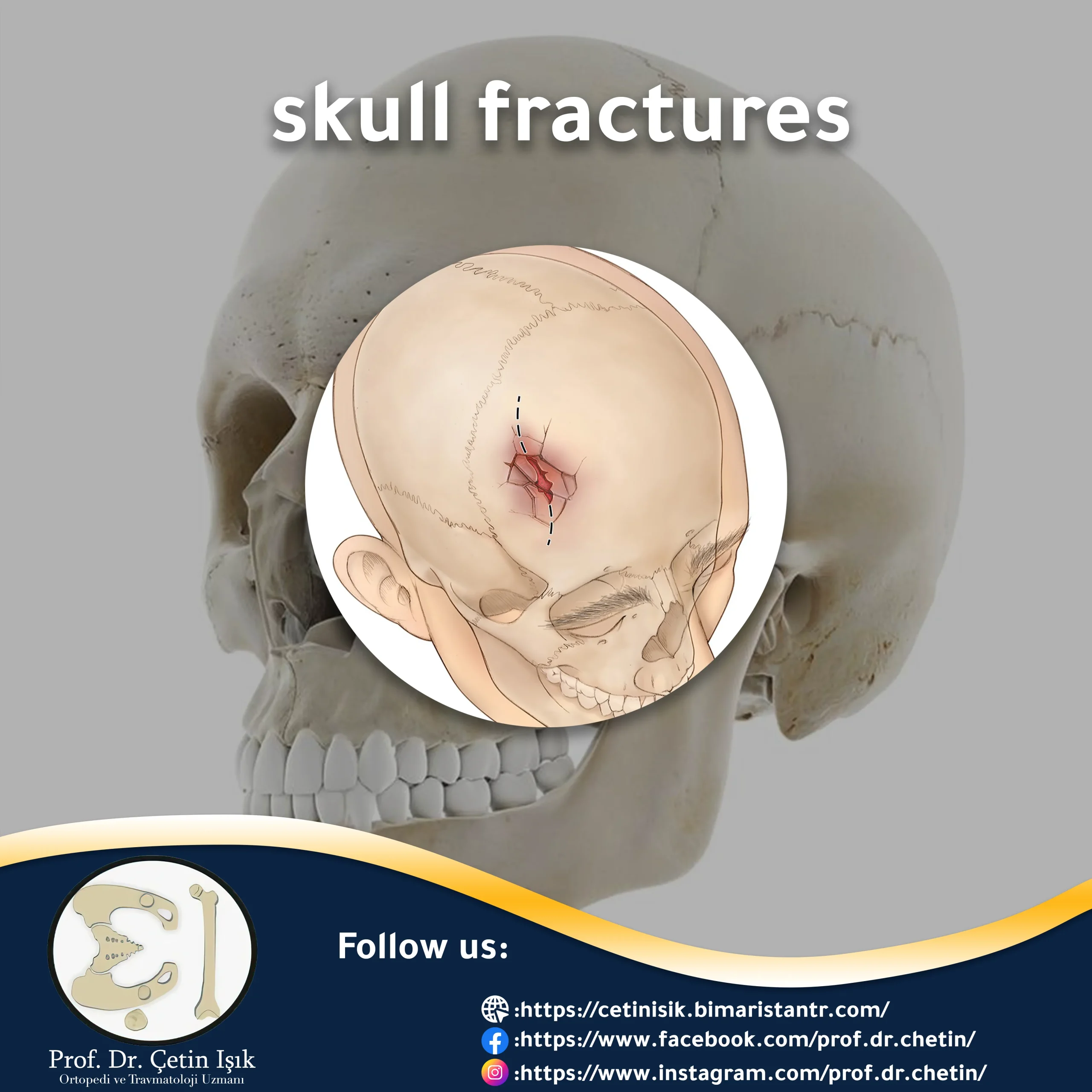
Skull fractures are fractures that occur due to injury to the bones in the head. A skull fracture is one of the most dangerous fractures in adults because this fracture may cause bleeding within the brain.
Skull fractures include fractures of the cranial bones and facial bones, and they often occur as a result of strong trauma to the head. Skull fractures may occur due to falls or car accidents. Skull fractures are classified according to the location of the fracture in the head. Depending on the location of the fracture, clinical signs and symptoms differ. Treatment methods for skull fractures vary between observations only. Or resort to surgery immediately, depending on the severity of the fracture.
In this article, we will present what are the types of skull fractures? And the most important symptoms and signs that appear after the fracture. How to treat skull fractures?
The most important information about skull fractures
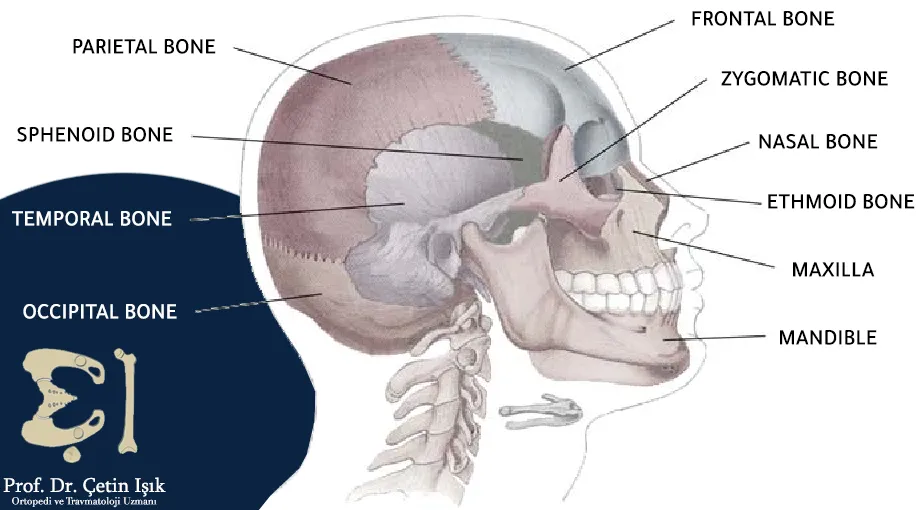
The skull consists of the cranial bones (the occipital bone, the two parietal bones, the sphenoid bone, the ethmoid bone, the frontal bone, and the two temporal bones, and these bones form the cranial part of the skull) and the facial bones which consist of the bones of the upper jaw, vomer, cheek, lacrimal, palate, mandible and nose Where the brain is located inside the cranial bones and protects it from trauma and trauma. The brain communicates with the spinal cord through the foramen magnum at the base of the skull.
. skull fracture It is a fracture in one of the cranial and facial bones. A skull fracture may occur when the skull is hit with a strong force that leads to a crack or a fracture in the bones of the head, which may cause brain damage with bleeding and fractures in the skull, depending on the severity of the force.
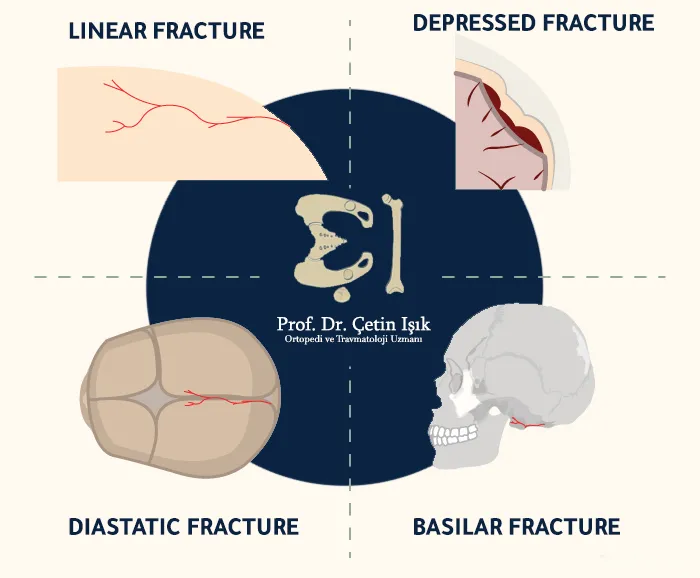
Types of skull fractures
Head injuries vary between brain concussion, intracranial hematoma, or skull fractures. The most important types of fractures are:
- Linear skull fracture: The most common types of skull fractures are in which the bones break linearly without moving from their position, and they need to be monitored in the hospital for several days, after which the patient can return to daily activities.
- Depressed skull fracture: These fractures may be associated with wounds in the scalp, where the fractured part collapsed due to trauma. This type of fracture may require surgical intervention to correct the deformity in the shape of the skull.
- Diastatic skull fracture: They are the fractures that occur along the suture connection (the sutures are the place where the cranial bones join each other and which fuse in childhood), and these fractures are often found in newborns.
- Basilar skull fracture: It is the most serious type of skull fracture, and the fracture is at the base of the skull. Patients often suffer from bruising around the eyes or ears due to skull base fractures and usually need intensive care.
Causes of skull fractures
Most skull fractures are due to severe trauma to the head, such as falling from a high altitude, exposure to a car accident, physical assault, and sports injuries, as these injuries may lead to many fractures in the head, as the patient may suffer skull fractures as well as fractures in the jaw. The patient may be injured during accidentsFracture of the collarbone or Rib cage fracture.
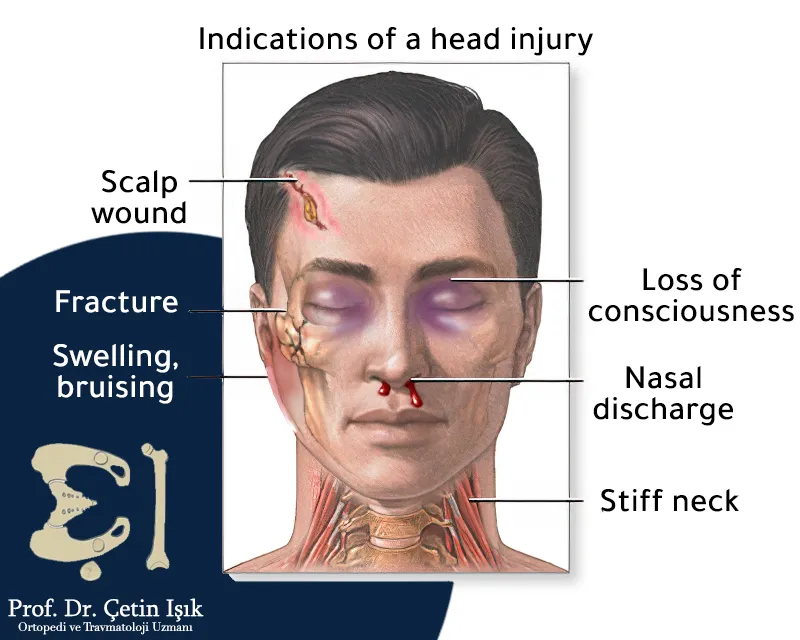
Symptoms of skull fractures
Symptoms change according to the severity of the injury that caused the skull fractures. Symptoms are divided into two parts according to the severity of the injury:
Symptoms of a mild head injury
These are the symptoms that appear in light-intensity bruises, which often do not require medical intervention and do not require intensive care:
- Swelling or bruising in the area of injury
- Small superficial wounds of the shallow depth in the scalp
- headache
- photosensitivity
- Irritability and confusion
- Balance problems
- Vertigo and dizziness
- nausea
- Weakness in focus
- Ringing in the ears
- Fatigue and lethargy
- blurred vision
- Sleep pattern change
Symptoms of moderate to severe head injury
They require intensive medical attention and include mild head injury and the following symptoms:
- Unconsciousness
- very severe headache
- Frequent nausea and vomiting
- Short term memory loss
- difficulty walking
- babbler
- Sweating
- bouts of convulsions
- pale skin
- Bleeding from the nose or ear
- A deep cut in the scalp
- The patient enters a coma
- Vegetative state (a condition due to brain damage in which a person loses the ability to think and be conscious but retains some essential functions such as breathing and circulation)
- Locked-in Syndrome (Quadriplegia with Remaining Consciousness, a neurological condition in which a person is conscious and can think but is unable to move or speak)
- One pupil is dilated, appears more significant than the other eye, and does not constrict when exposed to light.
Diagnosis of skull fractures
To diagnose a skull fracture, the doctor asks about blood thinners such as warfarin, performs some physical examinations, and orders some x-rays and blood tests, according to the patient's condition, such as:
- X RAY showing bone fractures
- CT scan. This scan is useful for detecting bone fractures, brain hemorrhages, or other brain injuries
- MRI image This image is useful in detecting brain tissue damage
- Blood tests to detect infection after the fracture
Treatment of skull fractures
The treatment of skull fractures depends on the severity of the injury, the patient's health condition, the type of fracture, and the patient's age, but in general, the treatment of skull fracture differs from the treatment of other fractures such as leg fracture or Hand joint fracture Which is often splinting, and the treatment of skull fracture is divided into the following according to the severity of the injury:
Treatment of a mild skull fracture
In this type of fracture, the patient must be monitored from 24 to 48 hours, with some of the following treatments applied, depending on the case:
- Put an ice pack
- Complete comfort for the patient
- Ointment for small wounds
- Suturing large wounds
- Use of analgesic medications A treatment for bone pain If necessary
Treatment of moderate and severe skull fracture
This type of fracture is treated in intensive care, and it includes the previous treatments, in addition to the following, depending on the case:
- Giving oxygen
- Intensive monitoring of elevated intracranial pressure
- Use of medications and intravenous fluids
- Supporting breathing, heart and blood pressure
- Use of medications to prevent seizures
- Infection control with antibiotics as needed
- Treatment of nausea, vomiting and stomach disorders
- The patient may need surgery to repair severe skull fractures or to remove blood pooling and bone fragments, depending on the case
At the end of the article, we conclude that skull fractures often occur after severe trauma to the head, and there are four types of skull fractures. Symptoms of skull fractures vary according to the severity of the fracture. A skull fracture is often diagnosed through clinical examination and CT imaging to ensure the integrity of the brain and diagnose bleeding in the brain, if any. Treatment varies according to the fracture's severity and the patient's age, from observation to surgical intervention.
Sources:
Common questions
According to the severity of the fracture, in simple fractures there are few complications, and the fracture heals on its own over time, unlike severe fractures, which may be associated with life-threatening complications and need surgical treatment.
Most of the simple skull fractures heal with observation only without the need for treatment, while serious fractures need treatment and intensive care, and they heal, but they need a longer time than simple fractures.
The duration varies according to the severity of the fracture. In simple fractures, it takes 3 to 4 weeks for the fracture to heal completely, and in severe fractures, the healing time may take between 3 to 6 months to heal completely.
The risk lies in the presence of complications on the brain, such as bleeding, leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, bruising and inflammation of the brain, and seizures.
Skull fractures result in different injuries depending on the type of fracture. A fracture may result in bruising in the brain, bleeding, infection, or concussion, or nothing may happen in simple fractures.
All skull fractures are monitored, and the severity of the fracture is what determines whether the fracture needs monitoring only or surgical intervention to protect the person from complications.
Simple skull fractures usually heal without death, and the type of fracture determines the risk of death, but fractures of the occipital bone in the skull are often associated with high mortality.