
- Alpha viruses.
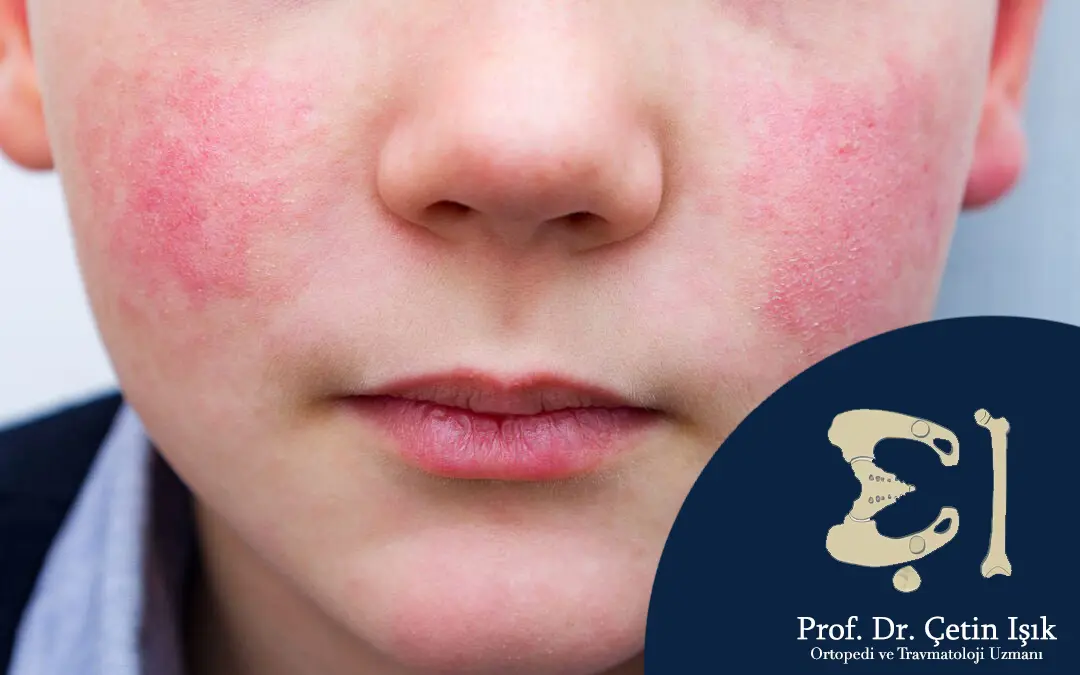
Risk factors for viral arthritis
Anyone can get viral arthritis, but the following factors have a multiplier role in causing the infection.
- Multiple sexual partners.
- Being in areas infected with viruses that cause viral arthritis.
- Doctors and nurses working in the health sectors and hospitals.
- Continuous use of intravenous syringes, such as patients with renal failure undergoing repeated dialysis sessions.
- Diabetic patients.
- People who have had artificial joints installed.
Symptoms of viral arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis in the body result from a viral infection, and they differ according to the type of viral cause, but most of the symptoms include the following signs:
- Joint pain, or pain in many joints
- Stiffness in the joints, especially in the morning after waking up
- Difficulty moving, with the inability to perform daily tasks comfortably
- skin rash;
- A rise in body temperature
- conjunctivitis (redness of the eye)
- Lymph node enlargement
- Swelling and irritation in the affected joint
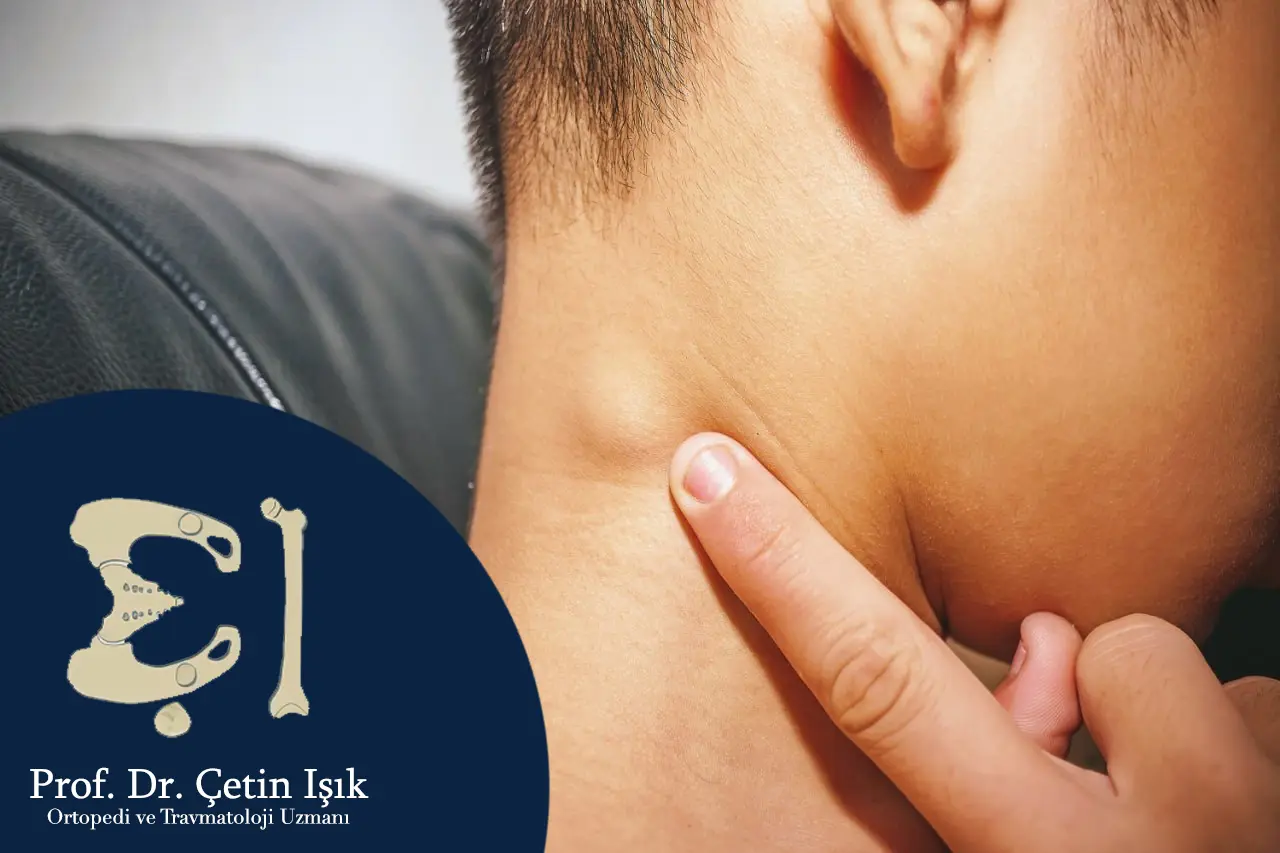
Differential diagnoses of viral arthritis
The symptoms of this disease are similar to other conditions and diseases that we mention
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Lyme disease
- Sjogren's syndrome
- psoriatic arthritis;
Diagnosis of viral arthritis
Diagnostics includes the following steps:
Clinical examination
It includes taking the patient's medical history, inquiring about his daily habits, and whether he is in endemic areas. He is also asked about current diseases, noting pathological changes in the body such as a rash that indicates infection with German measles and inflammation or enlargement with mumps, which is likely to be infected with a virus. Mumps, inquiring about the vaccinations that were taken recently, then moving to examine the joints that the patient suffers from, seeing the swelling and redness in the joints, and examining the movement of the affected joint and the strength of the muscles around it.
Virus studies
It includes taking a sample of the sick person’s blood and conducting laboratory tests; its positivity includes positive antibodies, which means activating the body’s immunity against the virus; antibodies include IgM and IgG, the IgM antigen indicates that the infection is recent (in the acute phase), serological tests are repeated after 2 to 3 weeks to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Other examinations
It helps to assess the general condition of the patient and to rule out other causes of inflammation, which includes a complete blood count, white blood cell count, measurement of active protein C, rheumatoid factor tests, liver function tests, and antibody tests for hepatitis viruses and parvovirus 19.
Treatment of viral arthritis
The treatment of this inflammation varies according to the type of virus causing it, but in the management of joint problems, most viral joint infections heal automatically. In the case of infection with hepatitis B or C virus or infection with AIDS, treatment of these cases aims to control other side effects of these viruses or treatment with antiretrovirals for AIDS patients.
Surgical treatment is not usually resorted to in the case of viral arthritis. Physical rehabilitation therapy is helpful in cases of muscle weakness resulting from the inability of the patient to move due to existing arthritis.
Prevention of viral arthritis
There is a set of instructions that prevent infection with viruses, including:
- Take vaccinations against hepatitis viruses and measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) viruses.
- Eat healthy and clean food, and avoid drinking contaminated water.
- Practice safe sex with healthy partners.
In conclusion, viral arthritis is a disease that always follows a viral infection. Many viral types can be caused by parvovirus 19, the most common of which remains for days or weeks. Serological examinations can diagnose viral inflammation in the joint, and the infection is self-healing.
Sources:
Common questions
The main symptoms of arthritis are pain in the articular areas (the areas where the bones meet), in addition to swelling, stiffness, and redness that occurs in them. Viral arthritis is preceded by symptoms of viral inflammation, such as coughing and diarrhea, depending on the type of virus causing it.
Antiviral drugs fight the viral spread in the body and contribute to its elimination, but some types of viruses, such as AIDS and hepatitis B virus, are chronic infections, and their treatment is by relieving symptoms.
The treatment of bacterial inflammation is by giving antibiotics. Many germs cause infection, and each germ has its appropriate antibiotic. As for viral arthritis, the virus is the leading cause of it, and it is useless to give antibiotics.
With mild viral types, the disease lasts for a week or two. As for viruses that cause chronic infections, there is no complete recovery and coexistence with the disease.
NSAIDs are a good option. Your doctor can prescribe an arthritis ointment that helps reduce inflammation.