A tear in the hand ligaments is the stretching and cracking of the ligaments that connect the bones of the hand together, causing difficulty in moving the hand joints, increasing the risk of arthritis, and affecting the patient’s activity.
Hand ligaments are among the ligaments most susceptible to tearing due to frequent use of the hands, and thus the possibility of injury is greater than the rest of the ligaments in the body. Learn with us about the causes of torn hand ligaments and their treatment.
What is a torn ligament in the hand?
Torn hand ligaments are the stretching and interruption of the ligaments that connect the bones together and maintain the stability and movement of the joints, which leads to pain and swelling of the hand and difficulty moving it as a result of the instability of the hand joints.
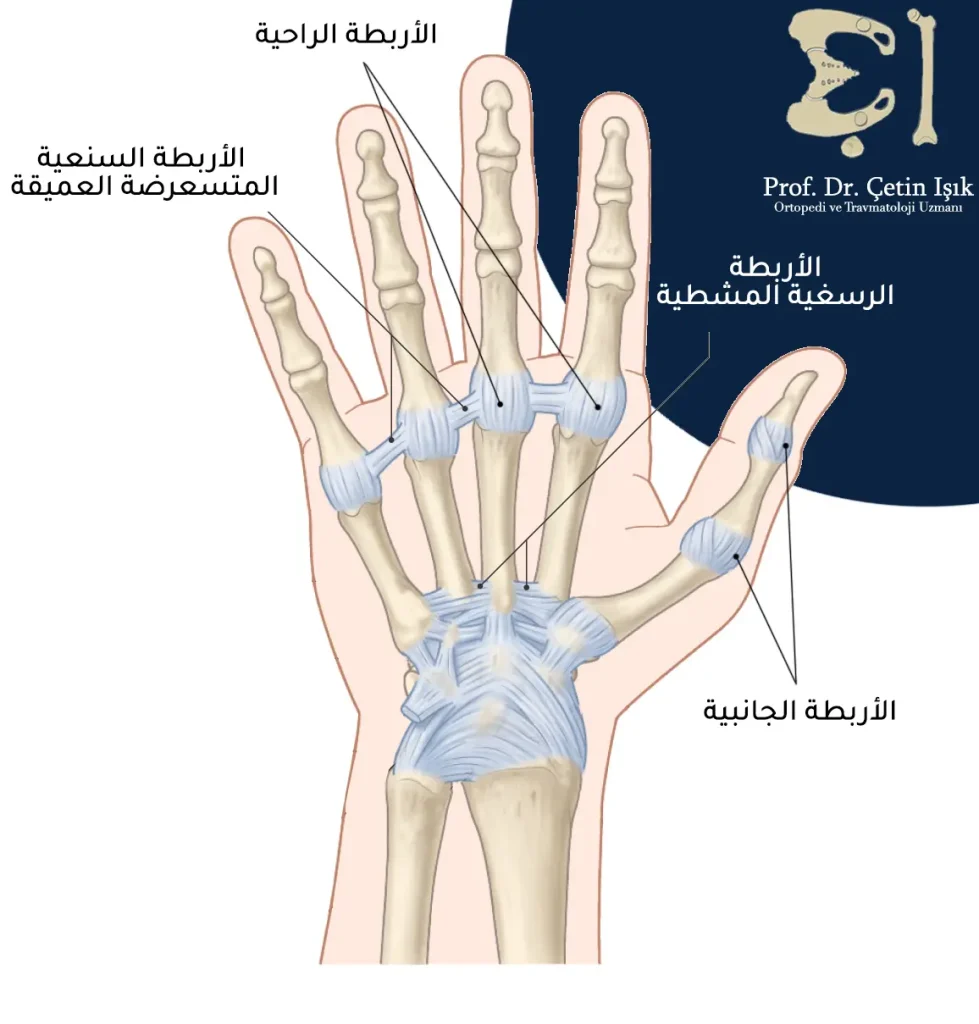
The hand contains a group of ligaments (strong fibrous cords) that prevent excessive movement and maintain joint cohesion, including:
- Collateral ligaments: They are located on the sides of the finger joints (phalanges) and provide stability to the joints and prevent excessive lateral movement
- Palmar plate ligaments: These ligaments are located in the palm of the hand, where they connect the first two bones in the fingers (phalanges) and provide stability to these joints and prevent the fingers from bending too far back.
- Palmar fascia: It is a thick, ligament-like skeletal structure that has a triangular shape (its apex is at the wrist and its base is at the base of the fingers). This fascia helps maintain the shape of the hand and prevent the skin from slipping when holding something.
- Deep transverse metacarpal ligaments: These are ligaments that connect the metacarpal bones in a transverse manner
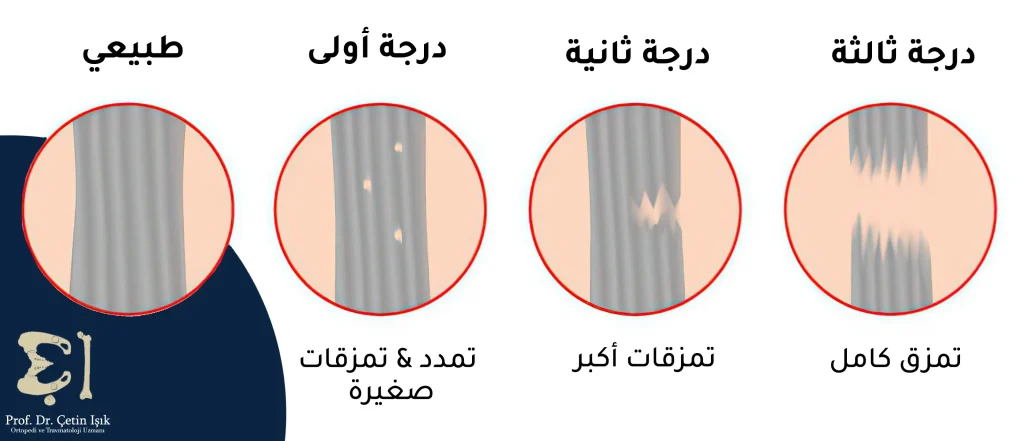
The rupture of hand ligaments is the most common among the ligaments of the rest of the body as a result of excessive use of the hand and its exposure to frequent injuries, especially among athletes. Ligament tears in the hand joint can be classified into 3 degrees depending on the severity of the injury, which are:
- Degree 1: It is a mild tear in which the ligament is stretched without a complete tear in the fibers. It may manifest as pain and swelling and limit the range of motion, but the joint remains stable.
- Grade 2: This is a moderate tear (partial tear), which leads to pain, swelling, and limited movement, and the patient may feel instability in the joint.
- Grade 3: This is a severe tear in which the ligament is completely torn, leading to severe pain, swelling, and instability of the joint, and a clear deformity of the hand may occur.
Causes of torn ligaments in the hand
There are many reasons that may cause tearing of hand ligaments, including:
- Bruises: This is one of the most common causes of hand ligament tear, resulting from falls, accidents, or during sports activities.
- Repetitive stress: Excessive use of the hand and fingers may cause increased pressure on ligaments, leading to their rupture. This is common in activities that require repetitive movements such as writing and playing.
- Hyperextension or hyperflexion: Excessive extension or flexion of the hand or fingers beyond the normal limit can lead to tearing of ligaments in the hand, as occurs when practicing some sporting activities.
- Degenerative diseases: They cause weakness in the hand ligaments and thus they easily tear while performing normal activities. These diseases include: Osteoarthritis (Osteoarthritis) andRheumatoid Arthritis (rheumatism).
Symptoms of torn ligaments in the hand
Symptoms of torn hand ligaments vary depending on the degree of tear, but there are some common symptoms:
- Pain: Torn ligaments in the hand cause severe pain, especially when moving or applying pressure to the affected area
- Swelling and bruising: may appear around the affected area as a result of damage to the blood vessels
- Limits the range of motion: Tearing of the hand ligaments leads to restricted movement of the hand and fingers, thus making it difficult to carry out daily activities
- Hearing or feeling a pop: A popping sound can be heard when ligaments are torn or when the hand or fingers are moved
- Instability and weakness: The patient feels instability and weakness in the hand joint
Diagnosis of torn ligaments in the hand
A torn ligament in the hand is usually diagnosed through a clinical examination and evaluation of the patient. The doctor evaluates the range of motion of the hand, joint stability, and strength of the hand and fingers. He may also perform other maneuvers to precisely determine the location of the injury and assess the severity of the injury.
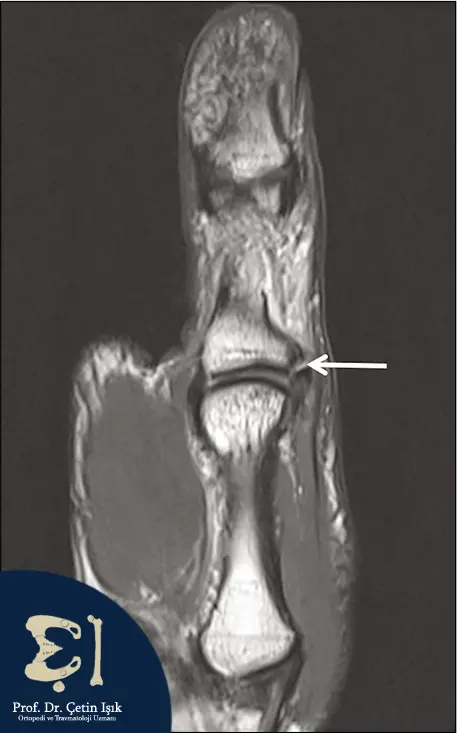
Radiological investigations may be required either to confirm the diagnosis or to rule out other pathologies, such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (echo).
Treatment of torn ligaments in the hand
Treatment for torn ligaments in the hand varies depending on the affected ligament and the severity of the tear, in addition to the general condition of the patient. Treatment options for torn ligaments in the hand include conservative (non-surgical) treatment, physical (physical) therapy, and surgical treatment.
Conservative (non-surgical) treatment
Mild tears can be managed through non-surgical treatment. This treatment includes the RICE method, which is:
- Rest: The hand should be rested and activities that strain the hand should be avoided and thus aggravate the pain
- Ice: Cold compresses are applied to the affected area to relieve pain and swelling
- Compression: An elastic bandage can be used to reduce swelling
- Elevation: Raising the hand above the level of the heart reduces swelling
You can also take pain relievers that do not require a prescription; Such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen; To manage the pain and swelling that occurs, a brace or splint can be worn to stabilize the hand, which allows it to provide support for the hand and restrict its movement, thus accelerating healing.
Physiotherapy
The physical therapist develops an exercise program for the patient to improve hand strength and flexibility and restore normal range of motion. Physical therapy exercises include the following:
- Range of Motion Exercises: These exercises are performed to reduce stiffness and restore full range of motion of the hand
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises target weakness that may result from torn ligaments in the hand, which helps in the healing process
- Stretching exercises: These exercises increase the flexibility of the hand muscles
Physical therapy can also include therapeutic methods to relieve pain if conservative treatment fails, and these methods include ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is used to treat severe toe ligament tears or injuries that do not respond to non-surgical treatment measures. Surgical treatment options include two procedures: ligament repair and ligament reconstruction.
Ligament repair
In this procedure, the ligament is directly repaired with sutures or other techniques to restore function and stability of the joint.
Ligament reconstruction
This operation is performed when direct repair is not possible, where the ligament is reconstructed using grafts or other synthetic materials, thus replacing the damaged ligament.
Complications of torn ligaments in the hand
A tear in the hand ligaments can lead to many complications, and the likelihood of these complications varies depending on the degree and location of the tear. These complications include the following:
- Chronic pain: The pain may turn into chronic pain when the tear is neglected or when the tear is severe, which affects a person’s daily activities.
- Joint instability: Ligament rupture can lead to joint instability because ligaments are what support the joints and ensure their stability.
- development Hand arthritisIn some severe cases, arthritis can develop, leading to pain, stiffness, and joint damage
- Nerve and blood vessel damage: Severe tearing can cause pressure on nerves and vessels, leading to damage
Preventing hand ligament tears
Several preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of hand ligament tears. These measures include:
- Strengthening the hand and wrist muscles: Improving the strength of the hand and wrist muscles helps provide stability to the hand ligaments and reduce the risk of their rupture, so it is necessary to practice strengthening exercises such as grip exercises and finger extensions.
- Taking breaks when practicing activities: Continuous and prolonged activity leads to stress on the hand ligaments, which increases the possibility of tearing them.
- Use of protective equipment: Protective equipment can be used in some sporting or professional activities that increase the risk of tearing hand ligaments. Protective equipment includes gloves and other support devices.
- Practicing physical activities correctly: Activities that put pressure on the hands should be practiced; Such as lifting heavy objects; Correctly to relieve pressure on the ligaments
A tear in the hand ligaments is the stretching and rupture of the fibrous cords that connect the bones together, which leads to pain and instability in the hand joints. A tear can be treated in several ways depending on the severity of the tear, with the need to adhere to appropriate therapeutic methods to avoid the occurrence of tear complications that affect a person’s activities and daily life.
Sources:
Common questions
Ligament rupture can be identified by the appearance of symptoms and signs of rupture, which are pain, swelling, and limit the range of motion and instability of the joint. A cracking sound can also be heard when it ruptures.
Treatment of a tear in the hand varies depending on the affected ligament and the degree of the tear. Treatment includes conservative treatment (RICE: rest, ice, compression, and elevation), drug therapy (painkillers), and physical therapy (exercises to treat torn ligaments in the hand). Surgical treatment can be resorted to in severe cases (repair). Ligament and ligament reconstruction).
The duration of treatment for torn ligaments in the hand varies depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s general health, as treatment may take from several weeks to several months (6 months) to achieve complete recovery.
A plaster or splint may be applied to immobilize the hand and thus allow for proper healing.
Voltaren cream is one of the best creams that can be used to treat torn ligaments in the hand.
The risk of tearing hand ligaments depends on the degree and severity of the tear. When the tear is third degree, it may cause severe pain and complications that may cause joint damage.