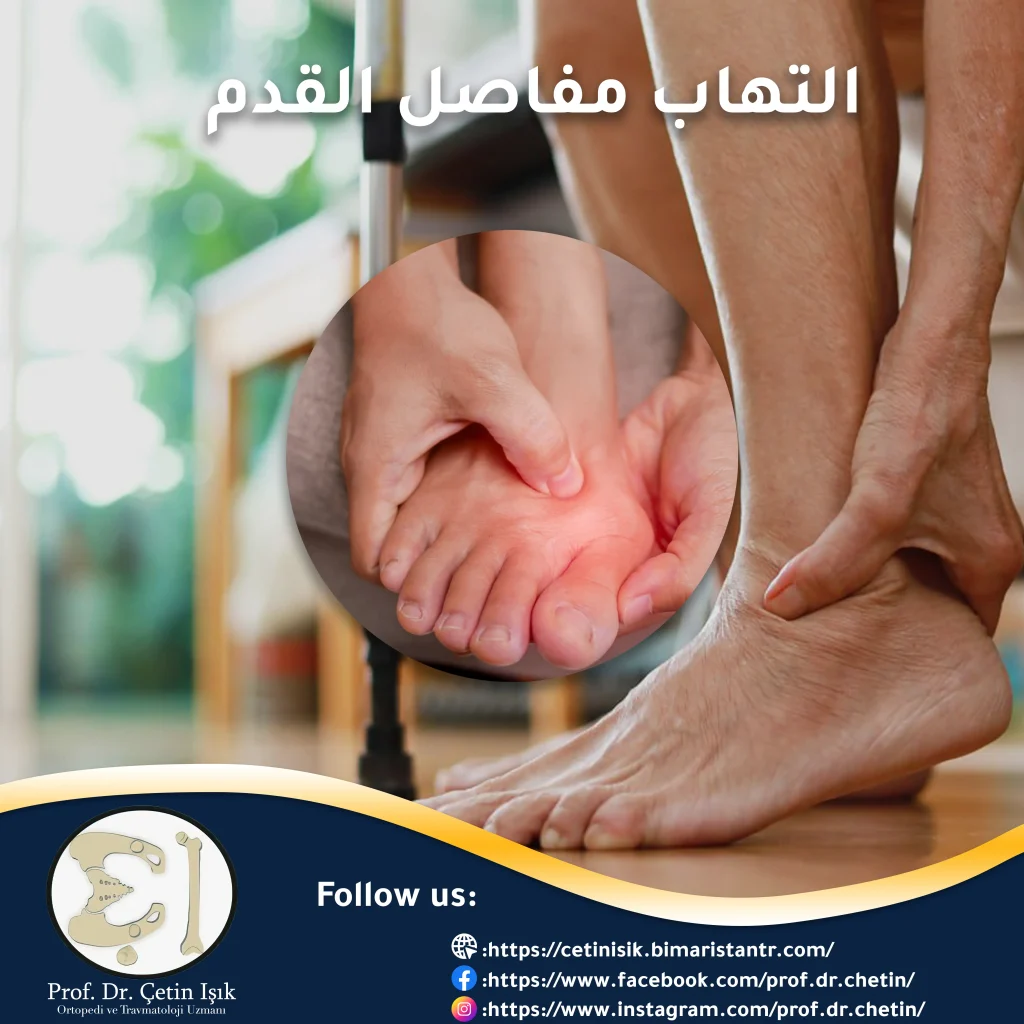
Foot arthritis is a common condition that includes irritation of the joints that connect the bones of the foot together, leading to pain and swelling of the foot, which hinders the patient’s movement and gait.
Foot arthritis is common in the elderly, obese people, and in foot injuries, and its danger lies in the possibility of deformation of the foot shape in the case of rheumatoid arthritis. Learn with us about foot arthritis and ways to treat it.
Overview of foot arthritis
Foot Arthritis is a disease characterized by irritation and damage to the joints, leading to pain and swelling in the foot and ankle joints. Inflammation can affect any of the 30 joints of the foot.
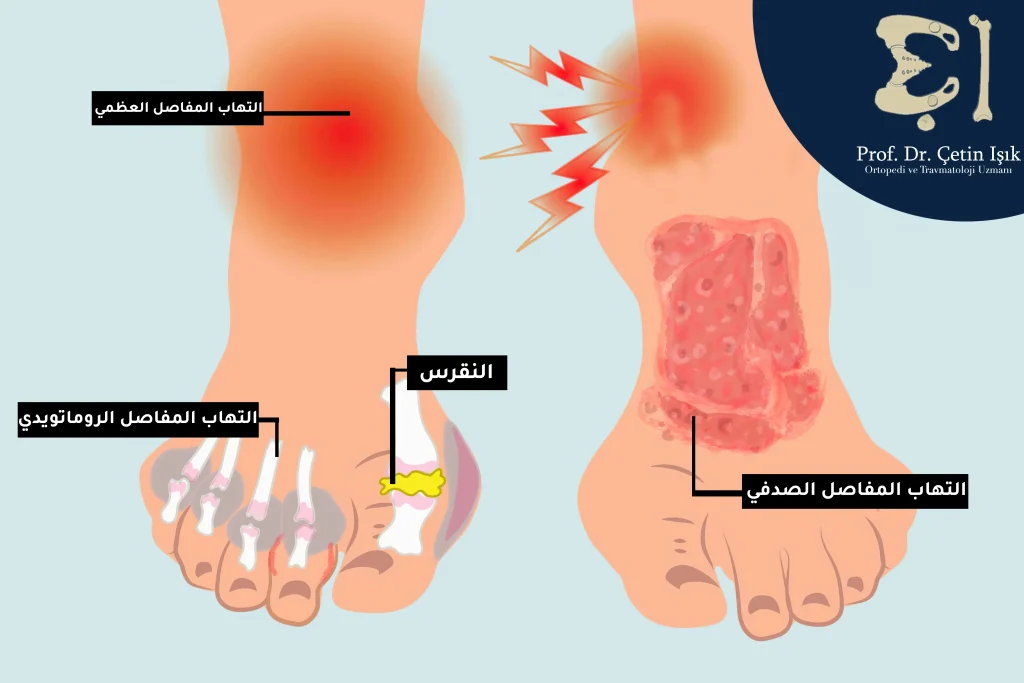
There are several types of foot arthritis, the most common of which are: Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis, the most serious of which is rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which may cause foot deformities.
Foot arthritis affects everyone, but it becomes more common with age and in obese people and those who engage in sports activities as a result of repeated exposure to foot injuries (such as fractures and dislocations). There may also be a role for genetics in the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis.
Types of foot arthritis
There are several types that differ in their prevalence and the type of individuals they affect. Types of inflammation in the foot and ankle joints include the following:
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis in the body, as its incidence increases with age and in obese people as a result of overuse of the joints and increased weight applied to the joints.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): It is an autoimmune disease in which the body attacks the joints, causing inflammation and damage.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: It occurs due to traumatic injuries such as dislocations, leading to inflammation.
- Gout: It occurs when uric acid accumulates in the joints, especially the big toe joint.
- psoriatic arthritis; Psoriatic arthritis: It can occur in one or more joints, including the ankles and tips of the toes (small joints), and may affect the toes, causing them to swell in what is called dactylitis (accompanied by skin psoriasis).
Symptoms of foot arthritis
Symptoms of arthritis in the foot vary depending on the severity of the inflammation and the affected joints. Symptoms include the following:
- Pain that worsens during activity or movement
- Tenderness (pain to touch) in the joint area
- Swelling of the joints is accompanied by heat and redness
- Joint stiffness that increases after sitting, resting, or being inactive
- Difficulty walking or moving
Diagnosis of foot arthritis
Diagnosis can be made through the patient's clinical history, which includes the symptoms that the patient suffers from and a clinical examination to evaluate the movement of the foot joints. The patient can also be asked to walk to measure steps and gait.
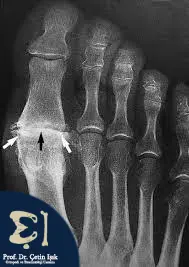
Radiographic methods such as X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of foot arthritis
Treatment of inflammation in the joints of the foot varies, such as: Hand arthritis Depending on the severity and type of inflammation, treatment ranges from non-surgical treatment to surgical treatment for severe cases, with the possibility of practicing physical therapy exercises to speed up the healing process.
Non-surgical treatment
Non-surgical treatment should be the first line of treatment for arthritis in the foot joints. Non-surgical treatment options include:
- Rest and use hot and cold compresses to reduce inflammation and relieve pain
- Pain relievers (NSAIDs)
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce joint pain and swelling
- Corticosteroid injections into the foot joint to relieve arthritis pain and inflammation
- Wearing shoes with supports to support and straighten the joints
- Use walking aids (such as canes) to relieve pressure on the affected joint
- Taking specific medications when knowing the type of arthritis, such as immunomodulatory and anti-rheumatic medications in cases of rheumatoid arthritis.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment may be used if non-surgical treatment techniques fail to treat arthritis. Surgical treatment options include the following:
- Arthroscopic surgery: Arthroscopic surgery can help treat the early stages of arthritis, in which an endoscope is inserted into the joint to clearly see the contents of the joint, and any foreign tissue or bone protrusions (bumps) present in the joint can be removed using special tools.
- Arthrodesis: Arthrodesis involves fusing the bones together using rods, screws, or plates. After healing, the bones remain fused together.
- Joint replacement: This surgery can be performed to treat severe cases and is called arthroplasty, where damaged cartilage and bone are removed and replaced with metal or plastic parts.
In most cases, patients are able to leave the hospital on the same day of surgery, but some patients may spend the night in the hospital. Recovery from arthritis surgery after discharge from the hospital varies from person to person, and usually takes from several weeks to months.
You should get plenty of rest after surgery and you can do physical therapy exercises to speed up your recovery and return to daily activities. Our physical therapists create customized recovery exercise programs depending on the severity of your condition and the type of surgery you had.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy exercises can maintain the strength and flexibility of the foot. These exercises include:
- Achilles tendon stretch: Stand in front of a wall, place the palms of your hands on it, then put one foot forward and one foot back, then bend forward while keeping your heels on the ground, then pull the tendon and the back of the leg for 10 seconds, and repeat this exercise three times Every side.
- Big Toe Stretch: Place a thick rubber band around your big toe, then use your muscles to pull them away from each other toward your other toes. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times.
- Toe pull: Place a rubber band around the toes of each foot, then spread the toes apart, and hold this position for 5 seconds. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
Prevention of foot arthritis
Foot arthritis cannot always be prevented, but the appearance of inflammation can be reduced by following the following tips:
- Exercise regularly to maintain foot strength and flexibility
- Maintain a healthy weight to relieve joint pressure
- Avoid sports activities that expose the foot to repeated injuries
Foot arthritis is a medical condition that includes several types and is characterized by pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty walking. Its treatment is non-surgical in most cases, with physical therapy exercises that speed up the patient’s return to his daily activities.
Sources:
Common questions
Symptoms of foot arthritis include pain that increases with movement, tenderness, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty walking.
Foot joint pain can be relieved by resting, taking over-the-counter pain relievers (such as NSAIDs such as ibuprofen), and using hot and cold compresses.
Some herbs can help relieve inflammation, such as chamomile and ginger.
Healing from foot arthritis takes from several weeks to several months depending on the severity of the inflammation and the patient's general health.
The duration of foot arthritis surgery varies depending on the type of surgery performed, but foot arthritis surgeries usually take about 1 hour.