Microdiscectomy surgery is a type of minimally invasive discectomy performed for patients with a herniated disc in the spine and is the best option for relieving disc symptoms.
Microdiscectomy is one of the very common surgical procedures, and it is characterized by relatively high success rates, as it constitutes the gold standard for removing the herniated part of the disc that is pressing on the nerves, especially in the lumbar column. Follow us in this article to learn about the technique of microdisc surgery, what are the reasons for performing it, and how to recover.
What is microdiscectomy surgery?
Microdiscectomy surgery or what is known as Microdiscectomy It is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving the pain and symptoms caused by a herniated disc by compressing the spinal cord's nerves by removing tiny portions of the disc, bones, and ligaments.
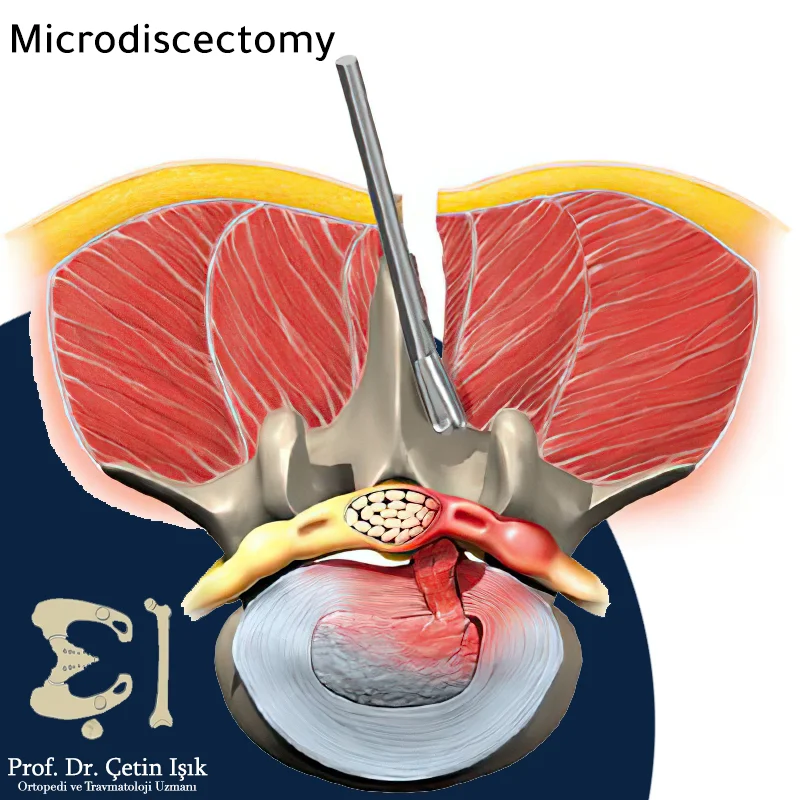
The operation is considered minimally invasive as it is performed through a relatively small incision and using a microscope or surgical glasses called magnifying lenses with precise surgical tools to work within the limited space available to the surgeon. As a result, the damage to the tissues surrounding the affected disc is minimal.
Microdiscectomy techniques
The surgeon chooses the technique used to remove the gelatinous part of the disc, which is pressing on the nerves, according to the patient’s condition:
- Microdiscectomy in the midline: It is similar to the traditional surgery but with a smaller surgical incision, in which the surgeon makes a precise vertical incision in the back of the patient, lifts the muscles surrounding the vertebrae, and then uses tools to separate the layers of tissue during the operation.
- Microtubular discectomy: in which a series of small tubes or dilators are inserted through a tiny incision to create a passage through the muscle, causing less tearing of the tissue.
- Laparoscopic microdiscectomy: In which a smaller incision is made using a camera and precise tools, this method also ensures less damage to the tissue surrounding the slip.
Candidates for microdiscectomy surgery
Herniated disks are rare in children and young adults who are more likely to recover without surgery.
Microdiscectomy surgery may be appropriate for adults between the ages of 80 and 70, with caution that there is an increased chance of medical or surgical complications in this age group.
The causes of intervention for disc microsurgery can be limited to the following cases:
- Conservative management such as physiotherapy, intravenous administration, or tablet injections fail to relieve pain and symptoms for 6 to 12 weeks
- Diagnostic tests that confirm the presence of a herniated disc (magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, myelography)
- severe pain or weakness and numbness (neurological symptoms) in the legs or feet
- leg pain (Sciatica) is more severe than back pain
- Leg weakness, loss of sensation in the groin, or loss of bladder or bowel control (cauda equina syndrome), in which the nerves at the bottom of the spine (lumbar spine) are affected by pressure from a slipped disc
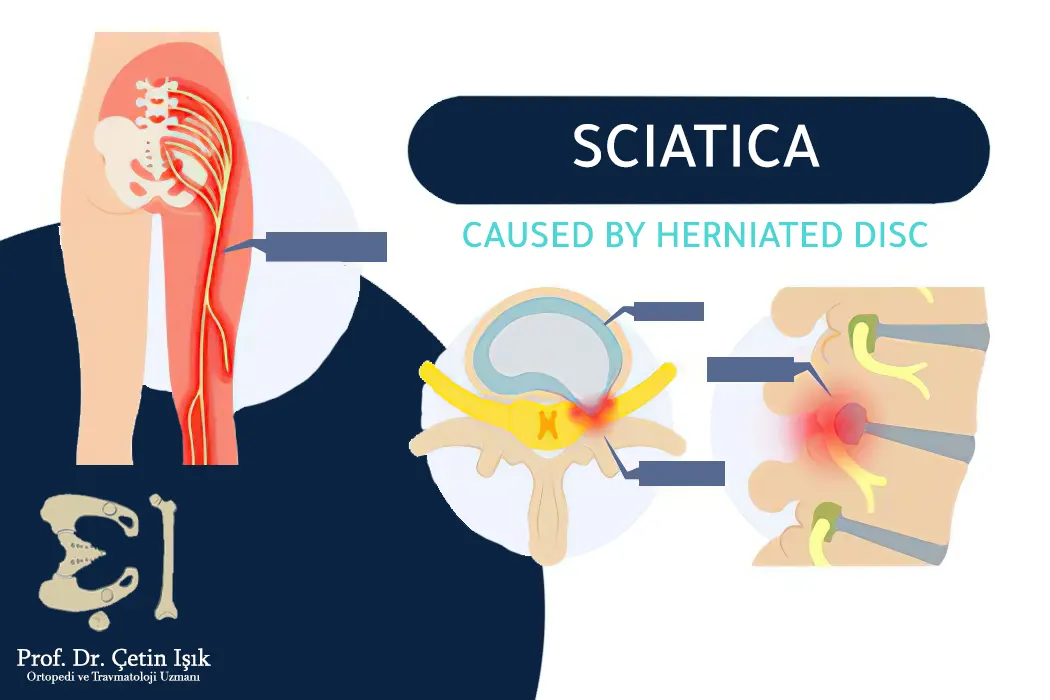
The most recent minimally invasive method for the treatment of herniated disc
In addition to microsurgery, which aims toTreatment of herniated nucleus pulposus For intervertebral discs, other forms of minimally invasive surgery are available, including:
- Endoscopic discectomy surgery
- Discectomy surgery by laser (ozone)
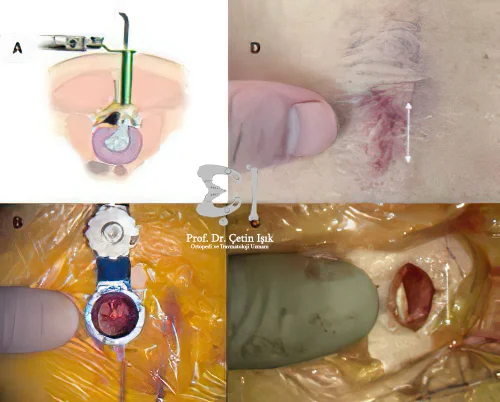
Microdiscectomy procedure
The goal of microdiscectomy surgery is to remove the slipped portion of the disc nucleus that is pressing on the nerves of the spinal canal.
The surgery is done under general anesthesia, where the patient is unconscious throughout the surgery so that he does not feel any pain during it.
The back is cleaned and prepared for surgery, as the patient lies face down.
A 10-cm incision is made in the patient's skin just above the affected disc.
The surgeon uses a lighted microscope to help him see the affected area.
The doctor opens a small window and removes part of the bone that protects the nerve root.
The nerves are gently moved to the side and protected with microsurgical instruments.
A scissor-like instrument is used with which the surgeon removes the damaged herniated tissue and relieves the pressure on the nerve.
Once the procedure is complete, the incision is closed with absorbable sutures, and a bandage is placed over the skin.
It should be noted that some patients with a herniated disc may have other problems in the spine that cause pain associated with nerve compression. In such cases, the surgeon performs another additional procedure, such as laminectomy in one or two vertebrae (laminectomy).
Microdiscectomy surgery usually takes between 30 to 60 minutes to complete, but since most patients are under general anesthesia they must spend enough time in the recovery room to monitor their vital signs and check up on their vital signs, from which time extends to about two hours.
after surgery
In almost all cases, people who have surgery go home the same day or the next morning.
Upon discharge from the hospital, the patient will be given a small amount of pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and a muscle relaxant, along with instructions regarding postoperative care.
Patients return to a relatively normal level of activities quickly as patients are encouraged to walk within a few hours after surgery.
The focus is on alerting the patient to follow up on any symptom that requires immediate medical intervention, such as disturbances in bowel and bladder function or severe and unexpected pain in the spine or leg.
Risks of microdiscectomy surgery
Complications are rare in microdiscectomy , but like any surgery, it has risks such as:
- Dural rupture, where cerebrospinal fluid leakage occurs in 1-7% of surgeries
- Nerve root damage
- Herniated disc regeneration
- Bowel or bladder incontinence
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Possible buildup of fluid in the lungs that may lead to pneumonia
The treatment of a herniated disc has witnessed a great development, especially with microdiscectomy surgery using minimal surgical interventions, which allows for faster recovery with a proven track record in relieving leg pain, especially in the event of failure to treat the disc with conservative methods.
Sources:
Common questions
The success rates of disc microsurgery are excellent, especially in relieving sciatica pain, at a ratio of 90-96%, careful preoperative examination and assessment as well as the patient's commitment to maintaining a healthy spine after microdiscectomy effectively improves outcomes and satisfaction with surgery.
Microdiscectomy is a specialized surgery that requires a specially trained surgeon with a surgery center featuring the best techniques, although it is useful and may be more expensive than other traditional spine surgeries.