Muscular dystrophy is the loss of muscle mass due to several reasons, such as lack of physical activity and neurological diseases, which leads to a poor quality of life for the patient and increases the possibility of developing diseases.
Muscular dystrophy can be caused by serious diseases such as congestive heart failure and cancer. Let us learn together about muscular dystrophy, its causes and methods of treatment.
What is muscular dystrophy?
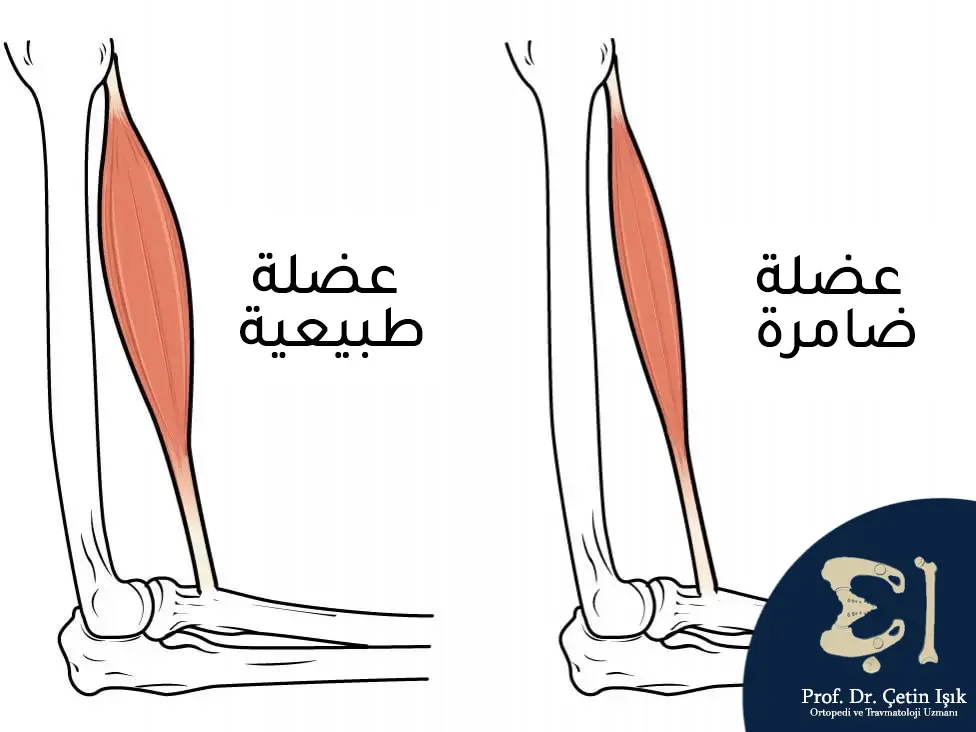
Muscle atrophy is a decrease in muscle strength and mass, which causes the muscles to become small, weak, and unable to withstand stress and become more vulnerable to injuries and diseases.
Atrophy can occur due to prolonged inactivity as the body breaks down muscles to conserve energy (physiological atrophy). Atrophy can also occur in some neurological diseases (neurogenic atrophy), which is the most dangerous type of muscle atrophy, in addition to atrophy caused by other diseases (pathological atrophy). ).
Muscular dystrophy is a muscle disease that manifests itself most clearly in the small muscles of the limbs, especially the first muscles between the bones in the hands, in addition to the gluteal muscles of the hand (thumb). It may include the forearm muscles, which are also symmetrical, in addition to atrophy of the facial muscles.
The duration of atrophy varies depending on the cause of the atrophy and the health condition. Atrophy can begin within two to three weeks in the case of inactivity (lack of use), and atrophy may develop due to a neurological disease earlier depending on the health condition.
Causes of muscular dystrophy?
The cause of muscular atrophy depends on the type of atrophy (physiological, pathological, and neurological), and the group of causes of muscular atrophy includes the following:
- Lack of physical activity for a long period of time and lack of use of muscles (physiological atrophy)
- Old age and malnutrition
- Burns and injuries such as rotator cuff tears
- Long-term treatment with corticosteroids
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), which affects the nerve cells that control voluntary muscle movement
- Dermatomyositis (causes muscle weakness and rash)
- Guillain-Barre: It is an autoimmune disease that leads to nerve inflammation and muscle weakness
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) is also an autoimmune disease in which the body attacks the nerve sheath
- Muscular Dystrophy (Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy): Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is a genetic disease that affects the muscles and causes weakness.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage that results in loss of sensation or movement
- Arthritis: such as Osteoarthritis andRheumatoid Arthritis Which leads to decreased joint mobility
- Polio: This is a viral disease that affects muscle tissue and can lead to paralysis
- Myositis: An inflammatory disease that causes muscle weakness and pain. It appears after a viral infection or as a side effect of an autoimmune condition
- Myotonic dystrophy (myotendinous dystrophy): This is the most common type and is characterized by prolonged muscle contraction and lack of relaxation.
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is called spinal muscular atrophy: SMA is one of the types of muscular atrophy and is a genetic condition that leads to arm and leg atrophy.
- carpal tunnel syndrome
- Inflammation of the sciatic nerve (Sciatica)
- Some heart diseases, such as congestive heart failure
- After surgery
- Tumors
Symptoms of muscular dystrophy
Symptoms of muscular dystrophy vary depending on the causes and severity of the atrophy, and the most obvious symptom is a decrease in muscle mass. Other symptoms experienced by patients with muscular dystrophy may include the following:
- Having one arm or leg noticeably smaller than the other
- Feeling of weakness in the extremities
- General weakness and fatigue
- Difficulty with balance or walking
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Staying inactive for a long time
- Numbness or tingling in the arms and legs
Diagnosis of muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is diagnosed through the patient's clinical history and symptoms, in addition to a physical examination that includes looking at the arms and legs and measuring muscle mass.
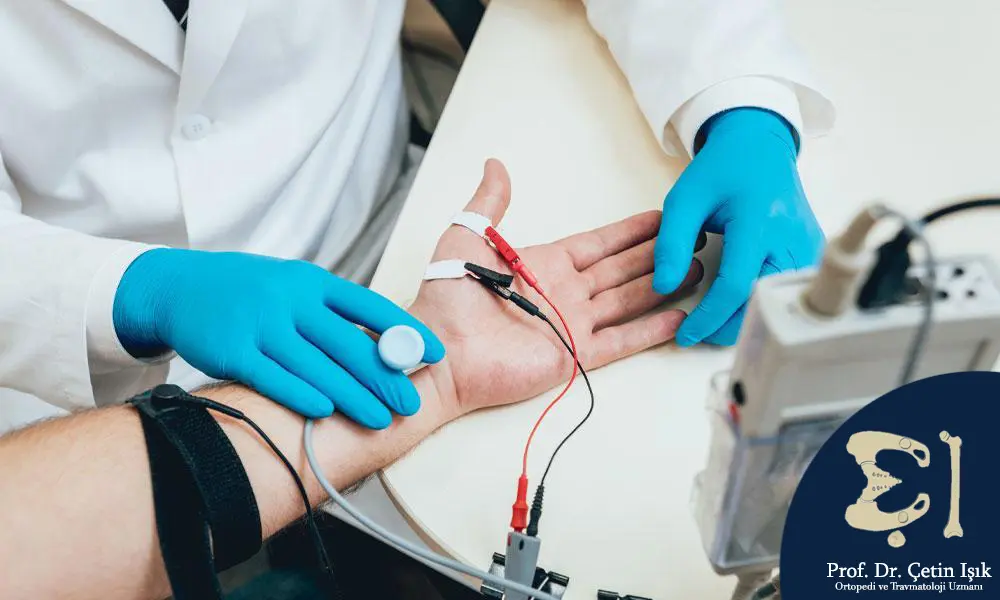
Some tests may be performed, such as a blood test, muscle or nerve biopsy, electromyography (EMG), nerve conduction studies, and radiological tests such as X-ray (X-ray), computed tomography (CT-Scan), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Treatment of muscular dystrophy
Treatment methods for atrophy vary depending on the degree of muscle loss and the underlying cause of the atrophy. Treating the underlying disease causing the muscle atrophy may help slow the progression of muscle loss.
Treatment options for muscular dystrophy include regular exercise, nutrition, physical therapy, and surgical treatment. Muscular dystrophy medications can also be used to treat spinal muscular atrophy, such as nusinersen and risdiplam.
Regular exercise and nutrition
Activity-related (physiological) atrophy can sometimes be managed with exercise and a healthy diet. Our healthcare provider develops a program that includes various and beneficial exercises.
Exercise aims to increase muscle strength and improve blood circulation. It is also useful in reducing spasm, which causes continuous muscle contraction.
Physical therapy
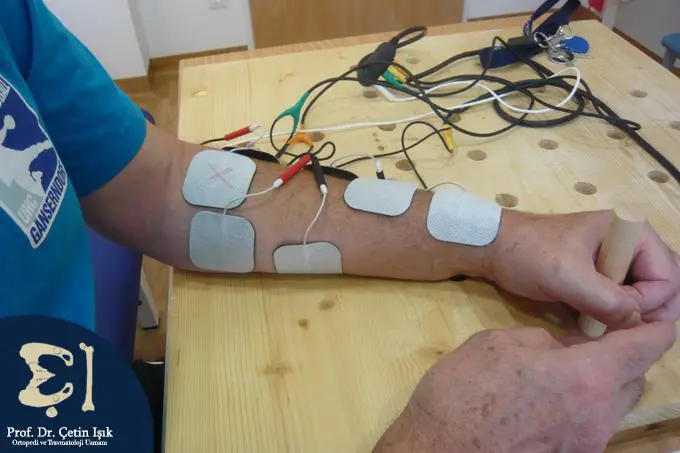
Physical therapy aims to restore the patient's activity through special exercises and the use of modern physical therapy methods that stimulate the body's muscles and restore their strength. Physical therapy options include the following:
- Functional electrical stimulation (FES): It is done by placing electrodes on the skin over the muscle. The electrodes then send mild electrical pulses to the nerves and muscles to stimulate them to contract.
- Ultrasound therapy: This technology delivers beams of ultrasound energy to specific places in the body. These waves stimulate the contraction of atrophic muscle tissue and promote their healing.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment can be used to improve muscle function in people whose disease is associated with some nerve injuries (such as a herniated disc). Surgery can also treat the contraction deformity caused by the tightening of tendons or ligaments and prevent them from moving.
Prevention of muscular dystrophy
Muscular atrophy can be prevented by following the following tips:
- Stay active and exercise regularly
- Good nutrition that helps build muscle
- Treating diseases that cause degeneration (Treatment of herniated disc)
Muscular dystrophy is a loss of muscle mass and strength for various reasons, leading to a feeling of weakness and general fatigue. Muscular dystrophy can be treated through exercise, nutrition, and physical therapy. Surgical treatment may be used to manage the atrophy and improve the patient's life.
Sources:
Common questions
Symptoms of muscular dystrophy include loss of muscle mass, having one arm or leg smaller than the other, general weakness, difficulty with balance, difficulty swallowing, and numbness or tingling in the arms and legs.
The possibility of recovery depends on the type of atrophy. Physiological degeneration can be cured by exercising and returning to activity. Some pathological degeneration conditions can also be treated (such as treating arthritis) and nerve degeneration (treating a herniated disc and carpal tunnel syndrome).
Patients with muscular dystrophy may experience some discomfort and pain.
Muscular atrophy is the loss of muscle mass and strength, while muscle weakness is a lack of muscle strength, and muscle atrophy can cause muscle weakness.