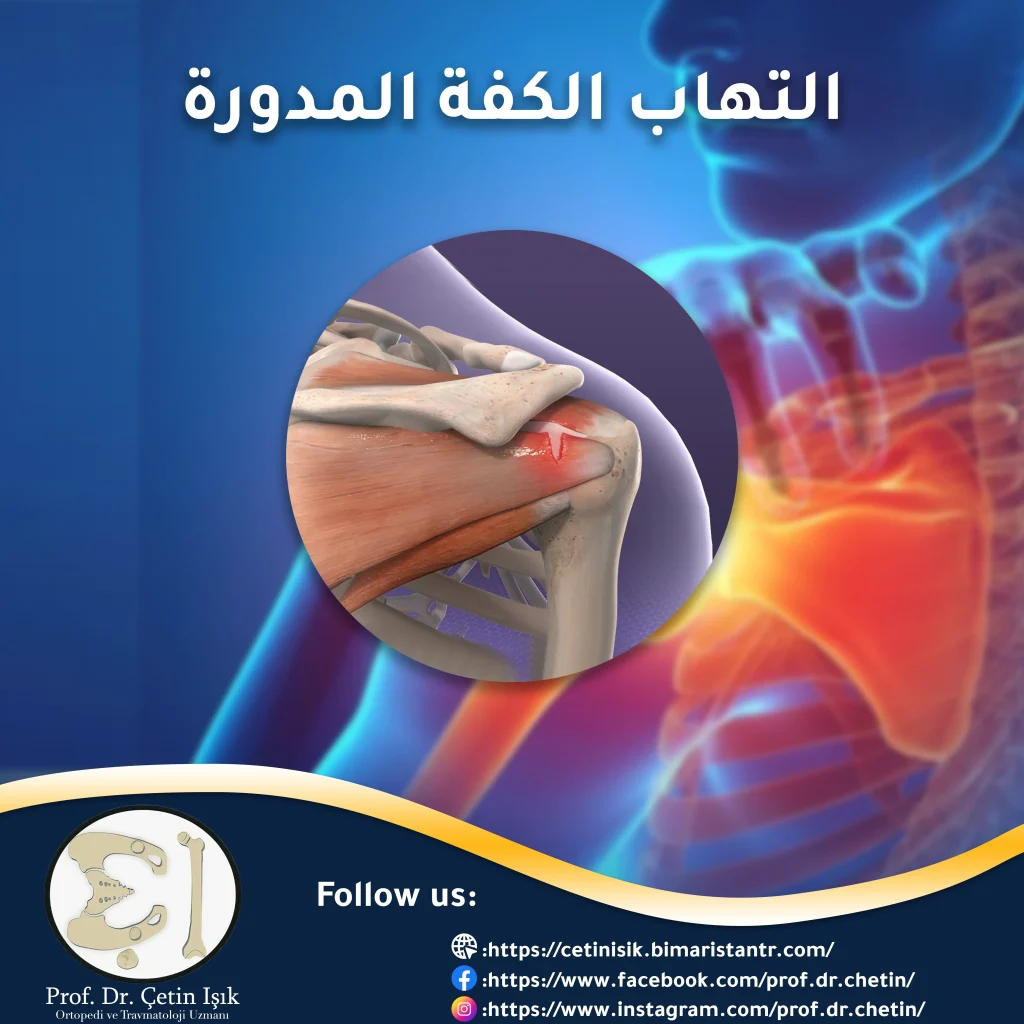
Rotator cuff inflammation is inflammation of a group of tendons inside the shoulder joint, which causes difficulty in moving the arm, and inflammation must be treated early before a tear in the shoulder tendons occurs.
The rotator cuff inflammation Rotator cuff tendinitis It usually affects people who use the shoulder joint for a long time. It affects athletes who practice swimming or shooting. It may also occur due to sleeping on the shoulder all night. It may cause Rotator cuff tendonitis Severe or minor pain depending on the severity of the inflammation, so the treatment varies. The treatment of rotator cuff tendonitis may be very simple and be at home, or it may need surgery when there is a tendon rupture, but fortunately, treatment is often conservative without resorting to surgery.
In this article, we will present what is rotator cuff tendonitis? The most important signs and symptoms seen, what are the rotator cuff treatment exercises, and all methods of treating rotator cuff inflammation.
Information on rotator cuff inflammation
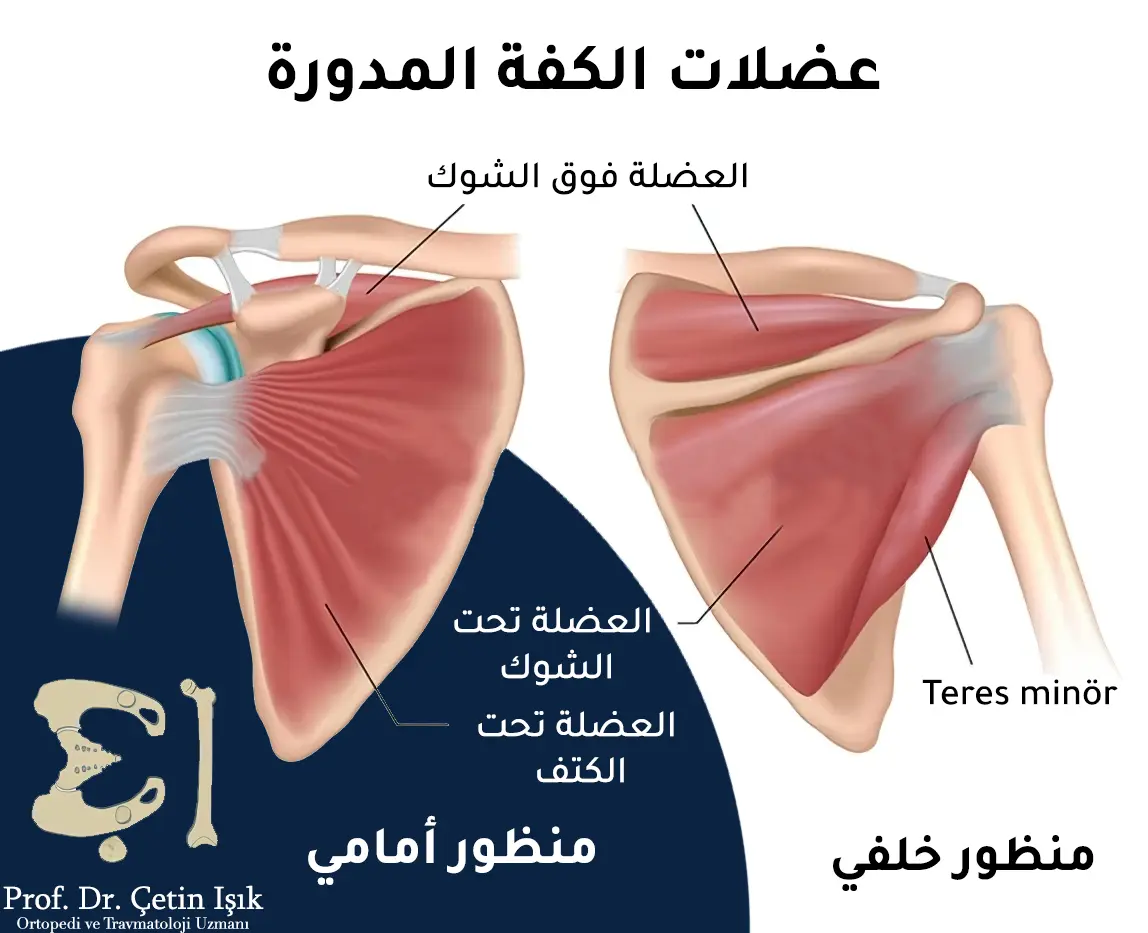
The head of the humerus is located inside the glenoid cavity of the shoulder joint and is fixed by the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles, which consist of four tendons, namely the infraspinous tendon, the supraspinal tendon, the subscapularis tendon and the teres minor tendon. The function of the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles is to maintain the stability of the glenoid joint The humerus and controlling the rotation of the shoulder away from the body.
Rotator cuff inflammation often occurs when the group of tendons in the rotator cuff is used excessively, such as carrying weights, swimming, and golf. Rotator cuff tendinitis is one of the most common causes of pain in the shoulder joint. Treatment is often in order to protect the patient from lacerations, relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore arm movement normally. .
In some cases, rotator cuff tendinitis may resolve automatically without any treatment. Bursitis within the joints in the shoulder differs from rotator cuff inflammation. Bursitis is a symptom of rotator cuff tendinitis.
Causes of rotator cuff inflammation
The cause of rotator cuff inflammation differs from one patient to another, depending on the patient’s age and the type of activity he performs. The most important reasons are:
- Excessive use of the arm, which usually occurs when practicing sports activities that require raising the arm, such as volleyball and other sports
- injury bCalcific tendinitis Which occurs as a result of the accumulation of calcium in the rotator cuff tendons, and it occurs in people between the ages of 30 to 60 years, and it may be very painful.
- Shoulder injury with several strong bruises during a fall during sports or exposure to violence

Symptoms of rotator cuff inflammation
There are many symptoms and signs seen when it occurs Shoulder tendonitis It may increase over time and become more severe, and the most important symptoms are:
- Pain when raising the arm, such as combing hair
- happening Joint stiffness and difficulty moving it
- Severe pain awakens the patient from his sleep
- Swelling in the front of the shoulder and on the upper arm
- Weak movement in the arm
- Hearing a popping sound when moving the arm
Diagnosis of rotator cuff inflammation
The rotator cuff tendonitis is diagnosed by examining the movement of the patient's shoulder joint and the ability to move the full arm and requesting some radiographic investigations in order to examine the muscles and tendons. The most important radiographic investigations are:
- Simple x-rays that help detect the presence of bony bumps
- Ultrasonography, which is a safe and useful diagnostic method for diagnosing rotator cuff inflammation
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the best diagnostic tool, as it clearly shows tendons and muscles and distinguishes between rupture and inflammation
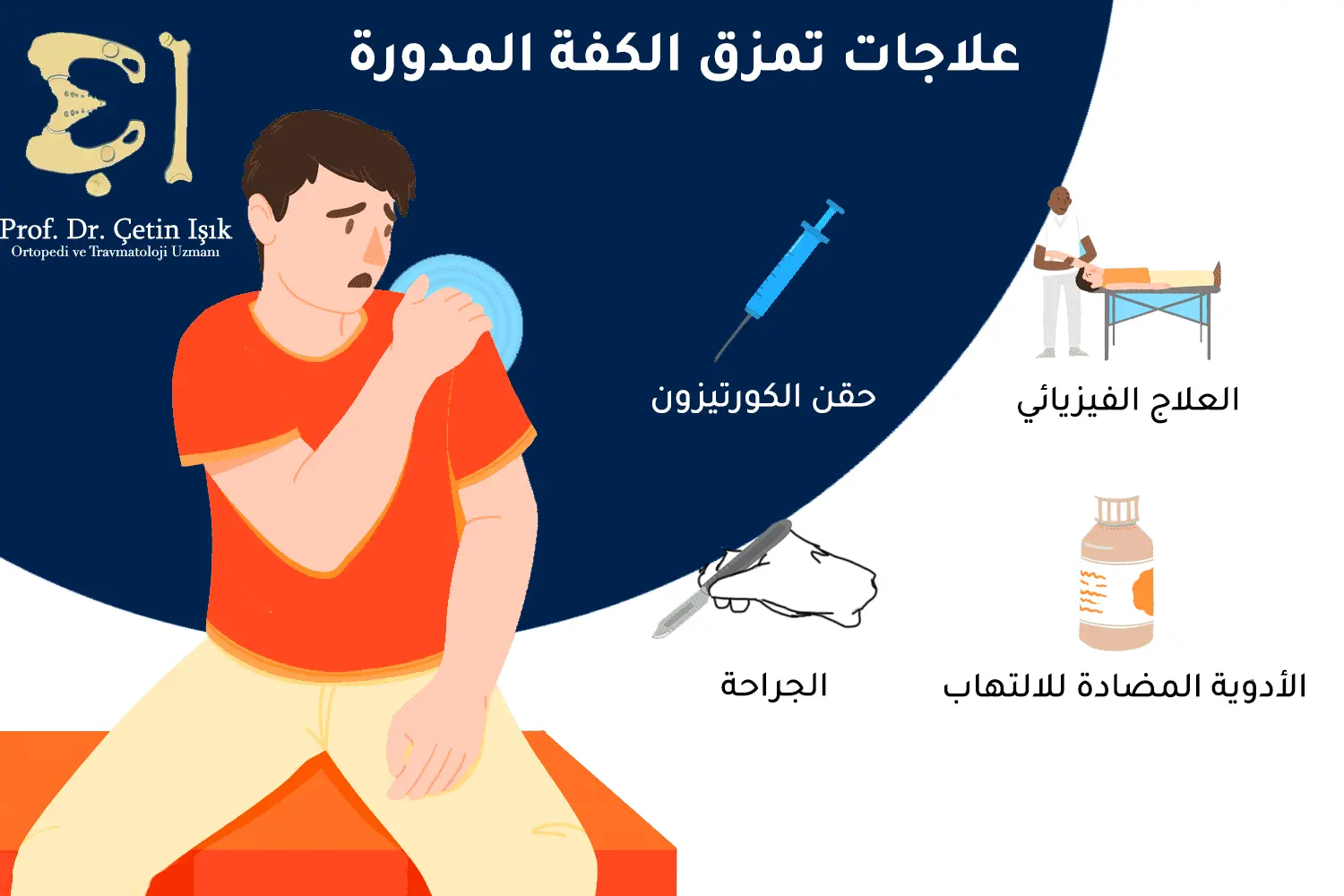
Treatment of rotator cuff inflammation without surgery
Conservative treatment is used to relieve the pain and inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons and protect the tendon group from any rupture due to severe inflammation. Treatment methods are:
- Avoid tiring sports activities of the shoulder joint that may cause stress in the tendons or traumatic injuries to the tendons and joint ligaments of the shoulder and take a rest until the inflammation heals
- Putting an ice bag, which helps relieve pain and swelling in the shoulder
- Take some painkillers for shoulder pain and anti-inflammatory drugs such as NSAIDs
- Cortisone injection into the shoulder joint, which reduces inflammation andShoulder pain It is used in some cases, but not all
- Follow physiotherapy, after the inflammation is completely cured, and this is done by doing some specific exercises after consulting doctors specializing in physical therapy
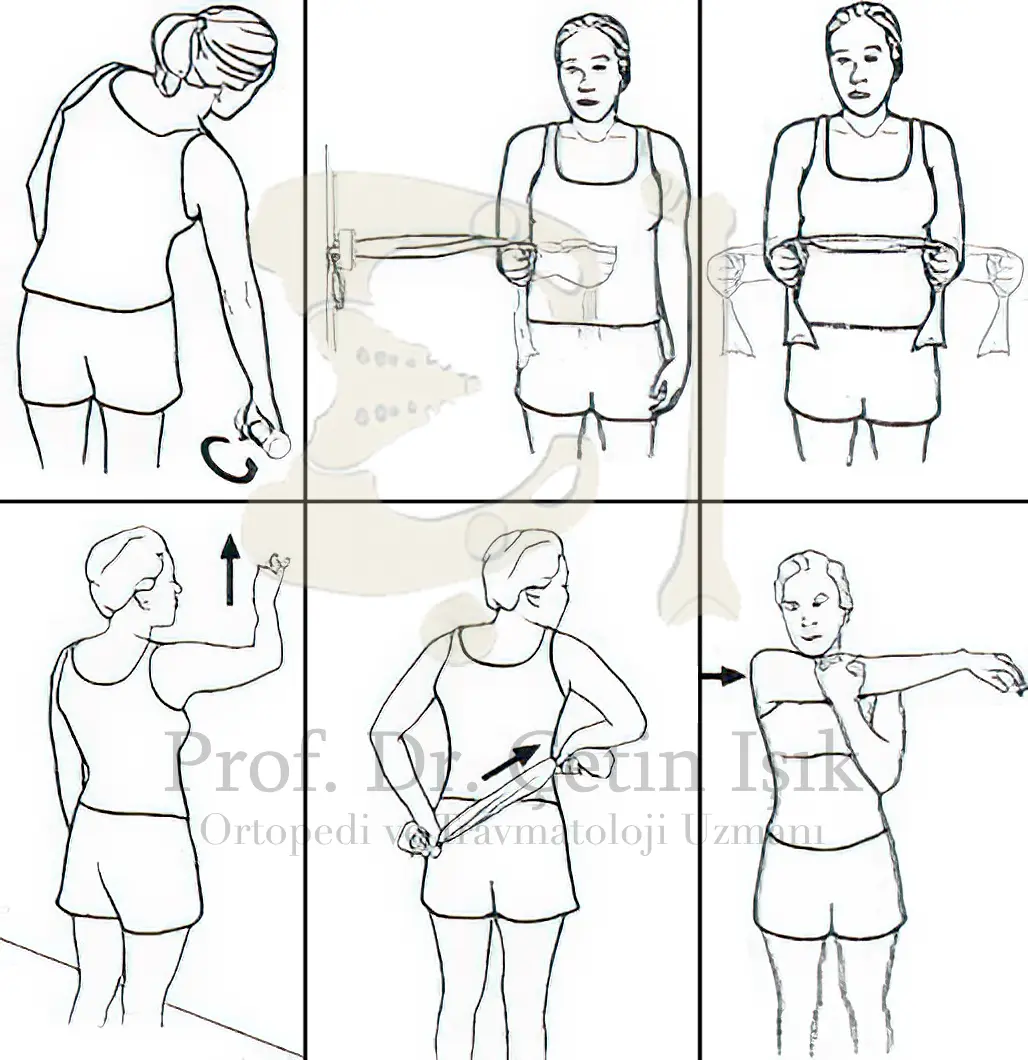
Exercises for rotator cuff inflammation
After the rotator cuff inflammation is completely cured, physical therapy is used for treatment frozen shoulder Which may affect the shoulder during the period of rotator cuff disease. The most important rotator cuff exercises are:
- Weighted pendulum exercise
- Towel stretch
- Cross-body stretch
- Finger walk
- Inward rotation
- Outward rotation
Surgical treatment of rotator cuff inflammation
When conservative treatment of tendonitis fails, signs and symptoms increase in severity, and when a rupture of the rotator cuff tendons occurs, the rotator cuff rupture and tendonitis must be treated surgically in order to repair the torn part of the tendons, remove the damaged parts, and provide more space for the tendon by removing the inflamed bursa as well.
There are two types of surgeries for the treatment of a rotator cuff tendon rupture, as the choice between them is made depending on the severity of the rotator cuff tendon ruptures and the damage to the shoulder joint. The types of surgeries are:
- Shoulder arthroscopy In which three small incisions are made in the shoulder area to insert surgical tools. This process helps to remove any pressure on the inflamed tendon and frees up enough space for it. It is one of the modern procedures that help in healing faster than the open shoulder surgery.
- Rotator cuff surgery or open surgery Shoulder replacement surgery Where this operation is used for severe lacerations and severe injuries to the shoulder joint, and it requires a larger surgical incision than the arthroscopy.
At the end of the article, inflammation of the rotator cuff that affects the group of tendons that fix the head of the humerus in the shoulder joint often occurs due to excessive use of the shoulder joint, which may cause weakness of the arm and the inability to raise it above the head. Between two to four weeks often and rarely resort to surgical treatment.
Sources:
Common questions
The treatment of rotator cuff inflammation varies according to the severity of the inflammation, but it is often treated by avoiding the tiring activities of the rotator cuff muscles, resting, taking some analgesics, or resorting to cortisone injections. Treatment rarely requires surgery except when there is a tendon rupture.
It is located within the shoulder joint, and it is a group of muscles that connect the shoulder bone and the head of the arm and come together to form a group of tendons that surround the head of the arm.
The severed tendons of the shoulder joint heal after the surgery, but the time needed for the tendons to heal varies, as it may take between 4 months to 6 months or a year, depending on the severity of the ruptures in the tendon.
There are several causes that may cause shoulder blade pain, the most important of which are rotator cuff inflammation and traumatic injuriesOsteoporosis and spinal stenosisscoliosis and shoulder fractures.
Massage while recovering from rotator cuff inflammation is beneficial in strengthening the sore tendons, relaxing tense muscles, and speeding up the healing process.