A fracture of the knee cap is an injury to the patella bone in front of the knee joint, and it is one of the fractures that must be dealt with quickly and carefully because of its effects on the human lifestyle.
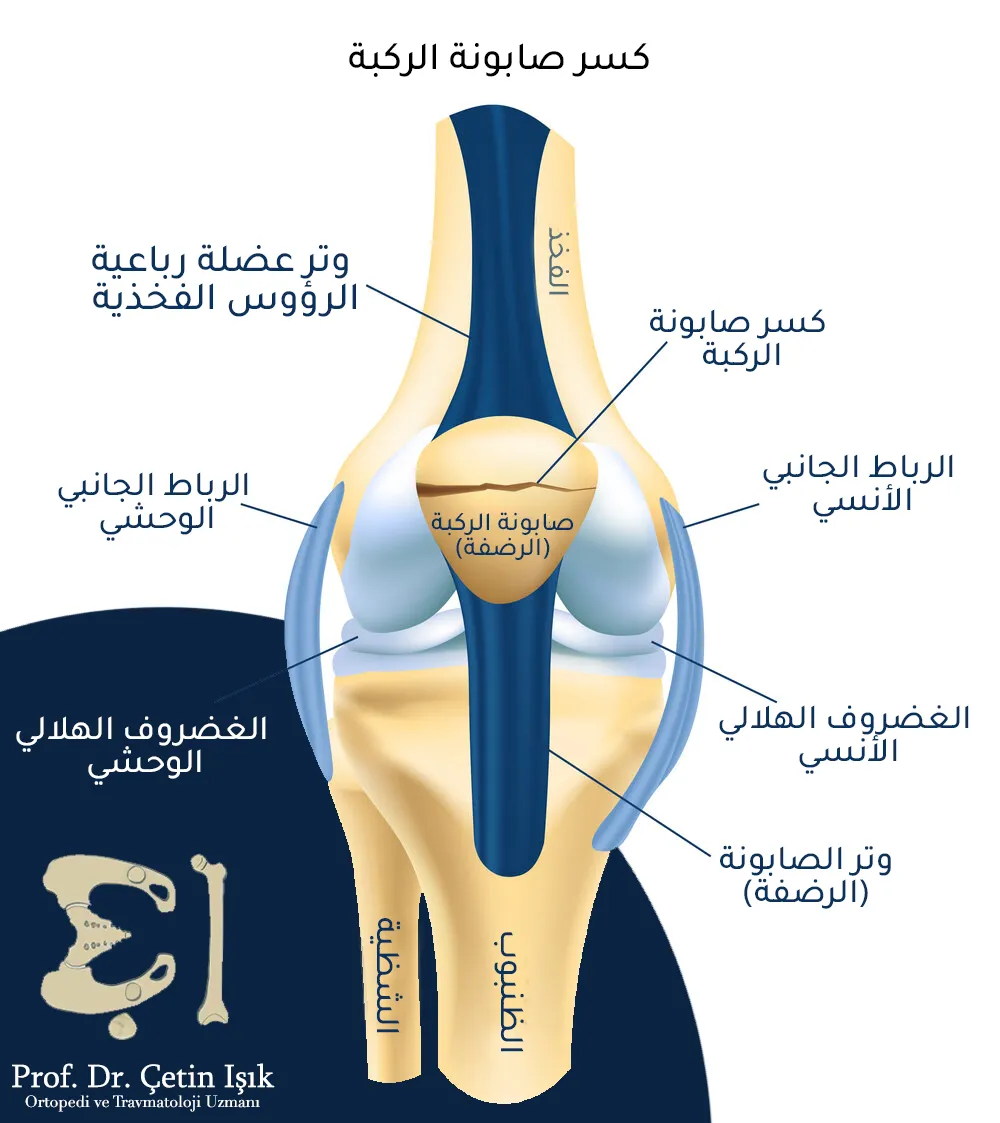
The knee joint is one of the largest joints of the body, connecting the bones of: the femur from above with the leg consisting of the tibia and fibula from below, and the patella (sapon) located in the front part. The surfaces of the bones in the knee joint area are covered with cartilage that provides ease Knee movement, in addition to the presence of crescent cartilage that helps absorb shocks.
What is a kneecap fracture?
A fracture is a complete or partial separation of the bone tissue or a break in the continuity of the bone for several reasons, the most common of which is the traumatic cause. Flat knee cap (knee cap) located in the front of the joint, which provides protection for the joint in the event of direct blows to it.
Types of kneecap fractures
Patella fractures occur in a number of ways, and depending on the severity of the damage, it can range from a simple hair or crack to a fracture that tears and fragments the bone. Types of soap fractures include:
- Stable Fracture: The parts of the broken bone remain in their normal position, just a hair in the knee is noted.
- Displaced Fracture: The parts of the broken bone are displaced and replaced in their original location (deformation of the broken bone), so they do not remain connected to each other as they were.
- Transverse fracture: the patella splits in two (transverse crack in the patella).
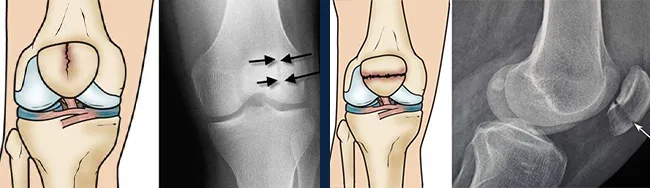
The two pictures on the right side show the fracture of the transverse kneecap - the two pictures on the left side show the fracture of the oblique (stable) kneecap. - Open fracture: exposure of bone tissue to the outside, with skin damage and damage to ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
- Comminuted fracture: in which the soap has broken down into many small pieces of bone.
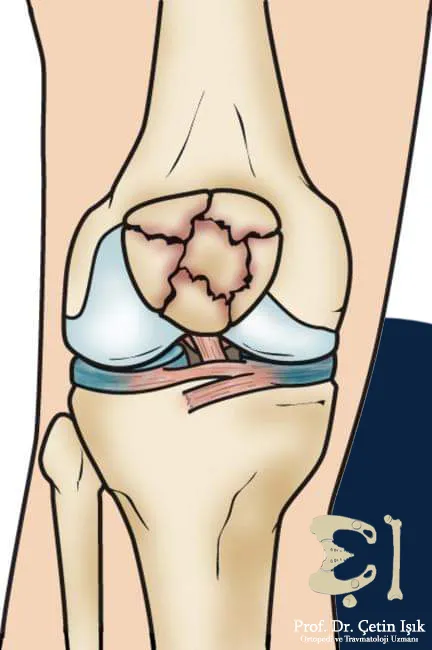
Breaking the crumbled kneecap
Reasons for breaking the kneecap
Knee fracture usually occurs directly as a result of strong bruises on it or due to a fall from a great height (such as falling from a ladder) or a traffic accident. Strong front thigh muscles).
Risk factors for a kneecap fracture
It was found that most people with a kneecap fracture have one or more of the following factors:
- advanced age; Knee and joint injuries and cartilage erosion occur frequently in the elderly and the elderly
- Patients Osteoporosis; Especially in women after menopause
- Previous knee injuries
- Malnutrition as a result of dependence on a diet low in calcium andVitamin D
- Patients with malabsorption
- Smoking and alcohol
- Excess weight and lack of exercise can lead to weak bones and muscles
- Doing vigorous sports activities, in addition to excessive stress on the calf and thigh muscles (marathon runners)
The above risk factors do not necessarily lead to an inevitable injury, but rather they may increase the possibility of injury and weaken the joint's resistance to the blows and injuries it is exposed to.
Symptoms of a kneecap fracture
Symptoms may vary from person to person (age and gender) and depending on the severity of the injury, but they often include:
- severe knee pain
- Bruises in the affected area
- inability to walk and move; So that it becomes difficult to perform important daily tasks
- Difficulty moving the knee jointKnee stiffness
- Fixing the knee in a flexed position (bending) and the patient's inability to extend it (straightening the leg) in the event of an injury to the extensor tendons
- Hematoma in the knee joint
- Hearing a crackling sound while moving the joint
- In some cases of fractures, the child may be able to walk after exposure to trauma, so it is difficult for parents to know that their child has a fracture
In the event that these symptoms appear after exposure to an accident or a blow to the knee, it is preferable to go to the nearest doctor or health care center to receive treatments and use the appropriate measure.
Complications of a kneecap fracture
Complications include the emergence of new pathological changes in all parts of the body away from the kneecap. We mention some of the complications of breaking the kneecap:
- osteomyelitis,; In an open fracture, the bone is exposed to germs that lead to infection
- Damage to blood vessels and nerves can occur from shards of crumbled soap
- Muscle deficit near the broken scaphoid bone or near the thigh (rare cases)
Diagnosis of a kneecap fracture
The fracture is always diagnosed by the doctor. First, the medical history is taken after traffic accidents or falls. Orthopedic surgeons perform a clinical medical examination of all the bones of the body and ask the injured person about the details of the accident and the presence of pain in the rest of his body to ensure the integrity of the rest of his bones. The presence of fractures or dislocations, and the examiner may be able to palpate the crumbled bone pieces from the knee cap through the skin.
After that, x-rays are required to confirm the diagnosis, according to each case:
- X-Ray imaging: X-rays show the extent of bone density and the extent of degenerative changes in the knee. This image can also show the femur (above the knee) in addition to the fibula, tibia (below the knee) and the kneecap bone, and the type of crack that occurs is determined. An image can be taken in the anterior or lateral (lateral) position. Sometimes doctors order an image of the other knee to compare the two knees.
- CT axial tomography: This imaging gives internal images of the knee that are more accurate and detailed than X-ray images, which gives doctors what they need to make an accurate and final diagnosis, and to determine the type of fracture in the kneecap.
- MRI: the most accurate, and the most expensive, helps detect injury to cartilage, ligaments, and ligamentsMeniscus rupture which does not appear on x-rays.
Knee fracture treatment
Treatment of a knee fracture depends on the type of fracture, as well as on age and general health status, and includes:
Conservative treatment (without resorting to surgery)
Doctors recommend placing a splint in the longitudinal and stable cracks of the kneecap (and in some cases of alternating fractures) to stabilize the movement of the knee joint, which leads to accelerating the fracture healing process. The knee splint also works to tighten and protect the knee and avoid pain as a result of movement.
Surgical treatment
A kneecap fracture may require kneecap surgery in the following cases:
- A transverse fissure (the spur breaks in two) requires surgery using a set of wires and screws to reattach and connect the bones.
- If a small part of the soap is cracked (wounded), Where the aforementioned part of the kneecap is removed.
- comminuted fracture (kneecap fracture in several places); The soap is completely eradicated and removed.
- altered fractions; Surgery (screw fixation) is performed.
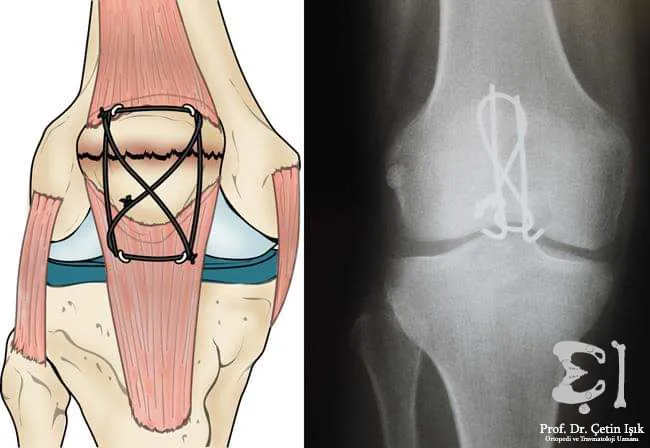
Physical rehabilitation and recovery period
Stiffness can occur in the muscles of the legs as a result of orthopedic doctors preventing the patient from walking for up to days or months, so it is very important to follow up with physical rehabilitation doctors in order to do certain exercises in order to strengthen the muscles of the legs and restore normal movement.
Reducing pain and speeding up the healing of a knee injury can be done by:
- Using crutches or a wheelchair to ensure easy movement from one place to another.
- Rest plays an important role in accelerating the healing process of the kneecap fracture.
- Use of painkilling medication (eg paracetamol) in order to control and relieve acute pain.
In conclusion, fractures of the kneecap 1% are among the fractures of the body, and the most common causes of them are accidents, so they are more common in men compared to women. They are diagnosed in the hospital by doctors, and after conducting imaging and knowing the type of fracture, a treatment plan is drawn up determined by doctors, then the physical rehabilitation doctors treat the patient in a period recovery.
Sources:
Common questions
In simple household accidents, swelling and redness may occur in the affected area or part. Cold water compresses are placed with the importance of immobilizing the knee and not walking. After a short period, if the injured person can stand and then walk without difficulty or pain, there is no fracture. Otherwise, he must go to the nearest hospital to receive Appropriate treatment.
Knee fracture is a serious injury that requires emergency medical attention. It is advised to seek help and avoid moving the knee joint or standing on it because of not putting heavy weight on it.
The pattern of the fracture determines the necessary surgical treatment. In comminuted fractures, the surgical treatment is to remove the entire patella (patella), this process takes one to two hours.
The period it takes for the fracture to heal depends on the age and health condition of the injured person, as well as on the type and severity of the knee fracture. The average period, if the patient adheres to the doctors’ recommendations, ranges from 3 to 6 months, and it can be longer in severe injuries.