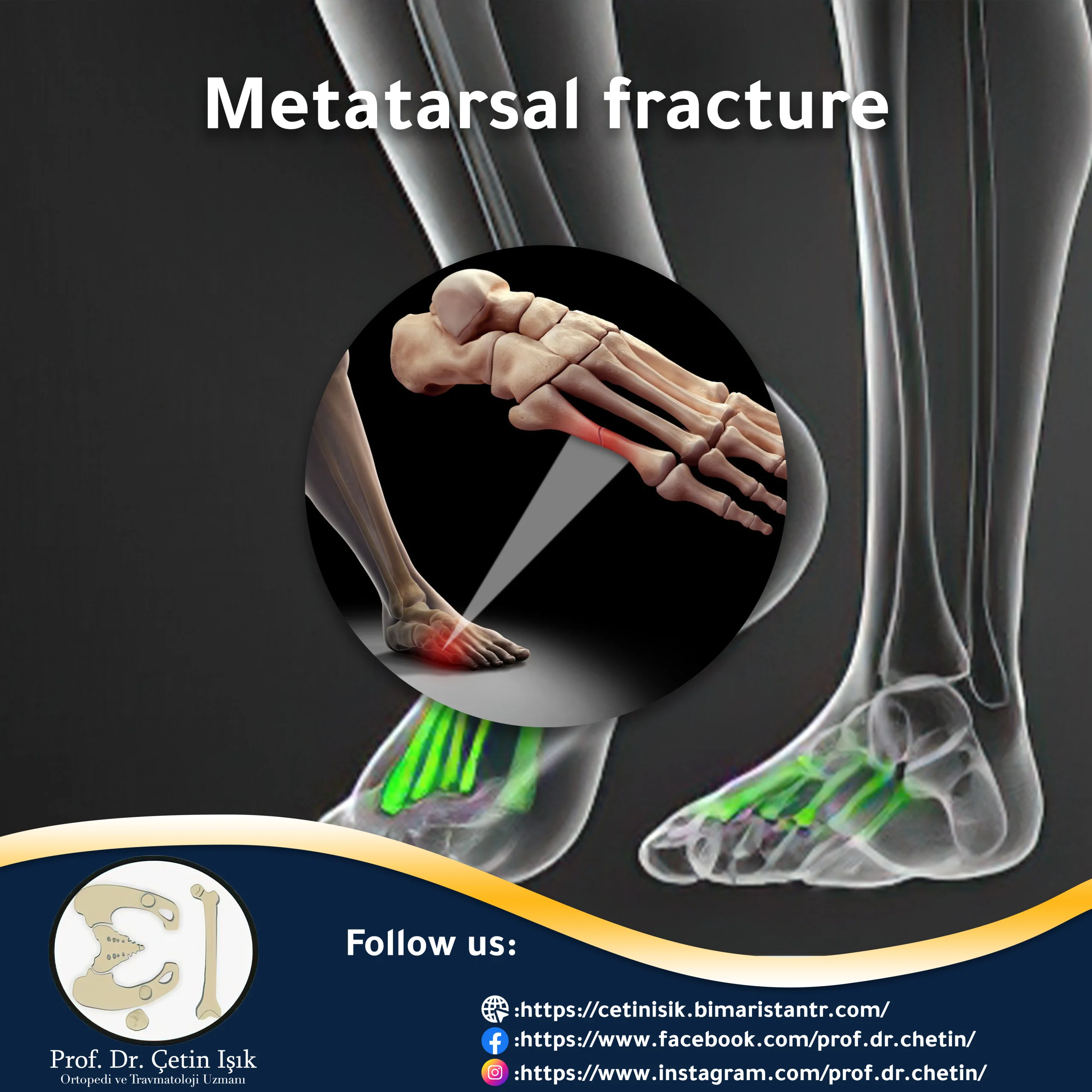
A metatarsal fracture is a fracture in one of the five metatarsal bones. The most common cause of fractures is direct or indirect traumatic injuries such as stress fractures that cause pain in the bones of the foot.
The fracture of the metatarsal is one of the most common types of fractures in the foot; specifically the fracture of the fifth metatarsal is the most common in adults, men and women alike, while the fracture of the first metatarsal is the most common in children under the age of 4 years, while the fractures of the middle metatarsal (second and third and fourth) they are often associated with each other and rarely occur in isolation.
What are the main types of metatarsal fractures? How is the treatment of a cracked foot without gypsum? And what is the method of splinting a metatarsal fracture?
Information about a metatarsal fracture
A metatarsal fracture is a minor crack or complete break of one of the bones. It is five long, thin bones located between the tarsal bones in the back and the phalanges in the front. Each bone consists of a head, neck, body, and base. Fractures may occur in any of these anatomical regions when a person jumps or twists his ankle incorrectly or because of excessive stress on one of the long bones in the foot.
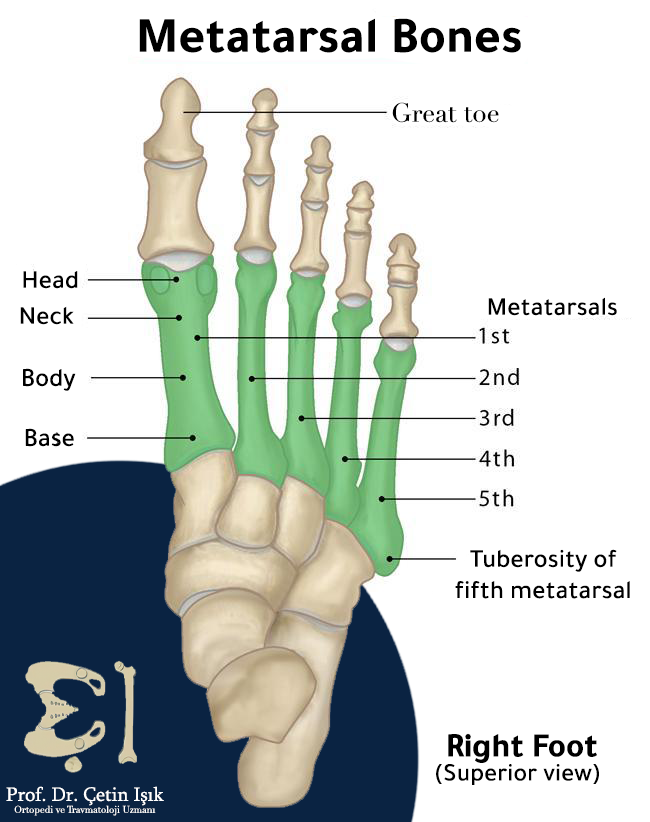
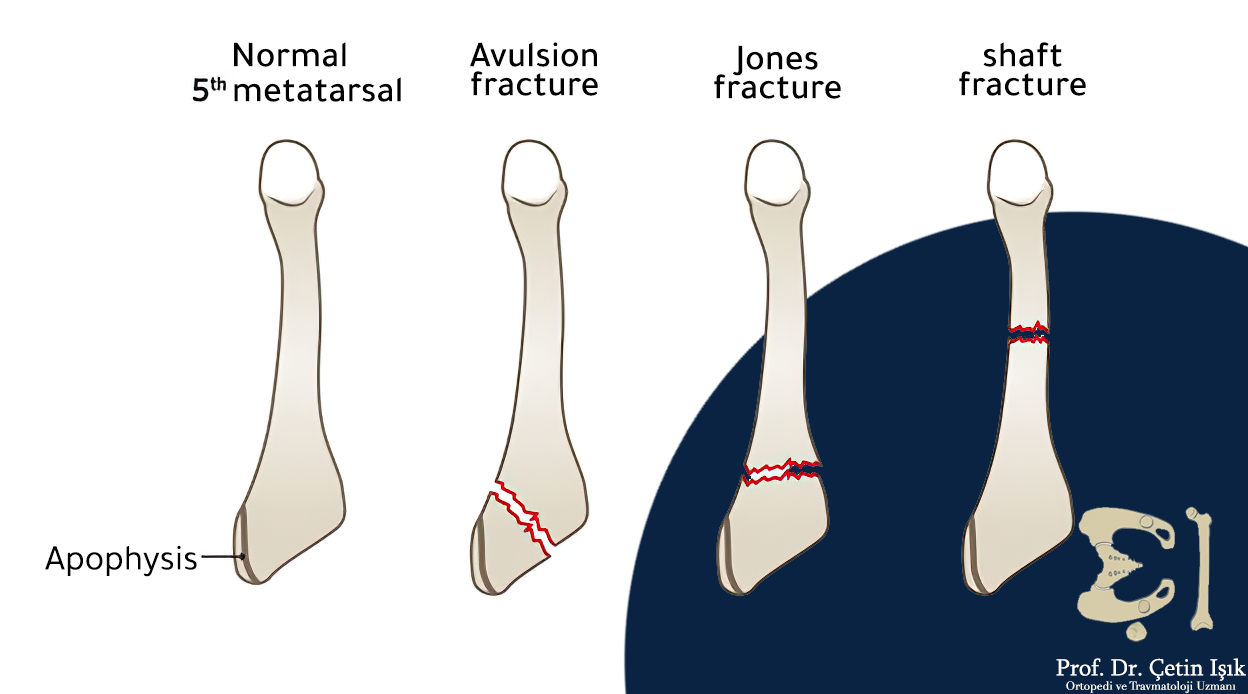
The fracture of the fifth bone of the right or left metatarsal is the most critical and common metatarsal fracture, which is the metatarsal that connects to the little toe in front. When the basal part of the fifth metatarsal is broken, then called Jones fracture It is a common fracture.
Types of metatarsal fracture
It is important to know the types of foot fractures In Metatarsal, to know the type of treatment, classification is made according to the following:
- open or closed:
- Open fracture: A fracture in which the skin has been torn over the broken bones and the tissues surrounding the bones are severely damaged. It may cause infection in the broken bones, which is the most severe fracture.
- Closed fracture: It is a fracture in which the skin is not torn and does not carry the risk of infection, and it is less dangerous than the open fracture, and treatment may be simple.
- displaced or non-displaced:
- Displaced fracture: It is the fracture in which the broken bones slip out of their regular places. This fracture requires special treatment as the bones must line up and stabilize normally. This may require anesthesia and surgery.
- fracture site:
- Metatarsal head
- Metatarsal neck
- Metatarsal body
- Metatarsal base (Jones fracture or avulsion fracture)
Causes of a metatarsal fracture
A person must know the reasons for their occurrence Foot fracture To avoid these fractures, the most important possible causes are:
- The patient's foot is exposed to direct and severe trauma, such as falling on the leg, which may also cause a fracture of the ankle or Torn ankle ligaments.
- Falling heavy weights on foot may also cause a toe fracture.
- Sprained ankle Or an ankle fracture may cause a fracture at the base of the metatarsal.
- Not resting the feet and repeated stress on the bones, because this can cause stress fractures that are often present in athletes who run long distances.
- Continue to exercise despite having painful feet, such as gymnasts or ballet dancers.
- Infection with some diseases that cause deformities in the structure of the joints and bones of the feet may increase the possibility of people suffering stress fractures and multiple fractures, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis or sickness Osteoporosis.
- A stress fracture may also occur in people with diabetes because they lose sensation in the feet in the advanced stages of the disease.
Symptoms of a metatarsal fracture
If symptoms Metatarsal fissure It may be clear and distinct in an acute fracture and not clear in a stress fracture. The most important of these symptoms are:
- Sharp and immediate pain after the fracture
- The pain is often localized at the fracture site
- The patient may hear a bone-cracking sound in the fractures of the foot
- Swelling or bruising under the skin
- There may be difficulty moving the broken foot and pain when walking
- It may be associated with symptoms of a broken toe
- Mild and widespread pain in the case of stress fractures when exercising and is relieved by rest
Complications of a metatarsal fracture
The patient may develop some complications as a result foot broke This is when the broken foot is stressed, or the correct treatment is not followed. The most important complications are:
- The fracture may affect the entire thickness of the bone, when the patient is repeatedly pressed on the leg with a stress fracture
- Inflammation of the big toe joint when the first metatarsal fractures
- A complication between the ankle crack and the metatarsal base fracture
- Chronic pain in the broken leg
- A deformity in the foot occurs when the broken bone fuses incorrectly and may lead to difficulty wearing the shoe
Diagnosing a metatarsal fracture
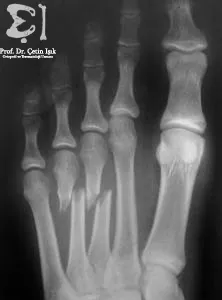
In the beginning, the patient's broken foot is examined and compared with the healthy foot; edema and bony cracking are noted in his foot. Then, radiographic investigations are required, consisting of the following:
- X-rays are usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis
- CT imaging
- MRI to rule out any other lesions
Metatarsal fracture treatment
The treatment of a metatarsal crack varies according to the type of broken metatarsal bones, the location of the fracture in the bone, and whether the fracture is an acute fracture or a stress fracture. It is divided into two parts:
Conservative treatment
This treatment is used when the fracture is not displaced and is not accompanied by severe injuries; it includes the following:
- Use of simple analgesics such as cetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs To relieve bone pain.
- Putting an ice bag immediately after the injury for 15 minutes helps relieve edema and pain. You should not put ice directly on the skin because it causes burns and is painful. Do not use it for more than 30 minutes.
- Lifting the leg and resting, as lifting the leg helps to reduce blood flow and protect against swelling and bruising; As it should be raised to hip level when you are sitting and placed on a pillow when sleeping, rest may be the only treatment for a fracture.
- Avoiding sports activities that caused the fracture in the event of a stress fracture and avoiding putting pressure on the broken leg. A wheelchair can also be used when needed.
- Putting a metatarsal splint when necessary, the splint is done by putting the splint with water and then wrapping it around the leg from the beginning of the toes to above the ankle without pulling it strongly, then tying it and leaving it to dry, and it is also possible to use shoes with a stiff sole in simple cases.
- Resorting to physical therapy In some fractures, such as massaging the leg's soft tissues, then doing some exercises that increase the flexibility and strength of the small muscles surrounding the metatarsal.
Surgical treatment
This treatment includes several options of operations, and surgical treatment must be resorted to in the event of displaced fractures, complications occur, or in the event of failure of conservative treatment of fractures. Among the most important methods of treatment are:
- Ankle and metatarsal screws or rods and plates to stabilize broken bones.
- The process of replacing damaged bones with a bone graft, in which surgery is performed to remove damaged bones, and bone grafts are used to restore the leg to its normal shape.
In conclusion, we must know that the metatarsal fracture is one of the most common foot bone fractures that usually occur in athletes and runners who walk long distances on their feet, bearing in mind that the symptoms of foot bone fractures are clear and distinct and are diagnosed by a doctor with a clinical examination and usually use x-rays. It must be emphasized that most metatarsal fractures are treated conservatively without resorting to surgery at early diagnosis.
Sources:
Common questions
The healing of a simple crack may take from 6 weeks or a month to several months, and this varies according to the period during which the patient gives rest to his feet and the type and severity of the fracture. In severe fractures, bone healing may take 3 to 6 months.
When undisplaced fractures and the ends of the metatarsal bones are opposite and not far apart, the gypsum should be placed for approximately 6 to 8 weeks. The gypsum should not be removed until healing and consultation with doctors.
You can walk after removing the gypsum, but this must be a few days after the removal of the gypsum to rest the feet, and the walking should be gradual and for short distances. When you feel any pain, you should rest and seek medical advice.
Walking on a cast should be avoided due to the inability of the gypsum to carry the weight of your body. A crack in the gypsum can occur or break and cause more damage to the fractures of the foot and also increase the pain of the leg.
This is done through proper nutrition and eating foods that contain calcium andVitamin D Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol, adequate rest for the feet, and avoid strenuous sports activity for the metatarsal bone.
Metatarsal fractures are fixed when the patient has multiple fractures in the leg and ankle, or when the fracture includes the entire thickness of the bone, when the metatarsal bones are displaced more than 3 or 4 mm, and after consulting a doctor.
The metatarsal bones are fixed by installing screws in the ankle or installing plates and screws in the metatarsals with complete rest and no stress on the feet.