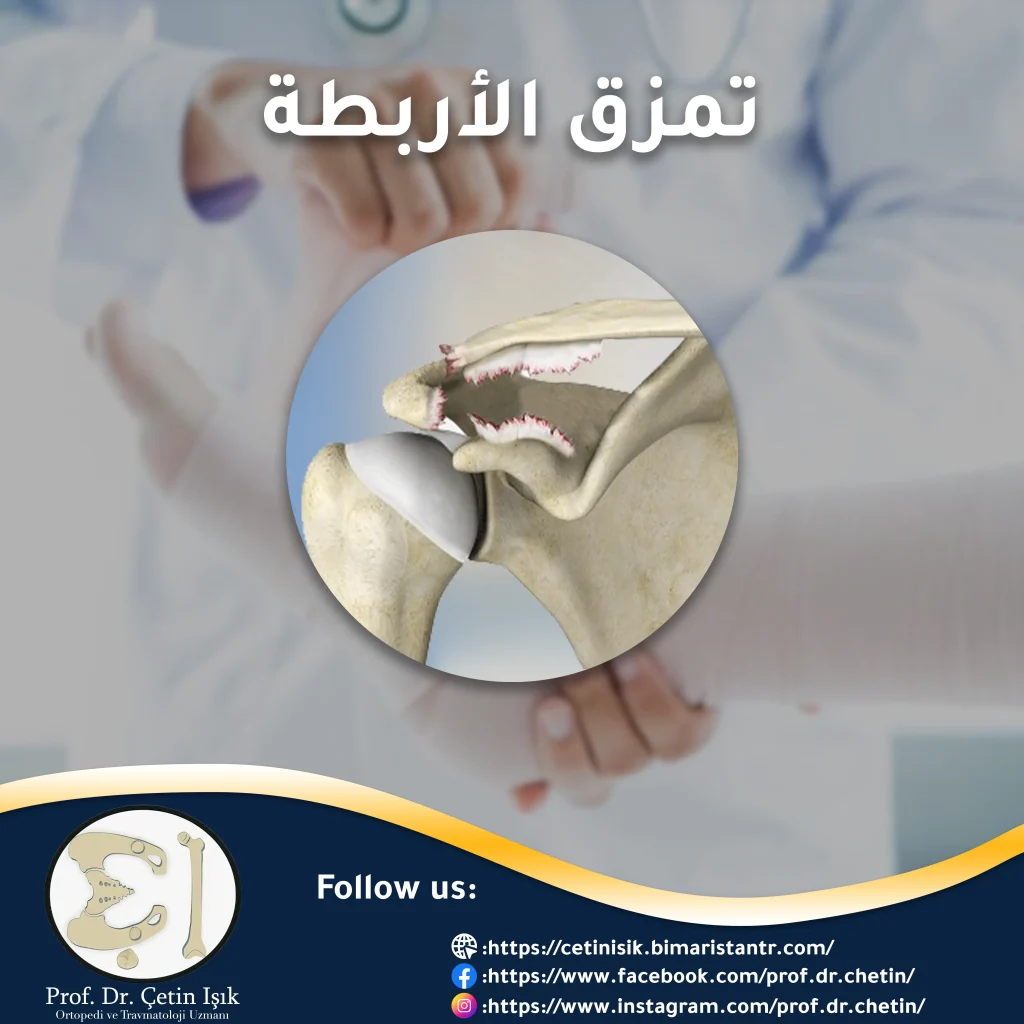
Ligaments rupture is one of the musculoskeletal system injuries that many sports practitioners face. It can occur in different parts of the body, and some types of it may require surgery.
Ligaments are strong and flexible bands found in all joints in the body. They are fibrous connective tissues of the body, and soft and elastic tissues that connect the bones together. They also help determine joint movement and give strength and stability to it.
The most important characteristic of ligament rupture is that it can occur at any age during work, play or exercise, and it also causes severe pain, the types of which vary according to the location of the injury. What are the most important types of ligament rupture and how to deal with it once it occurs? Follow us to learn more about Articular ligaments rupture.
Profile of ligament rupture
The ligaments can be exposed on a daily basis to stretching and pressure, but they can stretch to a certain degree. If the stretching exceeds the absorptive capacity of the ligaments, damage will occur that may lead to rupture. Any joint can rupture ligaments.
Ligament rupture may cause instability in the joint in addition to pain and swelling. The degree of sprain is classified as mild, moderate or severe.
Causes of ligament rupture
Ligaments can rupture at any age, but it occurs more often in the elderly compared to children and adolescents. The reason for this is that the tendons and ligaments lose their elasticity with age, and because of the increased incidence of diseases in them.
Ligament tears often occur as a result of:
- Taking a blow to tight ligaments (such as a sudden fall), most often during a contact sport such as (football, rugby).
- Excessive pressure on the joint, which increases the risk of ligament rupture around it.
- Moving the joint outside its normal range of motion, resulting in a complete or partial rupture (sprain) of the joint ligaments.
Different types of ligament tear injuries
The knee and ankle ligaments are the most susceptible to sprains or ruptures due to their bearing the weight of the body and the excessive pressure on them. We mention the most common joints in which ligament rupture occurs:
Ankle ligament rupture
one of the importants:
- Sprained ankle Ankle sprain: It can happen when walking or running
- Achilles tendon rupture
Knee ligament rupture
It is common among football players and traffic accidents, including:
- MCL medial collateral ligament rupture
- LCL distal collateral ligament tear
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture
- Patellar dislocation
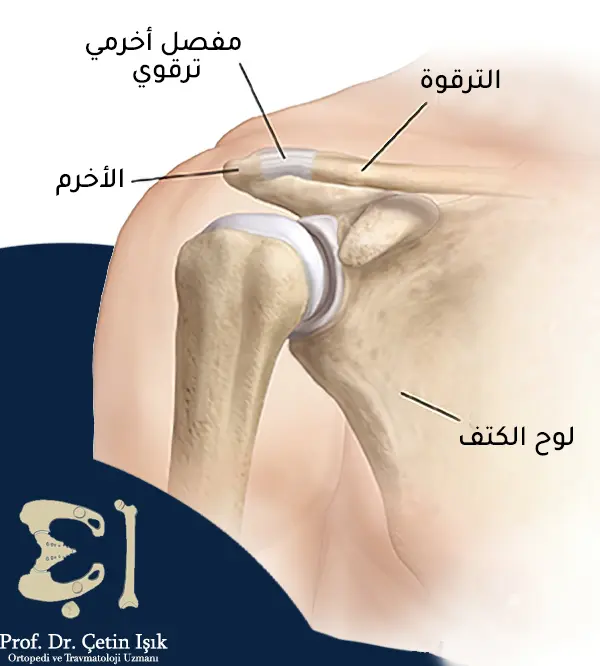
Shoulder ligament rupture
It occurs as a result of repetitive movement of the shoulders (ball throwing and weightlifting) or as a result of direct trauma to the shoulder. Among the most important shoulder injuries are:
- Shoulder dislocation
- Rotator cuff tear
- Acromioclavicular joint injury
Injuries to the ligaments of the wrist and hand
As in a sprained thumb.
Spinal ligament injuries
- Back ligament sprain
- Textual neck sprain
Symptoms of ligament rupture
The symptoms of ligament rupture differ according to the severity of the injury and the type of rupture in the ligaments. Partial ruptures cause severe pain, while complete ruptures may not feel pain. Symptoms of ligament rupture include the appearance of one of the following signs:
- Sudden pain in the affected joint or place that does not improve after 1 to 3 days
- Swelling or bruising around the injured area
- Poor joint movement (extension and flexion)
- A crackling or popping sound may be heard when injuries occur
- Increased intensity of pain when putting pressure on the affected joints
How to accurately diagnose a ligament tear
Diagnosing a ligament tear can be a complex process that requires sufficient clinical experience. It is important to know the signs and symptoms of a ligament tear to make an accurate diagnosis and then develop an appropriate treatment plan. Diagnostic procedures include:
- Physical Examination: An examination conducted by the attending physician, in which he checks for swelling, bruising, or the possibility of a crack in the bones, and examines active joint movement (the patient moves the joint himself) and passive movement (the doctor moves the joint) to find out if there is a defect in the movement of the joint, as well Muscle strength is checked.
- X-ray X-ray: This type of imaging is often requested in the event of suspicion of a broken bone after strong injuries. An imaging of the affected joint can be performed from several sides (anterior or lateral) to help make a more accurate diagnosis.
- MRI: gives better pictures of the internal structure of the joints, and helps to identify any damage to the ligament or cartilage and make an accurate diagnosis to provide an effective treatment plan.
Ligament rupture treatment
The treatment options for ligament rupture (depending on the severity and location of the injury) range from simple home treatment to surgical intervention, and include:
first aid
It is necessary to avoid walking immediately after the injury, especially in the event that the ligaments of the ankle and knee joints are injured, and to follow a set of measures that the injured can take, which include:
- Rest without putting weight on the affected joint for at least two days.
- Putting ice packs on the affected area (every half hour, compresses are placed for ten minutes).
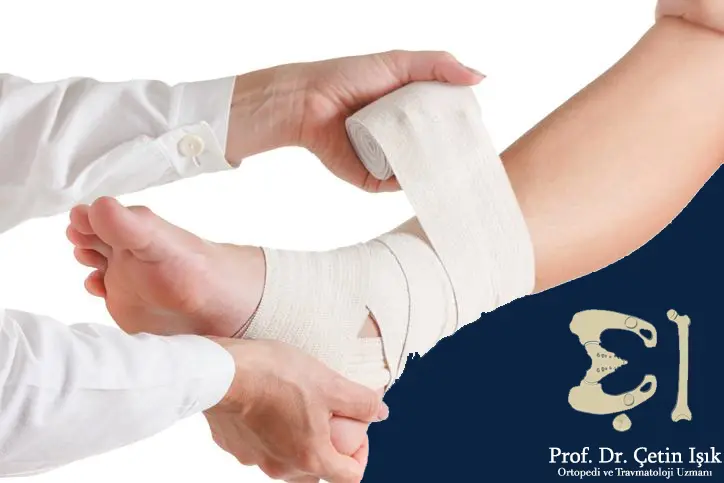
- Putting pressure bandages or corsets on the affected areas.
- Elevating and immobilizing the joints (by lying down and raising the affected joint, where pillows can be placed under it).
- Crutches may be used if the ligaments in the ankle or knee are injured.
Medications
Doctors may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) to reduce inflammation, and in cases of severe pain, pain-relieving medications may be prescribed.
Surgery
In cases of complete ligament rupture, surgical treatment can be resorted to, and doctors recommend surgery according to the pattern and location of the injury. For example, the treatment of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture in the knee is by removing the ruptured ligament and implanting a new ligament in its place.
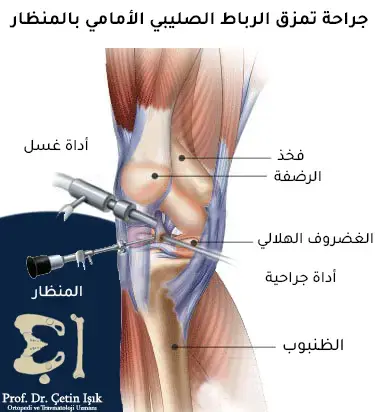
An endoscopic technique can be used to repair damaged ligaments, as in: Shoulder arthroscopy andKnee arthroscopy Ankle arthroscopy.
Follow-up physical therapy is necessary after surgery.
Physical rehabilitation
After periods of inactivity, the muscles of the body may lose their flexibility and range of motion. Physical rehabilitation specialists train the injured person from time to time to perform certain movements and exercises to restore normal movement and restore the muscles to their former strength.
Prevention of rupture of ligaments
Ligament rupture can be prevented by practicing exercises that strengthen the ligaments, tendons, and muscles and support the structures around the joints, paying attention to the need to perform stretching exercises to reduce the possibility of ruptures in the tissues, warming up the muscles of the body before starting the exercises, and not loading excessive weights beyond the ability of the ligaments and muscles to bear them. .
In conclusion, ligament rupture is one of the most common injuries that occur to practitioners of sports that involve intense physical contact (such as football), and the knee and ankle ligaments are the most common joints in which this type of injury occurs, so medical professionals must prepare for these cases and know how to deal with them. manage it.
Sources:
Common questions
When swelling and pain occur after making a wrong movement of the joint or after receiving a strong blow during sports activity, if the improvement does not occur within 24 to 72 hours, it is likely that the ligaments were torn. Hearing a strong crackling sound when injured increases the possibility of diagnosis. Suspicion of a rupture to receive an appropriate treatment plan from doctors.
The severity of ligament rupture depends on the degree of rupture of the ligaments and its effect on the stability of the joint. Mild ruptures that do not affect the stability of the joint are treated by resting the joint, while severe ruptures affecting the stability of the joint may require surgery.
In cases such as rupture of the ligaments (sprain) of the mild ankle joint, treatment can be done at home without going to the hospital. In this case, doctors recommend following the RICE system, which includes rest, applying ice to reduce swelling, applying pressure to the joint ligament injury site, and elevating the joint.
The doctor can tell you about the expected period for a full recovery. Determining this period depends on the pattern and amount of rupture in the ligaments of the patient’s body (ligaments of the knee or ankle joint…). The estimated period for complete recovery in minor ruptures is 6 weeks if the patient adheres to the doctors’ instructions. It increases in the most severe ruptures.