Endoscopic herniated disc treatment is one of the most innovative surgical techniques of the past decade, which accurately locates the root source of pain causing back and leg problems.
Endoscopic treatment of herniated disc
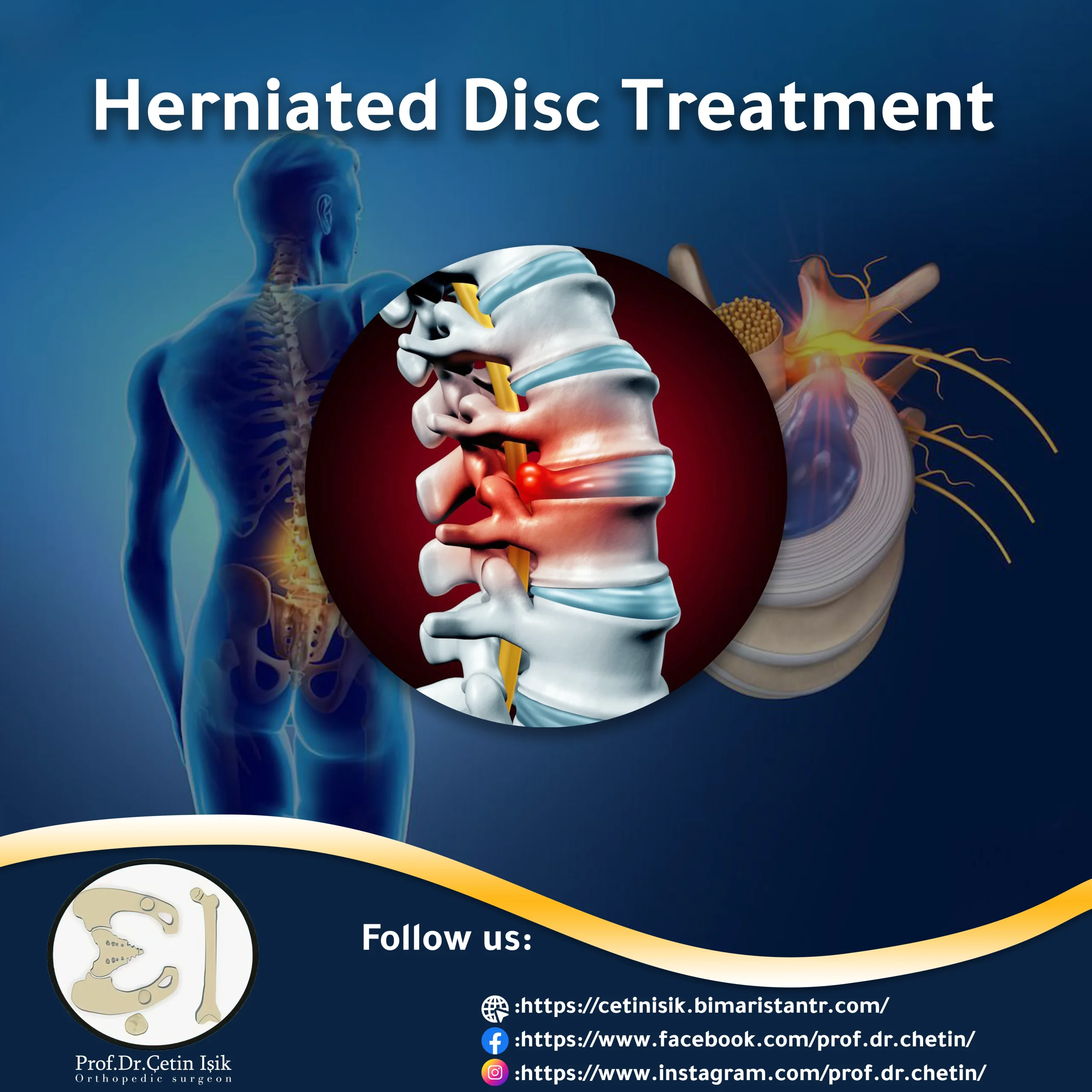
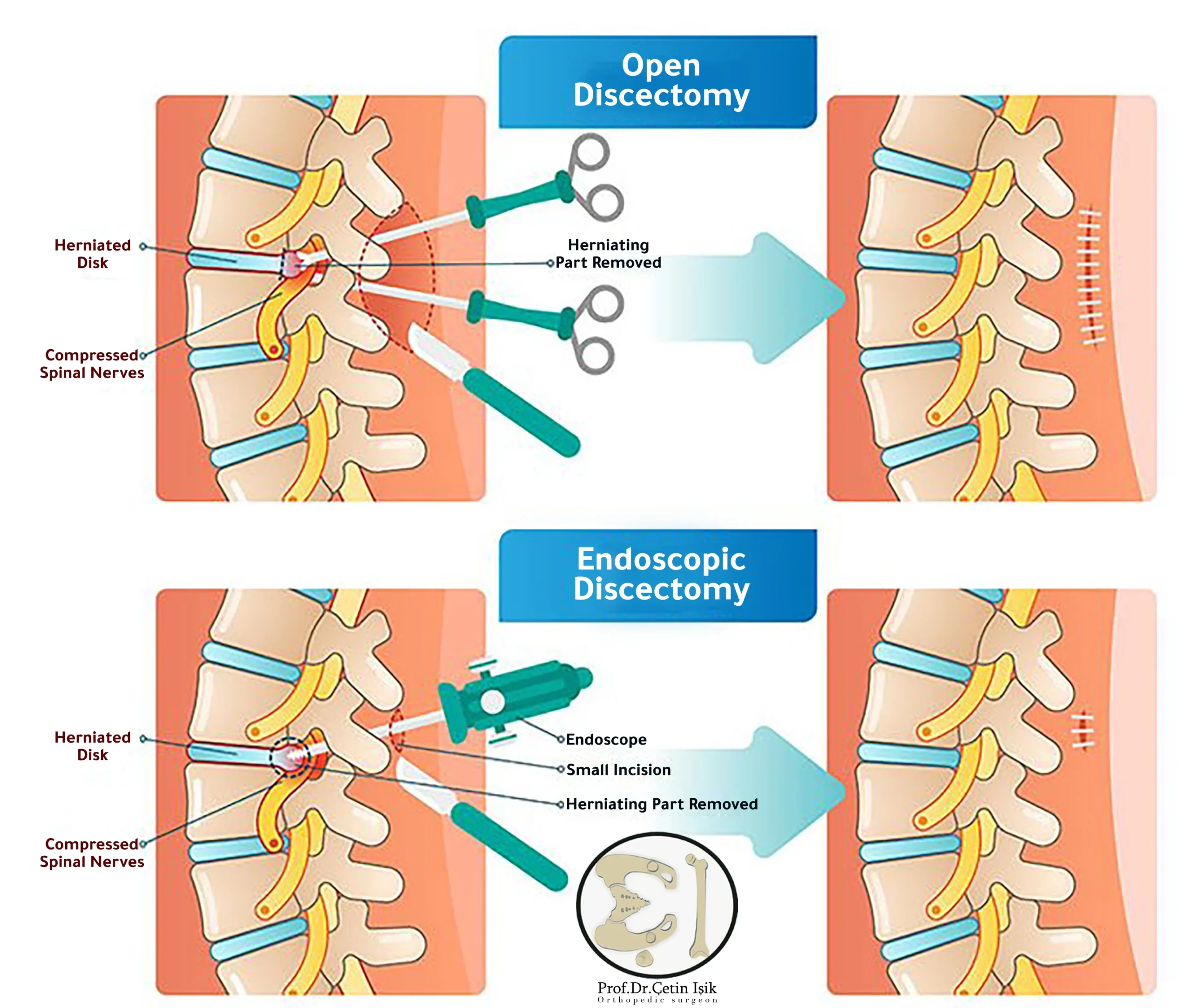
Herniated disc or what is known as the disk A relatively common condition in which the nucleus pulposus is displaced from the space between the vertebrae, causing pressure on the spinal canal. It can occur anywhere along the spine but is most common in the neck and lower back.
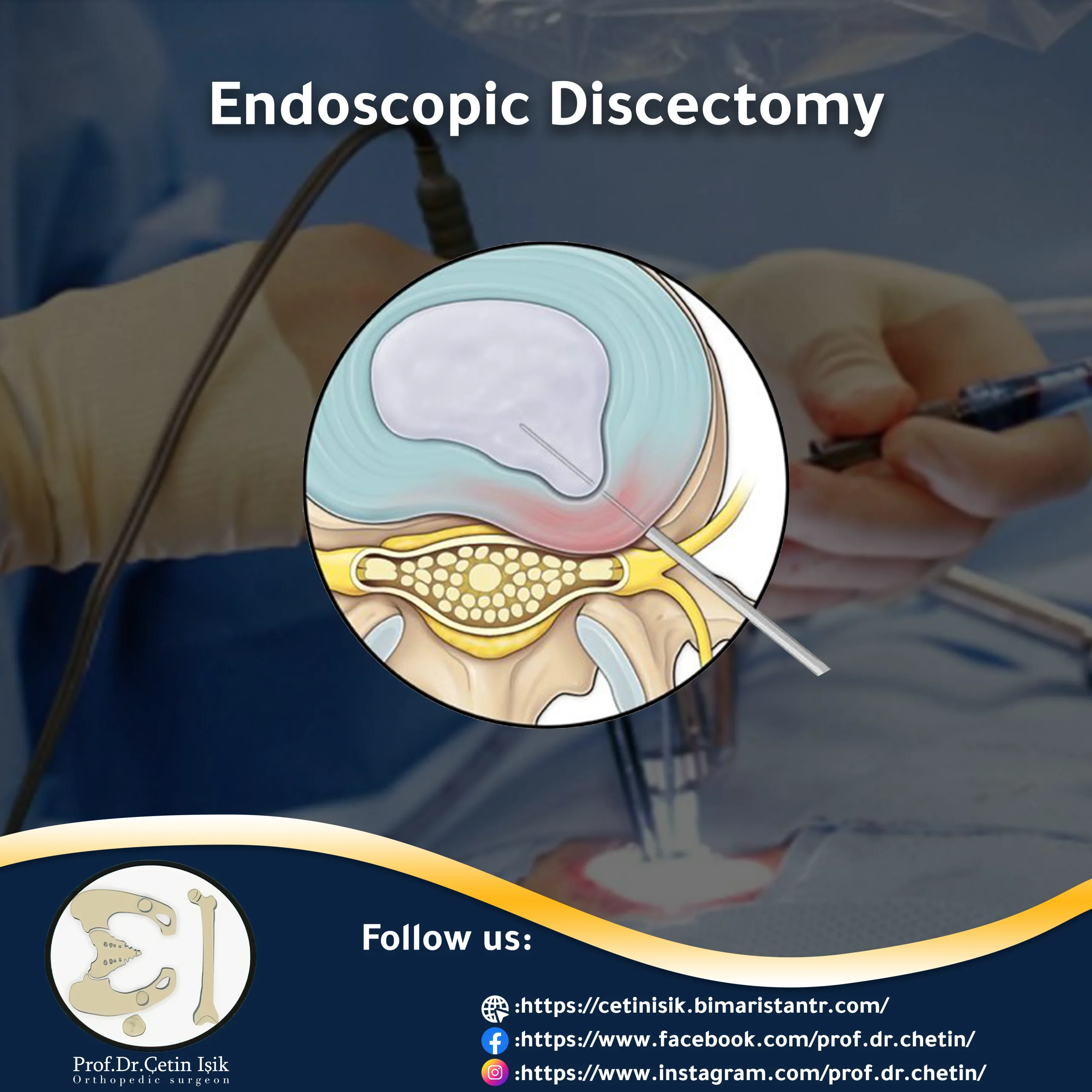
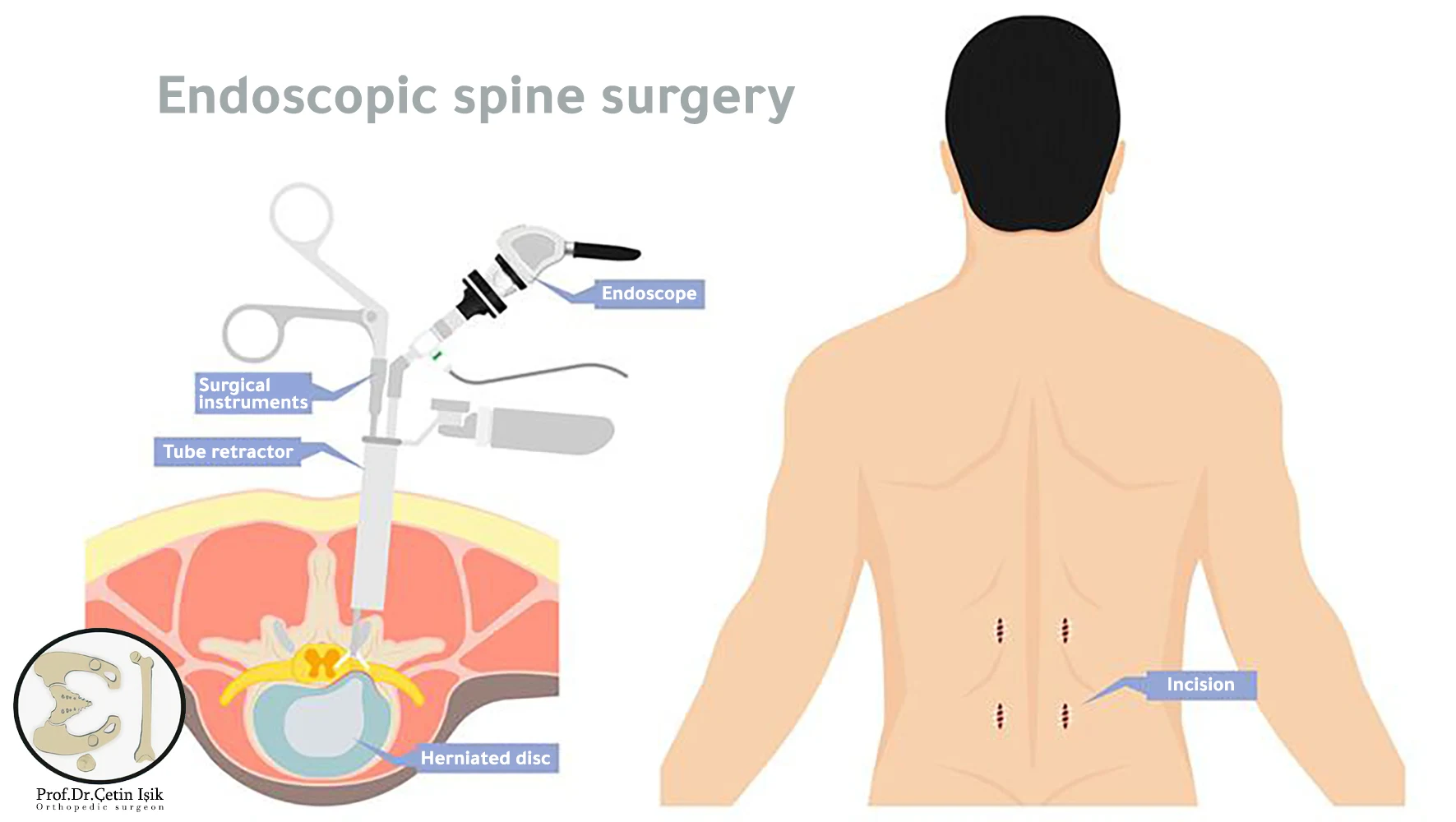
Herniated disc can be treated with Endoscopic discectomy It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows the removal of the protruding part of the nucleus and relieves pressure on the spinal cord and nerves through a delicate incision in the back using an endoscope that allows for a better view without harming the tissues or bones surrounding the disc, thus reducing the pain and symptoms associated with a slip in both spine and legs.
Endoscopic treatment of a herniated disc, in addition to pain relief, avoids serious complications such as fusion of the vertebrae and preserves the anatomy of the patient's spine to reduce the need for future surgery.
Benefits of endoscopic herniated disc treatment
There are many advantages in favor of endoscopic herniated disc treatment over treatment by conventional surgery, as it is a minimally invasive surgery and a successful surgical procedure, as it is a good option for many patients because:
- The procedure relies on the use of a high-resolution camera coupled with an endoscope that provides a better view for the surgeon
- There is no tearing of the muscles or tissues, thus reducing scarring on the skin and maintaining the mobility of the spine
- Local anesthesia reduces the risks associated with general anesthesia
- Pain after endoscopic herniated disc surgery is less than conventional surgery
- Less recovery time after surgery, and sooner return to work
Candidates for endoscopic discectomy
Patients need an endoscopic discectomy in the event of a herniated disc in one of the vertebrae along the spine and conservative measures fail to relieve acute symptoms such as back pain, muscle weakness, tingling and numbness in the back or leg.
Arthroscopic intervention can also be done to treat some cases of slippage that have developed into problems and complications that need immediate treatment, such as pain Sciatica.
The most commonly used non-surgical methods of treatment include: Slipped disc Which must be followed first:
Exercise, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications or epidural steroid injections.
There are also other minimally invasive methods for treating herniated discs that differ from discectomy by laparoscopic method, such as: Treatment of slipped discs by means of laser (ozone) or through microscope technology.
In the event that you have any questions about the appropriate herniated disc treatment methods for your condition, you can: Contact us To answer your questions.
Preparing for an endoscopic discectomy
Before surgery, it is necessary to X-ray the spine to accurately locate the slipped disc and to plan the surgical procedure
Blood tests, urine analysis, and a general examination are conducted to detect any previous diseases. Psychological evaluation may be necessary in certain circumstances before starting treatment for a herniated disc if the patient's health history dictates the need for that.
Two weeks before the endoscopic herniated disc surgery, the patient must stop all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), aspirin, and alcohol. If he suffers from heart disease or thrombophlebitis, he can follow the doctor's instructions.
Stop eating or drinking after midnight or eight hours before the endoscopy to treat a herniated disc.
Surgical procedures for the treatment of herniated disc endoscopically
Endoscopy discectomy surgery for a herniated disc takes about one hour.
In which the patient is given local anesthesia so that he does not feel any pain or discomfort during the operation, and he can undergo general anesthesia after discussing that with the specialist doctor.
The medical staff monitors the patient's vital signs during the procedure, including heart rate and blood pressure.
The surgeon makes a small incision of about 5-6 mm in the back at the level of the slipped disc after locating it under X-ray guidance.
The doctor inserts a wire into the space between the vertebrae and then pushes a slightly larger tube over this wire. This will gently push the muscles and tissues down the vertebrae.
The doctor removes the herniated portion of the disc with precise instruments including light and a camera guided by continuous x-rays.
Finally, any instrument or tube is withdrawn and a small dressing is applied after the incision is closed.
Slipped patients can start physical therapy the day after the endoscopic spine surgery.
Recovery after laparoscopic discectomy
Patients can generally go home on the day of endoscopic herniated disc surgery, provided that the initial pain of the surgery is relieved with pain medication.
The doctor advises to follow some instructions after laparoscopic hernia removal operations to protect the back and ensure full recovery, such as:
- Avoid bending and twisting and avoid high-impact activities and repetitive range for a few weeks
- Wearing a back brace while resting helps maintain a correct spine position
- Follow a proper diet rich in vitamins, especially vitamin A, which is necessary for wound healing
The nerves may take some time to heal as some experience temporary numbness and tingling in the legs.
After six weeks, the patient has x-rays to check spinal alignment, and the incisions for the operation are evaluated.
Most patients can return to work about 2 to 4 weeks after surgery if the work is in an office setting, but for athletes and those with hard physical work, it may take longer.
Risks of endoscopic discectomy
Endoscopic discectomy is a safe and minimally invasive procedure. However, as with any surgery, there are risks including:
- Severe bleeding
- Reaction to the anesthetic
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Spinal fluid leak
After surgery, there is also a risk of recurrence of the herniated disc if all the disc tissue is not appropriately removed during the operation, in which case the pressure on the nerve continues, and symptoms of the herniated disc remain present.
Sources: