A tear in the thigh muscles is a common injury that occurs when the muscle fibers are stretched beyond their normal limit, which leads to severe pain and bruising in the thigh, which hinders the patient and limits his activities.
Tears of the thigh muscles are common in athletes, especially tearing of the posterior thigh muscle in sports activities that include running and contact with others (soccer players). Let us learn together about the tear of the thigh muscles and ways to treat it.
Glimpse of quadriceps tear
Thigh Muscles tear is an excessive stretching of the muscle fibers, causing them to tear and the appearance of symptoms that include pain and difficulty walking. The tear occurs frequently near the point where the muscle connects with the fibrous connective tissue of the tendon.
The thigh area consists of 3 main muscle groups: the quadriceps (front quadriceps), adductor muscles (medial quadriceps), and hamstring muscles (posterior quadriceps). A quadriceps tear refers to a tear in any of the muscle groups of the thigh.
The term hamstring and quadriceps tendon rupture can be termed as being particularly at risk for muscle strain as they cross the knee and hip joints and are used for high-speed activities such as track sports (running, long jump), football, and basketball. Rectus femoris) is more common than an anterior quadriceps muscle tear.
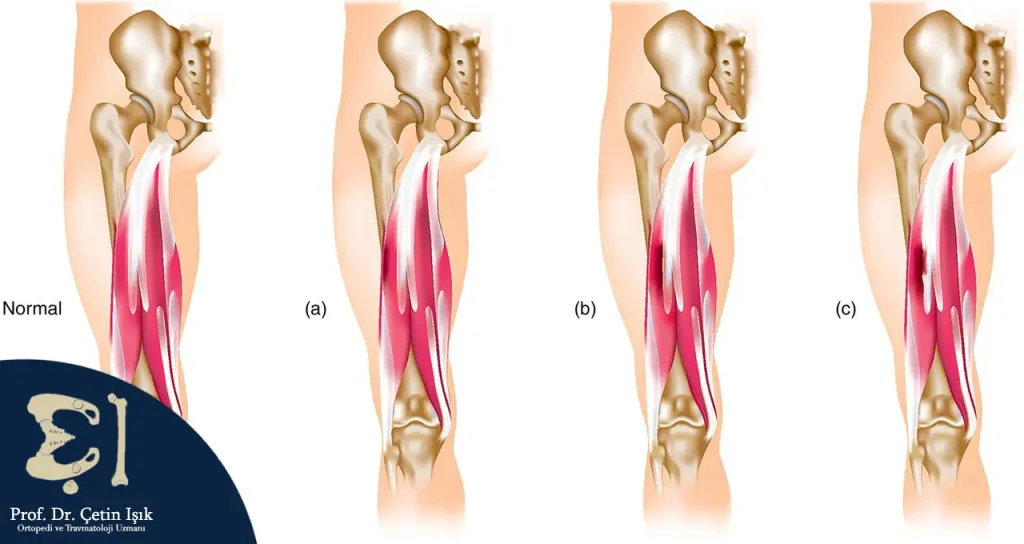
A tear in the quadriceps muscle can be classified into 3 degrees depending on the severity of the tear, which are:
- Grade I: It involves tearing of a few thigh muscle fibers
- Second degree II: is the tear of a larger number of muscle fibers
- Third degree: complete tear of the muscle
Causes of thigh muscle tear
- The causes of muscle ruptures in the thigh are varied, and the affected muscles vary, and ruptures are common in athletes. The causes of muscle ruptures in the thigh include the following:
- Sudden or strong movement (such as a sudden change in direction)
- Repetitive use and strain of muscles
- Falling and exposure to direct trauma may cause a tear in the thigh muscle
- Muscle imbalance where one muscle group is much stronger than its opposite group
- Muscle weakness and inability to bear effort
Symptoms of a torn quadriceps muscle
Symptoms of a muscle tear in the thigh vary depending on the degree of tear, and common symptoms of a tear include:
- Sudden pain in the thigh, the severity of which varies depending on the severity of the tear (most common)
- A popping or crackling sensation as a result of the tear
- Bruising and swelling (damaged blood vessels)
- Tenderness to touch (pain)
- Difficulty walking and moving the leg
- Pain when sitting in torn hamstring muscles
Diagnosis of quadriceps rupture
The methods for diagnosing a tear in the quadriceps are similar to the methods for diagnosing a tear in the quadriceps muscle rupture In general, it includes the patient's clinical history, knowledge of the activities he performs and his exposure to injuries, in addition to knowledge of the symptoms that the patient suffers from. The thigh is then examined for pain and bruising and the limb's range of motion is evaluated.
We may resort to imaging methods to assess the severity of the injury. These methods include ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Treatment of torn quadriceps muscles
Our doctor will discuss all applicable quadriceps strain treatment options to determine the best option for your injury, as most quadriceps strains can be treated with non-surgical (conservative) treatment measures.
Non-surgical (conservative) treatment
Mild quadriceps muscle tears can be treated using the RICE method, which includes:
- Rest: Rest can reduce the pressure applied to the joint and thus relieve hip pain
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected muscle area can help reduce inflammation and pain. Apply ice for 15-20 minutes, once or twice daily
- Compression: To prevent further swelling, the affected area can be gently wrapped with a soft bandage
- Elevation: Groin swelling can be reduced by raising the leg to a level above the heart
In addition to RICE, you can take non-prescription pain relievers to relieve pain and swelling, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, in addition to using hot or cold compresses to relieve pain and inflammation.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is also often recommended to speed up the recovery process, as it improves range of motion and strength. The muscle must become fully strong and pain-free before returning to exercise, which prevents additional injuries.
Treatment exercises for quadriceps tendons include static quadriceps stretches and hip flexor stretches, as well as special exercises after hamstring injuries in athletes (posterior quadriceps tendinosis exercises).
Stretch the fixed quadriceps femoris muscles
- Stand or lie on your front
- Pull the foot of the affected leg toward the buttocks until you feel a gentle stretch in the front of the thigh
- Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat 3 times.
- Do this at least 3 times daily
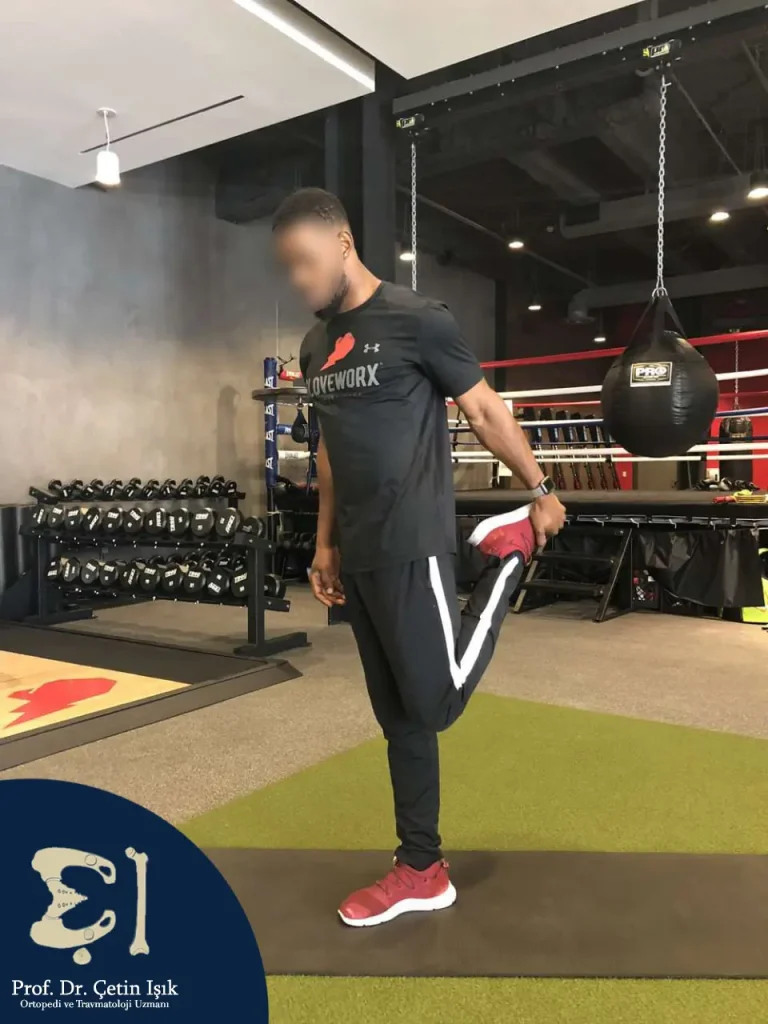

Stretch your hip muscles
- Sit on one knee and the other foot forward with the knee bent
- Push your hips forward and keep your back straight
- You should feel a stretch in the front of your hips and upper thigh
- Hold for 20-30 seconds, repeat the exercise 3 times
- Do this at least 3 times a day

Surgical treatment
Although most cases of muscle tear in the thigh are treated successfully without the need for surgery, surgical intervention may be considered in the event of a serious injury, i.e. a complete tear of the muscle or tendon (third degree).
To repair a complete muscle tear, your orthopedic surgeon will sew the area of the muscle tear together. While repairing a tendon dislocation involves removing any formed scar tissue and reattaching the muscle tendon to the bone using sutures, the surgery takes 1-1.5 hours.
After surgery, we will work closely with our physical therapist to protect your surgical repair and maximize your recovery. Using crutches to avoid stress on affected muscles can also be helpful.
Complete recovery from a quadriceps tear may take from 10 days to three weeks in the case of mild tears, and the recovery period may reach up to six months in severe tears.
Preventing thigh muscle tears
It is not always possible to prevent a torn muscle in the thigh, but following some tips can reduce the possibility of injury. These tips include:
- Do exercises regularly to increase the strength and flexibility of your thigh muscles
- A good warm-up before practicing any sporting activity
- You should drink fluids during training and sports
A tear in the quadriceps muscle is a common injury, especially in athletes, causing pain and difficulty walking. The tear often heals with non-surgical (conservative) treatment.
Sources:
Common questions
A thigh tear can be identified by the symptoms of a tear, which include sudden pain in the thigh that varies in severity depending on the severity of the tear (the most common), bruising, swelling, tenderness to the touch (pain), and difficulty walking and moving the leg.
Most cases of muscle tear in the thigh can be treated with non-surgical treatment measures (rest, ice, compression, and elevation), in addition to physical therapy exercises. Surgical treatment may be used in severe cases.
It may take from 10 days to three weeks for the quadriceps muscle to fully heal in the case of mild tears, and severe cases may take several months to heal.