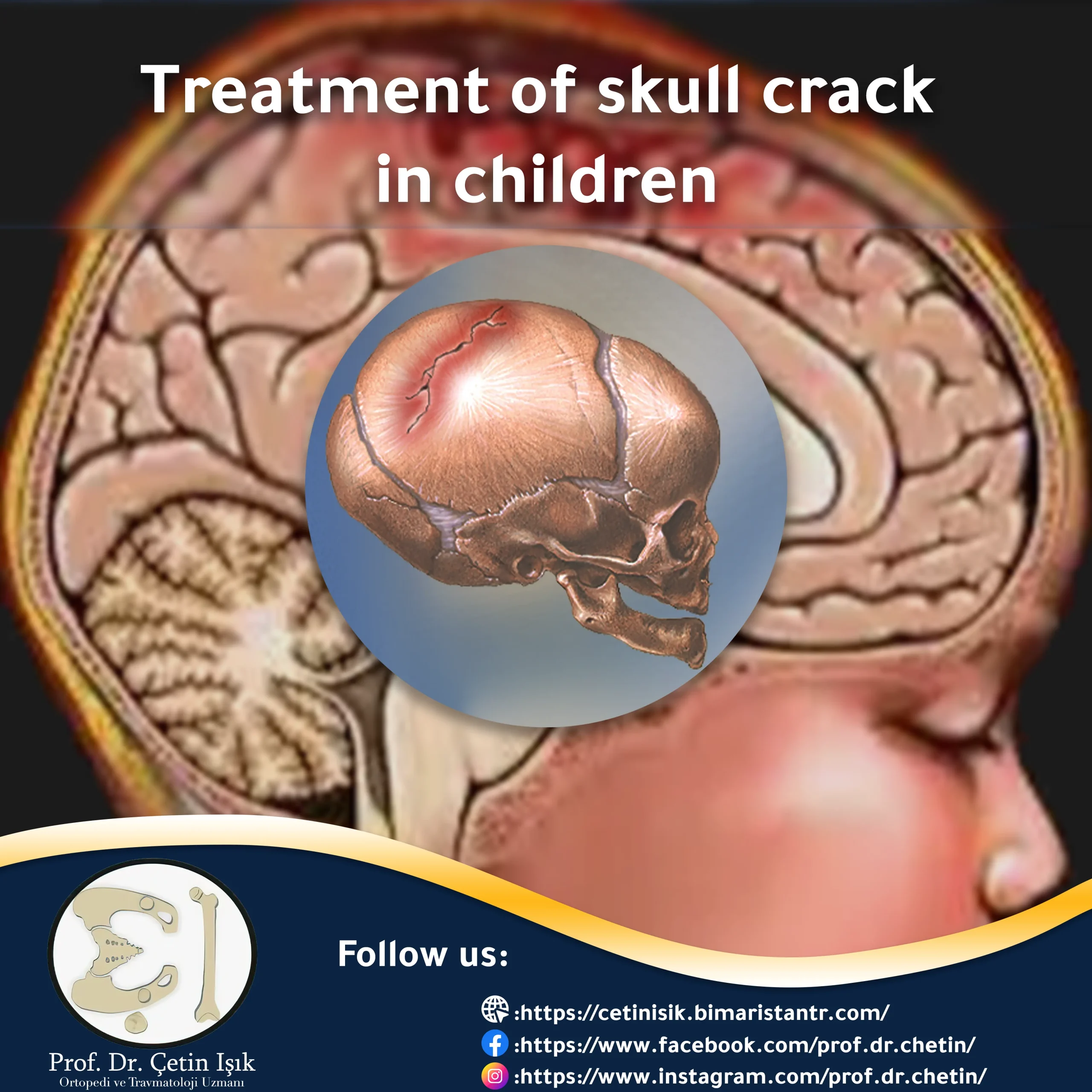
Treatment of a skull fracture in children depends on the severity of the head bone injury and brain damage. The treatment is either conservative or surgical. The skull fracture is one of the most common types of skull fractures in children.
The treatment of a skull fracture in children should be quick and direct after a head injury, especially when symptoms of a brain injury appear. How to treat a skull fracture in adults differs from the treatment of a skull fracture in children because the bones of the child’s skull are more flexible than the bones of the adult skull, and therefore there is less protection for the brain. Therefore, the delay in treating a skull fracture in children is a common cause of child death. The treatment is by closely monitoring the child in the hospital and treating the fracture symptoms or resorting to surgery if a hematoma forms in the brain.
In this article, we will learn about the most important first aid before treating a skull fracture in children and methods Treating a skull fracture in children without surgery or through surgery.
An overview of the treatment of skull fracture in children
Treatment of linear skull fracture in children It is different from treating other fractures in the body, such as: Metatarsal fractures or Hand joint fractures Which is often treated through splinting, where the treatment of skull fracture in children may be either conservative treatment or surgical treatment, depending on the severity of the head injury and the age of the child and whether there is serious brain damage or not.
A skull fracture is a serious fracture or a simple crack, depending on the severity of the injury. Since children have a larger head size than the rest of their body parts, they are more vulnerable to skull fractures when they fall from heights than adults, and simple cracks are usually not serious and are treated through observation in a Hospital and treatment of symptoms without resorting to surgery, unless there are serious complications such as severe bleeding in the brain and the formation of a hematoma in the skull.

Symptoms of a skull fracture in children
Some symptoms and signs appear when a child's head is injured, which should not be neglected, and a doctor should be consulted immediately. These are the ones that need treatment for a crack in the skull in children. The most important symptoms are:
- Exit of blood or cerebrospinal fluid from the nose or ear
- Increased child anxiety and sleepiness
- Asymmetry in the size of the child's pupils
- Weakness in arm or leg movement, the child may stumble and have difficulty walking or moving
- Hearing impairment
- slurred speech
- Blurred vision
- Erupted fontanelles in infants
- vomiting
- Exposure to seizures
- difficulty breathing
- Difficulty getting to know family and friends

First aid for children's skull fractures
The priority in skull fracture is the treatment of brain injuries, so some first aid must be performed in the hospital to prevent serious complications in the brain before starting treatment of skull fracture in children. The most important procedures are:
- Nothing should be put in the child's mouth
- During a seizure, the child should not be moved; anticonvulsant medications should be given and supervised closely
- Not moving the child
- If the child is vomiting, he should be placed on his side, holding his head and shoulders from both sides
- Monitor the breathing and pulse of the child and initiate pulmonary resuscitation when needed
- Putting a sterile bandage on the bleeding sites and pressing them
- Putting a cervical collar to prevent moving the child's head
Children most exposed to head injuries
A group of children are exposed to a lot of head trauma, so they must be protected, placed in a safe environment, and monitored constantly. The most important of these children are:
- Male children, where male injuries are twice that of females
- Very active youngsters, a lot of movement, and young adolescents, especially in the spring and summer seasons
- Children who engage in some sporting activities, such as riding horses or playing football
Treating a skull fracture in children without surgery
treatment of skull fractures Depending on the location and type of fracture, skull cracks are also treated according to their severity and effect on the brain. Most skull fractures are simple cracks and do not contain serious complications. Conservative treatment of skull fractures in children According to the following:
- Make the child get complete rest and not let him fall asleep for more than two hours during the day, and ensure that the child sleeps for at least eight hours at night
- Giving some pain relievers in the event of a headache, such as acetaminophen, which is given to children over the age of three months, or ibuprofen, which is given to children over the age of six months, after medical consultation.
- Wound care and disinfection to protect the brain from infection by making the wound clean using some antibiotic ointments
- Suturing wounds in the head when needed and not washing sutured wounds with water
- The child should be encouraged to eat well, drink plenty of fluids, and avoid foods that are high in sugar
- Prevent the child from practicing sports activities during the recovery period
- Putting an ice bag on the area of swelling or pain to reduce swelling and pain, taking into account avoiding applying an ice bag for a long time because it may cause damage to the skin
- The child may need to have intracranial pressure monitored because head injuries can cause an enlarged brain
Surgical treatment of skull fractures in children
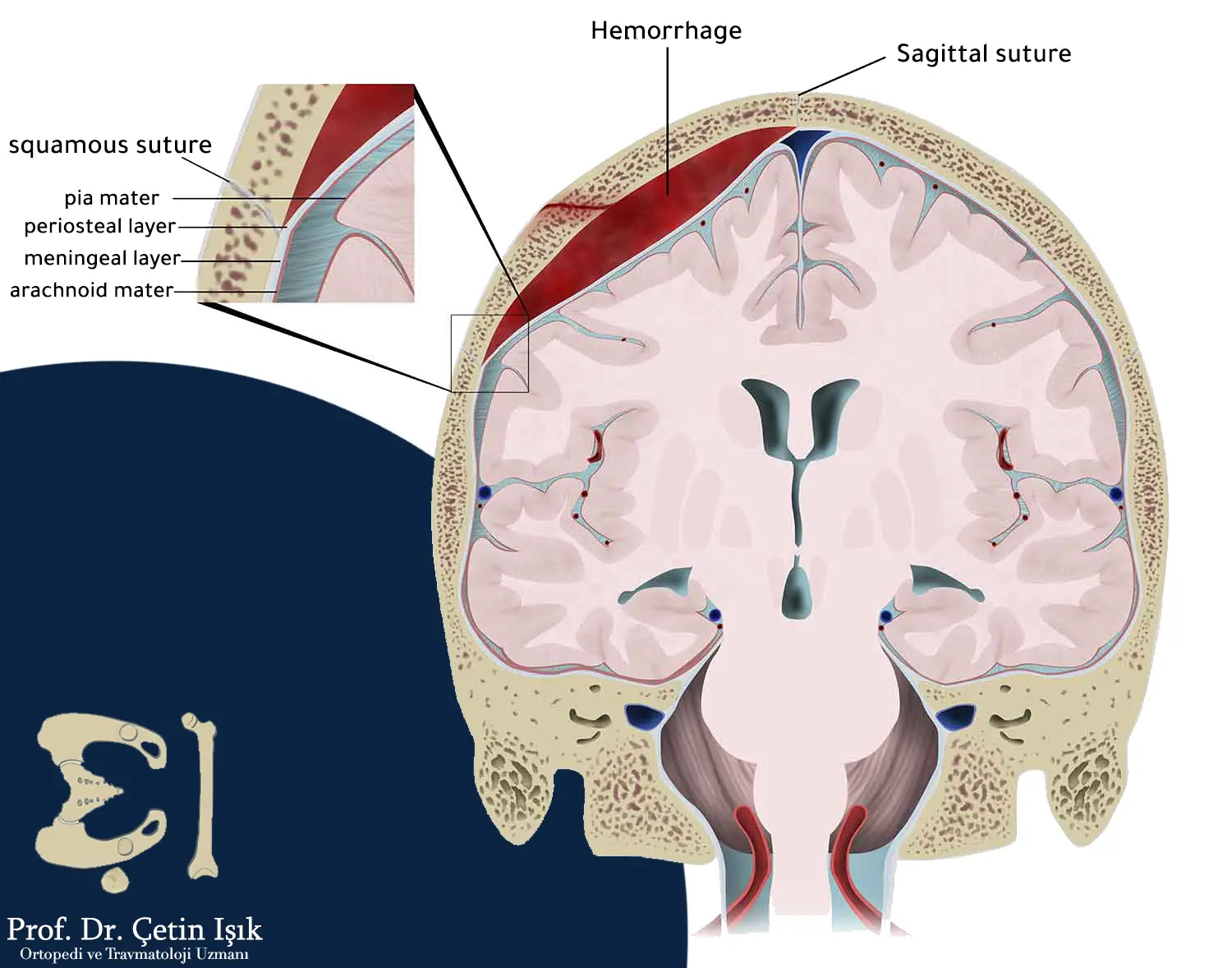
The treatment for cracks of the skull in children is rarely surgical because the cracks are usually simple and the treatment is conservative. When the cracks are serious, the treatment of skull cracks in children may need to resort to some surgical operations in order to remove the blood pool inside the skull, especially the subdural hematoma. To relieve pressure on the brain or when the meninges are injured, or an abscess is formed due to pollution.
At the end of the article, the treatment of a skull fracture in children changes according to the trauma's severity, the child's age, and the crack's location. The child should not be neglected when symptoms of a skull fracture appear after exposure to trauma and taking him to the doctor. Often, the treatment of a skull fracture in children is conservative, by observing the child in the hospital for several days and treatment Symptoms because the skull crack usually heals on its own. The period of healing of the bones of the skull in children takes approximately 3 to 6 months during the treatment of the skull fracture in children.
Sources:
Common questions
Skull fracture in children can be very dangerous because the bones of the child's head are flexible, which reduces the protection of the brain and fractures cause serious injury to the brain.
It may take between 3 to 6 months for the crack to fully heal and heal, depending on the severity of the crack and the form of treatment. The fracture usually heals faster in younger children.
The bones of the skull fuse in children in the second year of life, when the sutures of the child are ossified.
When serious symptoms of a head injury appear, such as temporary or permanent loss of consciousness, loss of concentration, and feeling sleepy.
It was believed that letting the child sleep might lead to coma, but this is not true. Rather, the child should get complete rest, because this speeds up the healing process during treatment.
The extent to which the child is affected depends on the severity of the blow. He may have a slight pain or a headache that does not need treatment, or a serious crack occurs in the bones of the head and he needs treatment for a crack in the skull in children.