Muscle stiffness is a common condition characterized by muscle stiffness as a result of stress, which leads to difficulty moving them and may be accompanied by pain that hinders the patient and prevents him from performing his daily activities.
Muscle stiffness can be evidence that it is working well and getting stronger, but it may also be caused by diseases that require medical treatment. Let us learn about muscle stiffness, its causes, and methods of treatment.
A glimpse of muscle stiffness
Muscle Stiffness is a feeling of stiffness in the muscles as a result of straining them through strenuous exercise, sleeping in an inappropriate position, or medical reasons, which leads to difficulty moving the muscles and may be accompanied by muscle pain.
Muscle stiffness is very common, especially among those who practice sports activities as a result of intense exercise or not warming up well. It is also common among office employees as a result of sitting for long periods.
Muscle stiffness differs from... Muscle spasm Stiffness is a long-term and continuous condition in which there is difficulty moving the muscle with the ability to move it, while spasm is usually a sudden, involuntary and painful muscle contraction with the inability to move the muscle during the spasm.
Muscle stiffness that follows exercise or sleeping in an awkward position is often easy to treat and nothing to worry about, but severe, chronic, or sudden muscle stiffness can indicate a serious health condition.
Causes of muscle stiffness
There are several common possible causes of muscle stiffness, including:
- Strenuous exercise: After strenuous exercise, what is called delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) occurs, which is a response in which symptoms often begin to appear 12 to 24 hours after exercise and reach their peak after about 24 to 72 hours.
- Traumatic injury: whether it is acute, such as a sprain, fall, or sudden blow to the body, or chronic, such as muscle overuse injuries resulting from repeated activity such that the muscles do not have sufficient time to rest between repetitions, and tendonitis (such as Neck tendonitis) and bursitis (eg Bursitis of the kneeExamples of overuse injuries.
- Spending long periods without doing any activity, such as sitting at a desk for long hours.
- Some medications, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins), antipsychotics, and anesthetics, are used during surgery.
- Dehydration and not drinking enough fluids, which leads to an imbalance of electrolytes that relax muscles (such as calcium and magnesium).
- Polymyalgia rheumatic: It causes muscle pain and stiffness and usually affects the upper body, including the shoulders, neck, and arms, and it also commonly affects the hips.
- Infections: such as tetanus, polio, meningitis, mononucleosis infection, and HIV (AIDS).
- Some chronic diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, fibromyalgia, and stiff person syndrome.
- Insect bites or stings, especially in the event of an infection (inflammation).
- Exposure to cold.

Symptoms of muscle stiffness
There are usually other symptoms in addition to muscle stiffness, especially in medical conditions resulting from infections and chronic diseases. Accompanying symptoms of muscle stiffness include the following:
- Pain and discomfort
- fever
- Headache
- Tired
- Swelling
- Dark urine
- Chest pain
- sore throat
- Joint pain
Treating muscle stiffness
Treatment for muscle stiffness depends on the underlying cause of the stiffness. However, most cases can be treated using home treatment options. We can also develop an appropriate physical therapy exercise program for you to relieve stiffness and prevent its reoccurrence.
Home treatment
Home treatment options include:
- Rest until stiffness decreases
- Using hot and cold compresses alternately (alternation therapy) for 20 minutes at a time several times a day
- Massage the tight muscle several times daily
- Take a warm bath to stimulate blood circulation and relieve muscle stiffness
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (such as ibuprofen and naproxen)

Physical therapy
Physical therapy exercises can improve muscle flexibility, reduce stiffness, and enhance muscle movement. Muscle stiffness exercises include both stretching and strength-increasing exercises.
Stretching exercises
These exercises are important because they improve muscle flexibility and enhance blood circulation. They include:
- Neck Rotation: Gently rotate your neck from side to side, holding each position for a few seconds
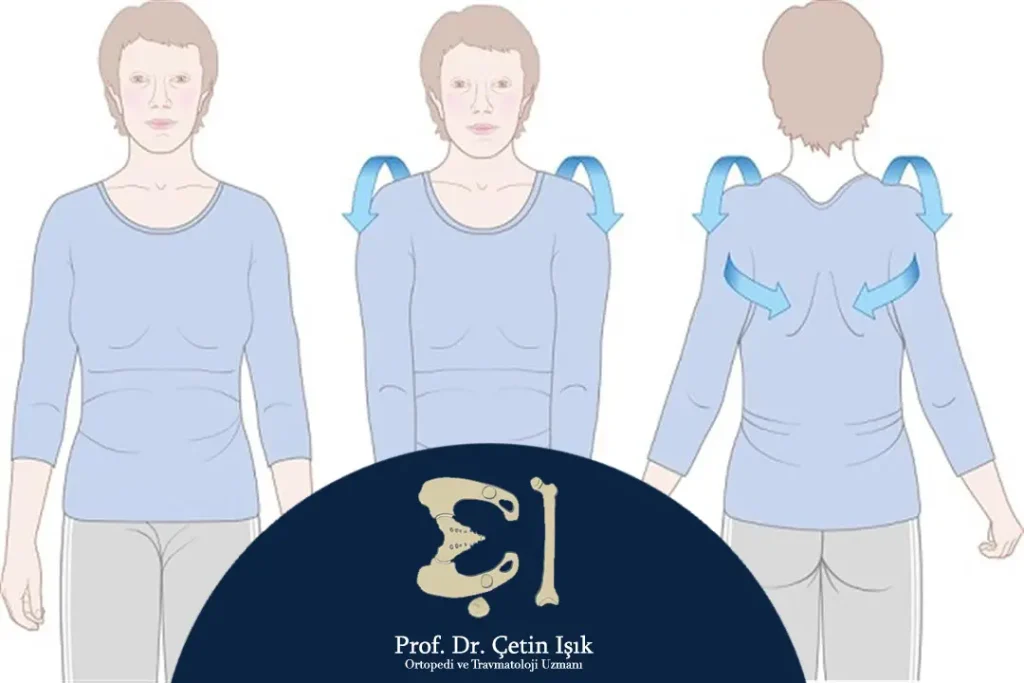
- Shoulder rotation: Rotate your shoulders back and forth in circular motions to relax your shoulder muscles
- Hamstring stretch: Sit on the floor with one leg extended and the other bent, then move forward from your hips to stretch the back of your extended leg.
Strength increasing exercises
Exercises to increase muscle strength include:
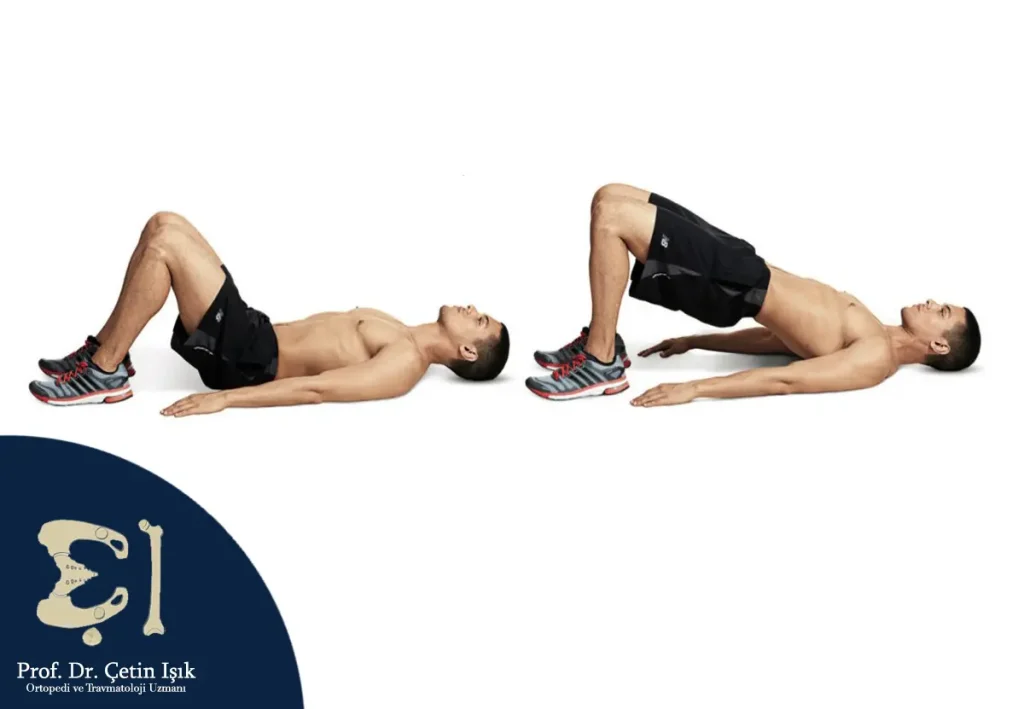
- Leg raises: Lie on your back and lift one leg at a time, keeping it straight. Wait for a few seconds and then lower it.
- Bridge exercises: Lie on your back with your knees bent, then lift your hips off the ground to form a straight line from your shoulders to your knees (like a bridge)

Preventing muscle stiffness
Muscle stiffness can be prevented by following the following tips:
- Maintain a healthy and appropriate weight
- Avoid sitting for long periods
- Eat a nutritious diet and drink plenty of water
- Exercise regularly and warm up well before exercise
- Stretch several times a day
- Wear appropriate shoes when exercising
Muscle stiffness is a common condition that results in most cases from strenuous activities and sleeping in uncomfortable positions, which requires some simple home remedial measures to treat it, along with the need to exercise regularly to avoid recurring stiffness.
Sources:
Common questions
Muscle stiffness is the feeling of muscle stiffness as a result of muscle fatigue or pathological causes, which leads to difficulty moving them and may be accompanied by muscle pain.
Symptoms of muscle stiffness include muscle stiffness and difficulty moving them, and pain may occur. They may be accompanied by other symptoms depending on the cause of the stiffness, including fever, headache, and fatigue.
Muscle spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of the muscles that can be painful, and often occurs as a result of stress, fatigue, or chemical fluctuations in the body. Muscle stiffness is a feeling of hardness or harshness in the muscles. This condition is usually continuous and causes difficulty in moving. Muscles may become stiffer when trying to move a stiff muscle.
There is a treatment for muscle stiffness, which is home treatment, which includes rest, massage, the use of hot and cold compresses, and physical therapy, which includes stretching and strengthening exercises.